Freely accessible large language models have accelerated the pace of innovation, computer scientists say.


Check out Fred Evrard’s Book (HOW MY IMMUNE SYSTEM BEAT CANCER) HERE: https://amzn.to/3MGjOE1
FRED EVRARD’S YOUTUBE CHANNEL:
https://youtube.com/channel/UCnJF5tsWLdZ7mZnjM5r0GrQ
AMAZON
Guy Tenenbaum Youtube Channels:
http://youtube.com/c/CancerTherapy.
http://youtube.com/c/SurviveFromCancer.
The cancer study, Dr. Berg and Guy Tenenbaum sponsored:
http://jscholaronline.com/full-text/JOCR/3_104/Inhibition-of…reases.php.
Inhibition of SCOT and Ketolysis Decreases Tumor Growth and Inflammation in the Lewis Cancer Model.

Scientists have used stem cells to create structures that resemble human embryos in the lab, in a first that has prompted calls for stricter regulation in the rapidly advancing field.
Several different labs around the world have released pre-print studies in the past seven days describing their research, which experts said should be treated with caution as the research has not yet been peer-reviewed.
The labs used different techniques to encourage human embryonic stem cells, which can become any type of cell, to self-assemble into a structure that resembles an embryo—without needing sperm, an egg or fertilization.
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — In people with epilepsy, seizure-alert dogs can smell small changes in body chemistry and warn of an impending seizure an hour or more before it occurs. Inspired by this feat of nature, a team of researchers has sniffed out a way to replicate the ability with technology.

Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have improved the landscape of cancer research over the past decade. These therapies, which target a patient’s own immune system aiming to make it stronger and more equipped to fight cancer, have provided novel and beneficial therapeutic options for patients with advanced and metastatic disease.
While ICIs can induce long-term responses and cures in patients with limited therapeutic options, they present significant challenges. First, different patients exhibit different levels of responsiveness to ICIs. So, when one patient achieves a cure, another with a similar type of cancer may remain non-responsive. While we don’t fully understand the reasons behind the disparate responsiveness of ICIs, this remains an active area of research globally. Second, ICI use can elicit toxicities known as immune-related adverse events (irAEs). In some patients irAEs can be managed and thus tolerable, especially given the anti-cancer effects. However, some patients experience severe irAEs that can significantly hinder the quality of life of cancer survivors. In some cases, serious and life-threatening irAEs can even require treatment discontinuation.
A pre-clinical study recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Cancer Research explores a potential regimen that may help confront both of these challenges. The researchers hypothesized that ICIs, if targeted directly to the lymph node (LN), could both enhance the anti-tumor response and reduce the associated irAEs.
Tell summer to go to … Well, at least keep from overheating indoors—or outdoors—with the right tips and gear.
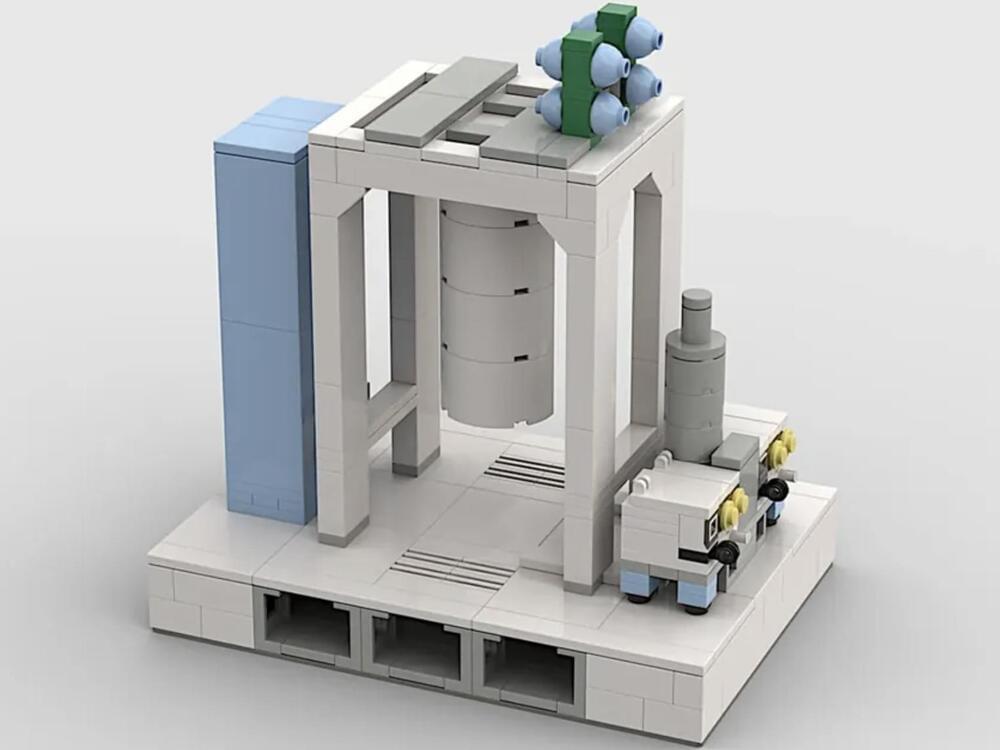



Disregarding an ever-increasing number of modalities and approaches and indifferent to the intense competition from savvy startups and techno giants, Lego could enter the race to build a quantum computer.
Well, at least one Lego fan designer is readying the Denmark-based toy company for the quantum era.
In a product suggestion, a Lego user pitched creating IBM Quantum Computer System in Lego Ideas, a site that allows users to submit suggestions for future logo sets.