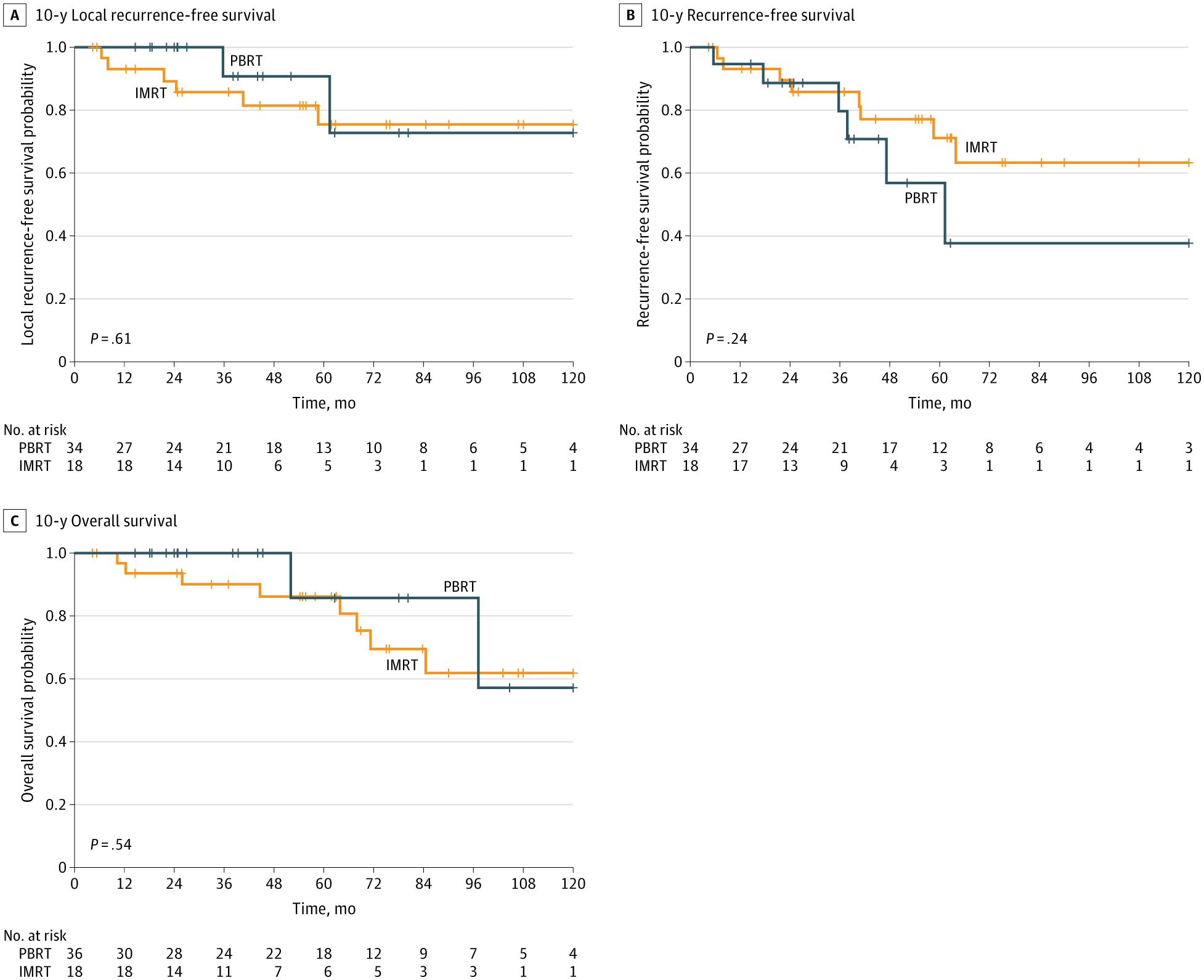
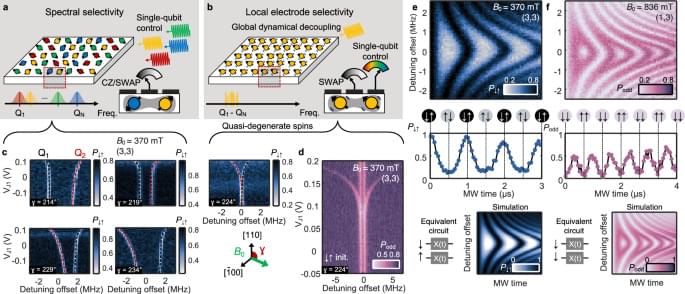
Collective behavior is an unusual phenomenon in condensed-matter physics. When quantum spins interact together as a system, they produce unique effects not seen in individual particles. Understanding how quantum spins interact to produce this behavior is central to modern condensed-matter physics.
Among these phenomena, the Kondo effect—the interaction between localized spins and conduction electrons—plays a central role in many quantum phenomena.
Yet in real materials, the presence of additional charges and orbital degrees of freedom make it difficult to isolate the essential quantum mechanism behind the Kondo effect. In these materials, electrons don’t just have spin, they also move around and can occupy different orbitals. When all these extra behaviors mix together, it becomes hard to focus only on the spin interactions responsible for the Kondo effect.