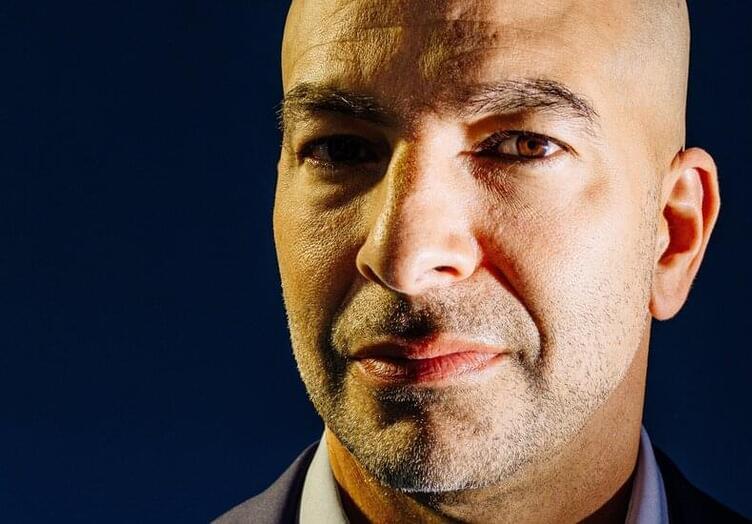
The doctor, podcast host and author of the bestseller “Outlive” says medicine needs to rethink longevity.
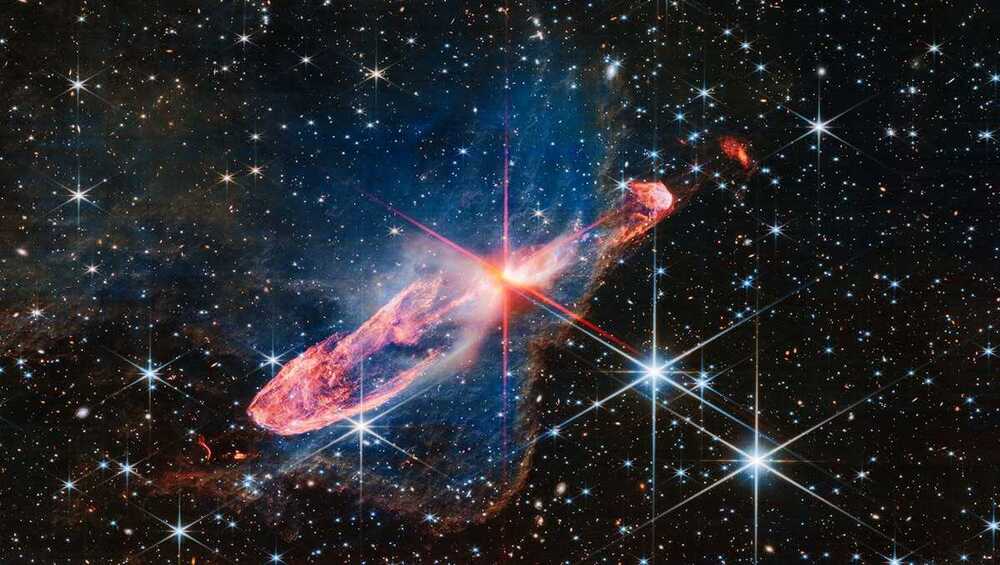
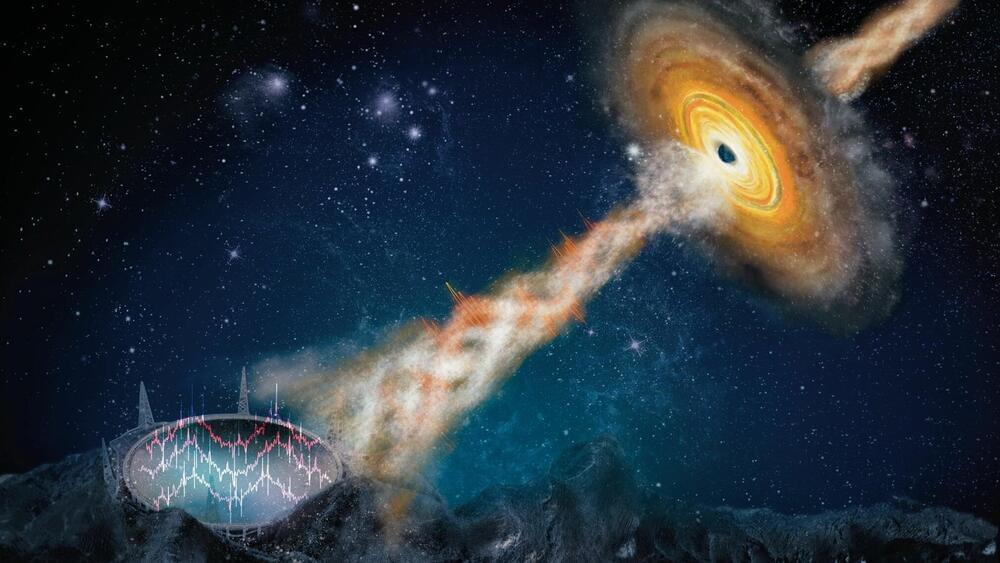




Black holes are the most mysterious objects in the universe, with features that sound like they come straight from a sci-fi movie.
Stellar-mass black holes with masses of roughly 10 suns, for example, reveal their existence by eating materials from their companion stars. And in some instances, supermassive black holes accumulate at the center of some galaxies to form bright compact regions known as quasars with masses equal to millions to billions of our sun. A subset of accreting stellar-mass black holes that can launch jets of highly magnetized plasma are called microquasars.
An international team of scientists, including UNLV astrophysicist Bing Zhang, reports in Nature on a dedicated observational campaign on the galactic microquasar dubbed GRS 1915+105. The team revealed features of a microquasar system that have never before been seen.


Adopting a curious mindset over a high-pressure one can enhance memory, according to recent research from Duke University. The study showed that participants who envisioned themselves as a thief planning a heist in a virtual art museum demonstrated better recall of the paintings they encountered than those who imagined executing the heist on the spot while playing the same computer game.
The slight variation in motivations — the urgent need to achieve immediate goals versus the curious exploration for future objectives — could have significant implications in real-life scenarios. These include incentivizing people to receive a vaccine, prompting action against climate change, and potentially providing new treatments for psychiatric conditions.
The findings were recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Humans have a distinctive skeleton, and are the only bipedal great apes (the great ape species are bonobos, chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and humans). While the evolution of the human skeleton enabled us to walk upright, it also led to the rise of musculoskeletal disease. It’s thought that cognitive development began to accelerate in humans once we started to move around, adapt to new environments, and make use of tools. Researchers have now used advanced computational tools and a trove of human genetic data in the UK Biobank to outline the genetic changes that occurred as primates started to walk upright for the first time.
These findings, which were reported in Science, have suggested that natural selection had a strong influence on the genetic changes that altered our anatomy, and gave early humans an evolutionary leg up.

Related: Worldcoin confirms it is the cause of mysterious Safe deployments
The stark contrast in the number of sign-ups before and after the launch suggests a lack of enthusiasm. However, the early on-boards also proved controversial, with one MIT report suggesting that the developers behind the project attracted the first million using deception, cash handouts and more, especially in developing countries where data laws are notably weak.
Worldcoin has drawn scrutiny and commentary from many well-known names in the crypto community, including Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin and Twitter co-founder Jack Dorsey. In its defense, the project has maintained that it doesn’t collect personal information and can delete the biometric data upon user request.

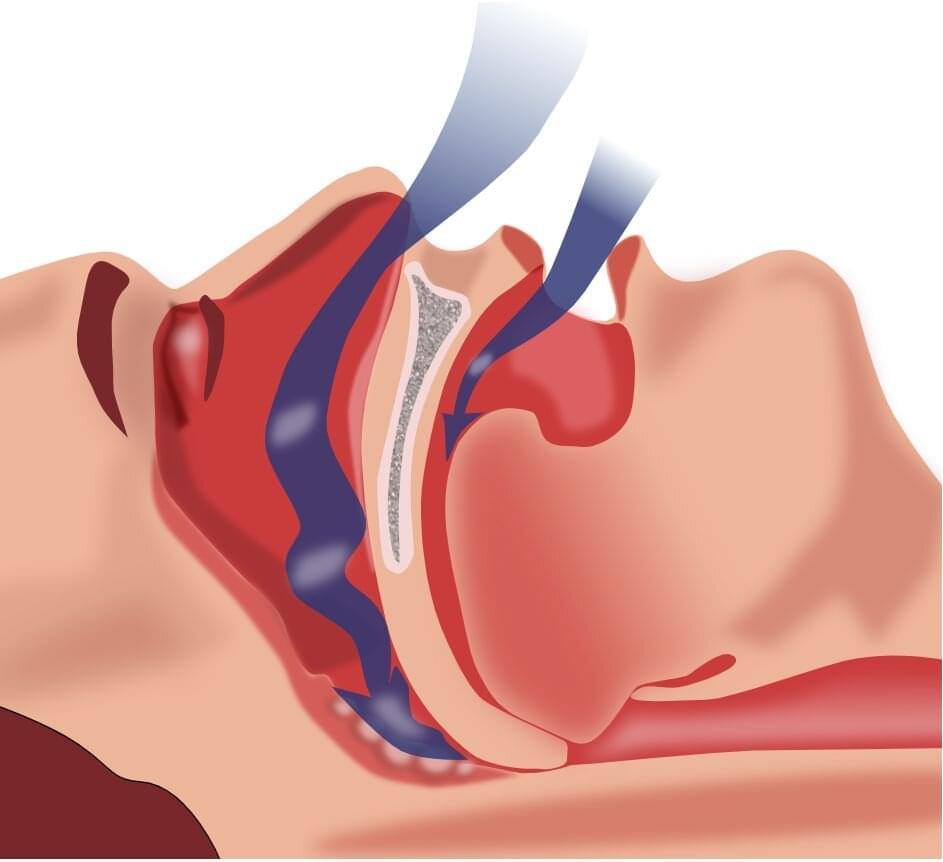
Researchers have found that people with obstructive sleep apnea have an increased cardiovascular risk due to reduced blood oxygen levels, largely explained by interrupted breathing. Obstructive sleep apnea has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular issues, including heart attack, stroke, and death, but the findings from this study, published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, show the mechanism mostly responsible for the link.
“These findings will help better characterize high-risk versions of obstructive sleep apnea,” said Ali Azarbarzin, Ph.D., a study author and director of the Sleep Apnea Health Outcomes Research Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston. “We think that including a higher-risk version of obstructive sleep apnea in a randomized clinical trial would hopefully show that treating sleep apnea could help prevent future cardiovascular outcomes.”
Researchers reviewed data from more than 4,500 middle-aged and older adults who participated in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study (MrOS) and the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), and sought to identify features of obstructive sleep apnea that could explain why some people were more likely than others to develop cardiovascular disease or related death.

Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)—small peptides that protect against microbial infection—are crucial immune effectors in both plants and animals. They not only fight against potential infections, they also influence the composition of the host’s microbiome. Little is known about the driving forces behind AMPs’ rapid evolution. Now, a study uncovers the selective pressures driving the evolution of AMPs and how they control bacteria in the host’s microbiome.
The work is published in Science in the paper, “Ecology-relevant bacteria drive the evolution of host antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila.”
The researchers focused on Diptericin (Dpt), a small antimicrobial peptide that mainly defends Drosophila against Gram-negative bacteria. The team examined how Diptericins function in Drosophila and evolve in response to their microbial environment.