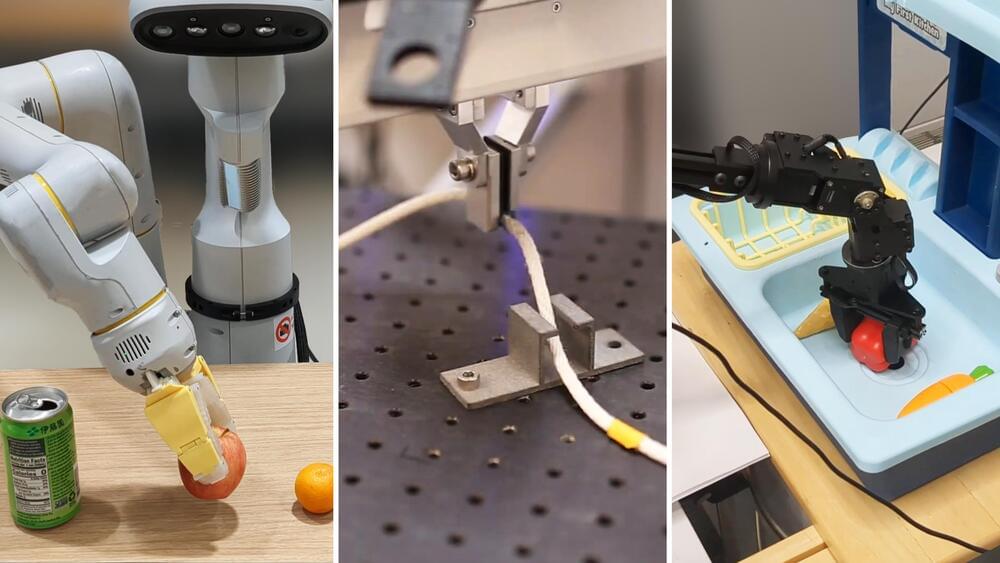
Robots are great specialists, but poor generalists. Typically, you have to train a model for each task, robot, and environment. Changing a single variable often requires starting from scratch. But what if we could combine the knowledge across robotics and create a way to train a general-purpose robot?
Today, we are launching a new set of resources for general-purpose robotics learning across different robot types, or embodiments. Together with partners from 33 academic labs we have pooled data from 22 different robot types to create the Open X-Embodiment dataset. We also release RT-1-X, a robotics transformer (RT) model derived from RT-1 and trained on our dataset, that shows skills transfer across many robot embodiments.
In this work, we show training a single model on data from multiple embodiments leads to significantly better performance across many robots than those trained on data from individual embodiments. We tested our RT-1-X model in five different research labs, demonstrating 50% success rate improvement on average across five different commonly used robots compared to methods developed independently and specifically for each robot. We also showed that training our visual language action model, RT-2, on data from multiple embodiments tripled its performance on real-world robotic skills.