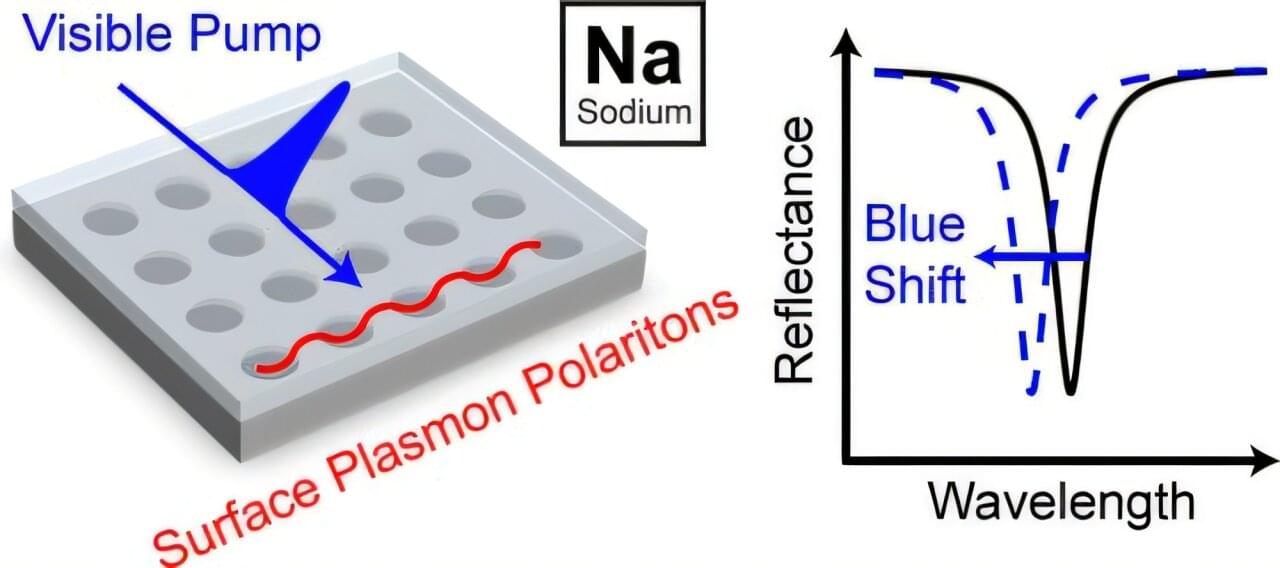
From solar panels to next-generation medical devices, many emerging technologies rely on materials that can manipulate light with extreme precision. These materials—called plasmonic materials—are typically made from expensive metals like gold or silver. But what if a cheaper, more abundant metal could do the job just as well or better?
That’s the question a team of researchers set out to explore. The challenge? While sodium is abundant and lightweight, it’s also notoriously unstable and difficult to work with in the presence of air or moisture—two unavoidable parts of real-world conditions. Until now, this has kept it off the table for practical optical applications.
Researchers from Yale University, Oakland University, and Cornell University have teamed up to change that. By developing a new technique for structuring sodium into ultra-thin, precisely patterned films, they found a way to stabilize the metal and make it perform exceptionally well in light-based applications.