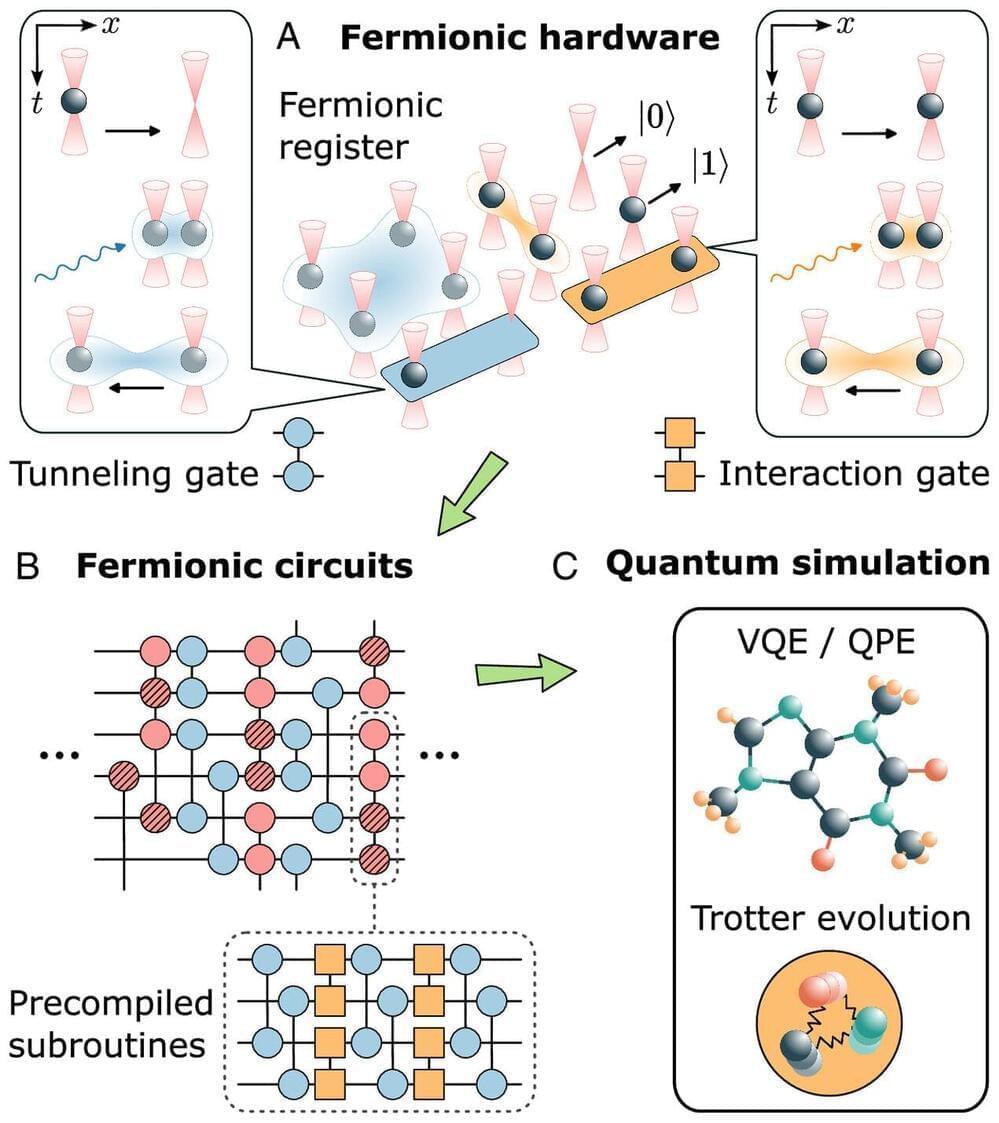
Researchers from Austria and the U.S. have designed a new type of quantum computer that uses fermionic atoms to simulate complex physical systems. The processor uses programmable neutral atom arrays and is capable of simulating fermionic models in a hardware-efficient manner using fermionic gates.
The team led by Peter Zoller demonstrated how the new quantum processor can efficiently simulate fermionic models from quantum chemistry and particle physics. The paper is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Fermionic atoms are atoms that obey the Pauli exclusion principle, which means that no two of them can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. This makes them ideal for simulating systems where fermionic statistics play a crucial role, such as molecules, superconductors and quark-gluon plasmas.