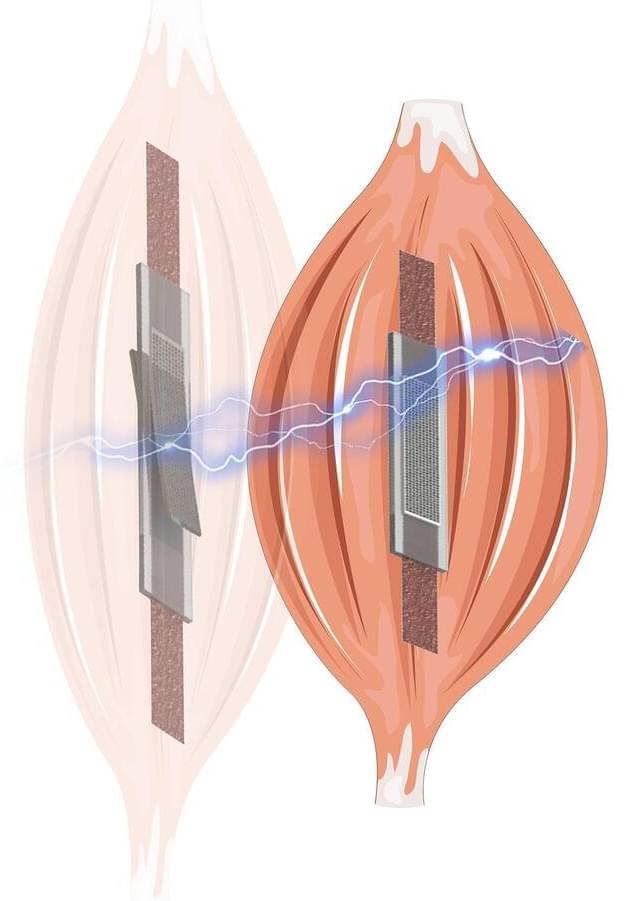
In a study published recently in Advanced Intelligent Systems, researchers from Queen Mary University of London have made significant advancements in the field of bionics with the development of a new type of electric variable-stiffness artificial muscle that possesses self-sensing capabilities. This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize soft robotics and medical applications.
Muscle contraction hardening is not only essential for enhancing strength but also enables rapid reactions in living organisms. Taking inspiration from nature, the team of researchers at QMUL’s School of Engineering and Materials Science has successfully created an artificial muscle that seamlessly transitions between soft and hard states while also possessing the remarkable ability to sense forces and deformations.
Dr. Ketao Zhang, a Lecturer at Queen Mary and the lead researcher, explains the importance of variable stiffness technology in artificial muscle-like actuators. “Empowering robots, especially those made from flexible materials, with self-sensing capabilities is a pivotal step towards true bionic intelligence,” says Dr. Zhang.