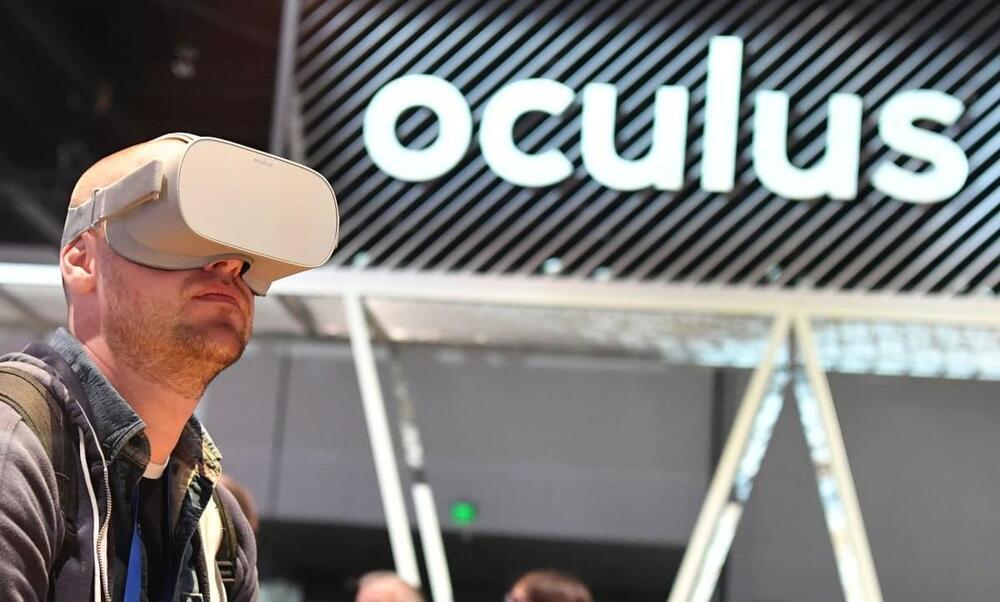
As Meta sets its sight on introducing its virtual reality headsets to the Chinese market, Mark Zuckerberg’s contentious remarks about Beijing in the past may pose a major obstacle to his China dream. According to a recent report by the Wall Street Journal, Meta is preparing to re-enter China by selling the Oculus Quest VR headset in China. If Tesla can sell cars and Apple can sell phones in China, why isn’t Meta present there? Zuckerberg asked in a recent internal meeting.
But some observers are quick to point out that Zuckerberg has a history of criticizing the Chinese government, a stance that will likely be amplified in the current climate of heightened tensions between the U.S. and China.… More.