There are already countless songs on Spotify, Apple Music, and SoundCloud. And as tunes become easier to create, anyone can add to the copyright din.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
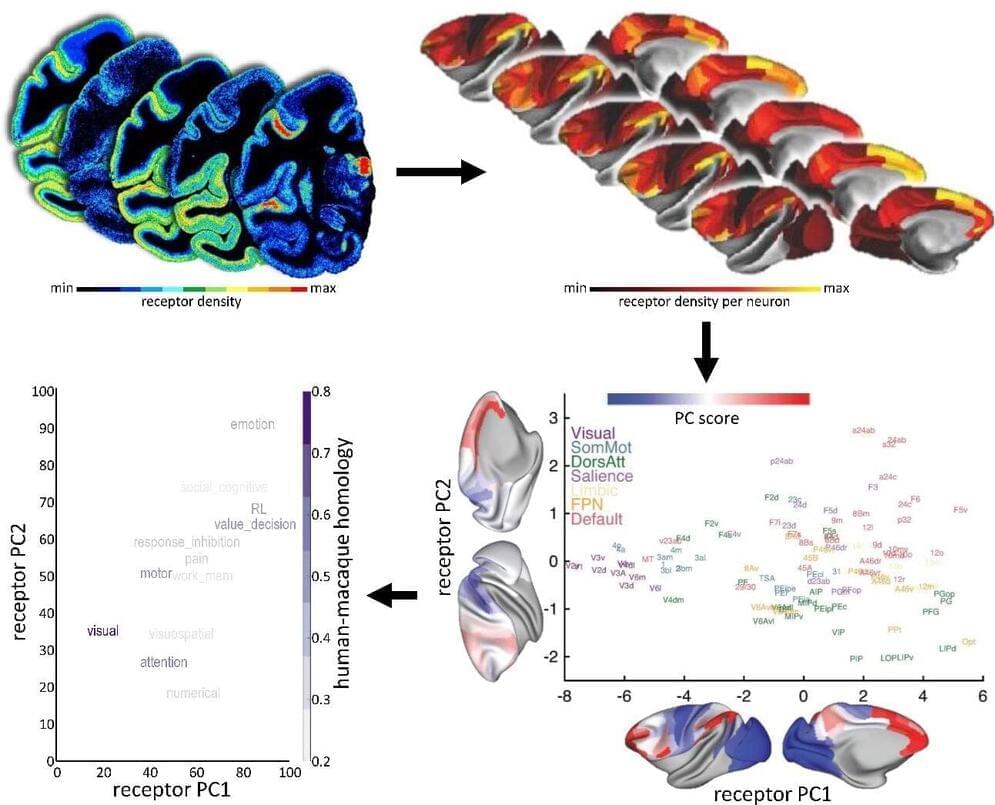
Human Brain Project study offers insights into neuroreceptor organization
A key challenge in neuroscience is to understand how the brain can adapt to a changing world, even with a relatively static anatomy. The way the brain’s areas are structurally and functionally related to each other—its connectivity—is a key component. In order to explain its dynamics and functions, we also need to add another piece to the puzzle: receptors.
Now, a new mapping by Human Brain Project (HBP) researchers from the Forschungszentrum Jülich (Germany) and Heinrich-Heine-University Düsseldorf (Germany), in collaboration with scientists from the University of Bristol (UK), New York University (U.S.), Child Mind Institute (U.S.), and University of Paris Cité (France) had made advances on our understanding of the distribution of receptors across the brain.
The findings were published in Nature Neuroscience, and the data is now freely available to the neuroscientific community via the HBP’s EBRAINS infrastructure.

NASA Will Engrave Your Name on a Microchip Destined for Jupiter
NASA is offering everyone the opportunity to have their name sent on the 1.8-billion-mile journey to Jupiter next year.
The “Message in a Bottle” campaign (Opens in a new window) invites people to submit their names to NASA before 11:59 pm EST on Dec. 31, 2023. Those names will then be engraved on a microchip alongside a poem titled “In Praise of Mystery: A Poem for Europa” written by U.S. Poet Laureate Ada Limón.
Once completed, the chip will be loaded on to NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft (Opens in a new window) scheduled for launch in October 2024. It won’t reach Jupiter until April 2030, at which point Clipper will orbit the planet and make close to 50 flybys of the Europa moon at altitudes as low as 16 miles (25 kilometers) above the surface. The aim is to investigate whether Europa has the potential to support life.

DIY Picosatellites Hack Chat
Join us on Wednesday, June 21 at noon Pacific for the DIY Picosatellites Hack Chat with Nathaniel Evry!
Building a satellite and putting it in orbit was until very recently something only a nation had the resources to accomplish, and even then only a select few. Oh sure, there were a few amateur satellites that somehow managed to get built on a shoestring budget and hitch a ride into space, and while their stories are deservedly the stuff of legends, satellite construction took a very long time to be democratized.
Fast forward a half-dozen or so decades, and things have changed dramatically. Satellite launches are still complex affairs — it’s still rocket science, after all — but the advent of the CubeSat format and the increased tempo of launches, both national and commercial, has pushed the barriers to private, low-budget launches way, way down. So much so, in fact, that the phrase “space startup” is no longer something to snicker about.

Japan arrests researcher for leak to ChinaーNHK WORLD-JAPAN NEWS
Police in Japan have arrested a Chinese researcher they believe leaked sensitive tech data to a firm in China. We have analysis on efforts to tackle industrial espionage. #japan #china #leaks.
More stories on Japan: https://www3.nhk.or.jp/nhkworld/en/news/tags/2/
Please subscribe HERE: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCSPEjw8F2nQDtmUKPFNF7_A?sub_confirmation=1
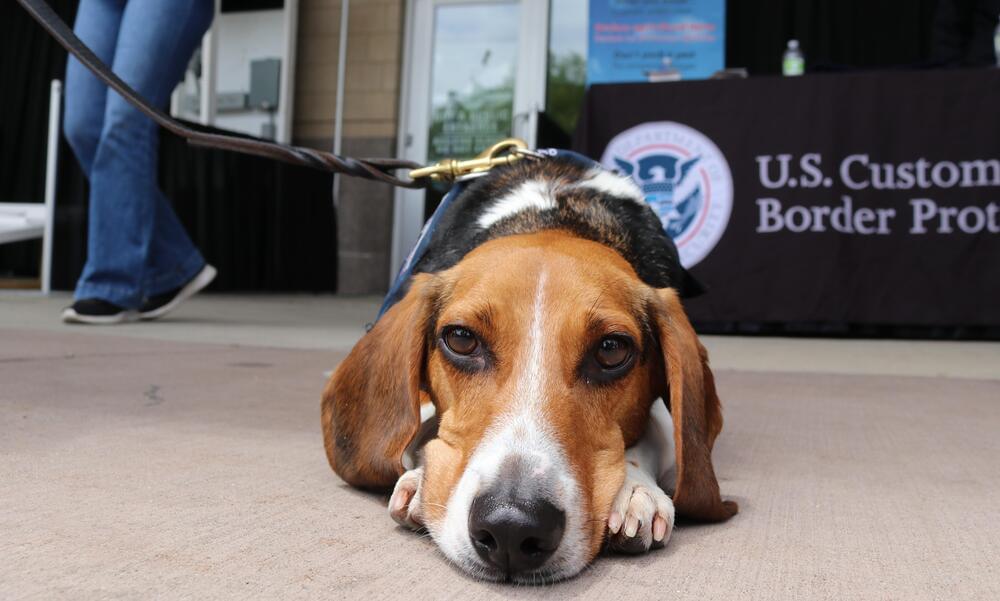


Meet the beagles protecting American agriculture
Scheele said that most of the dogs are rescues coming from the Atlanta area, which is near the USDA National Detector Dog Training Center.
Before they can be trained, the dogs are tested for temperament and to make sure they can detect five basic scents. Scheele said the detector dogs have to be food-driven animals, which he said (suprisingly) all dogs are not.
“That’s pork, beef, citrus, mango and apple,” Scheele said. “That’s to prove that the dog has the capability to do it and has the temperament to work in an environment like an airport or at a cargo facility, around the darkness or chaos that goes with imported goods or that sort of thing.”

Nikon Fights Back Against AI Images, Touts ‘Natural Intelligence’
As AI image generators continue to rock visual industries such as photography and illustration, Nikon is taking a stand against AI and on behalf of humans, cameras, and “natural intelligence.” Little Black Book reports that Nikon Peru recently partnered with the ad agency Circus Grey Peru on a new “Natural Intelligence” ad campaign.
Even though AI can now generate photorealistic images with just a simple text prompt, Nikon wants to remind everyone that the real world is full of incredible scenes that are best captured with a camera rather than imagined with AI.

Resurrection — Scientists Discover It Is Not Due to a “Miracle Gene”
Certain plant species.
A species is a group of living organisms that share a set of common characteristics and are able to breed and produce fertile offspring. The concept of a species is important in biology as it is used to classify and organize the diversity of life. There are different ways to define a species, but the most widely accepted one is the biological species concept, which defines a species as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce viable offspring in nature. This definition is widely used in evolutionary biology and ecology to identify and classify living organisms.