The bibliometric infrastructure of citations has become an inescapable organising feature of academic life. Drawing on a range of evidence of the use and misuse of citations data, Stuart Macdonald argues its ubiquity has rendered authorship a questionable concept in modern scholarship.
New research suggests that dark energy isn’t needed to explain the acceleration in the expansion of the universe — instead suggesting giant voids in space are creating an illusion.
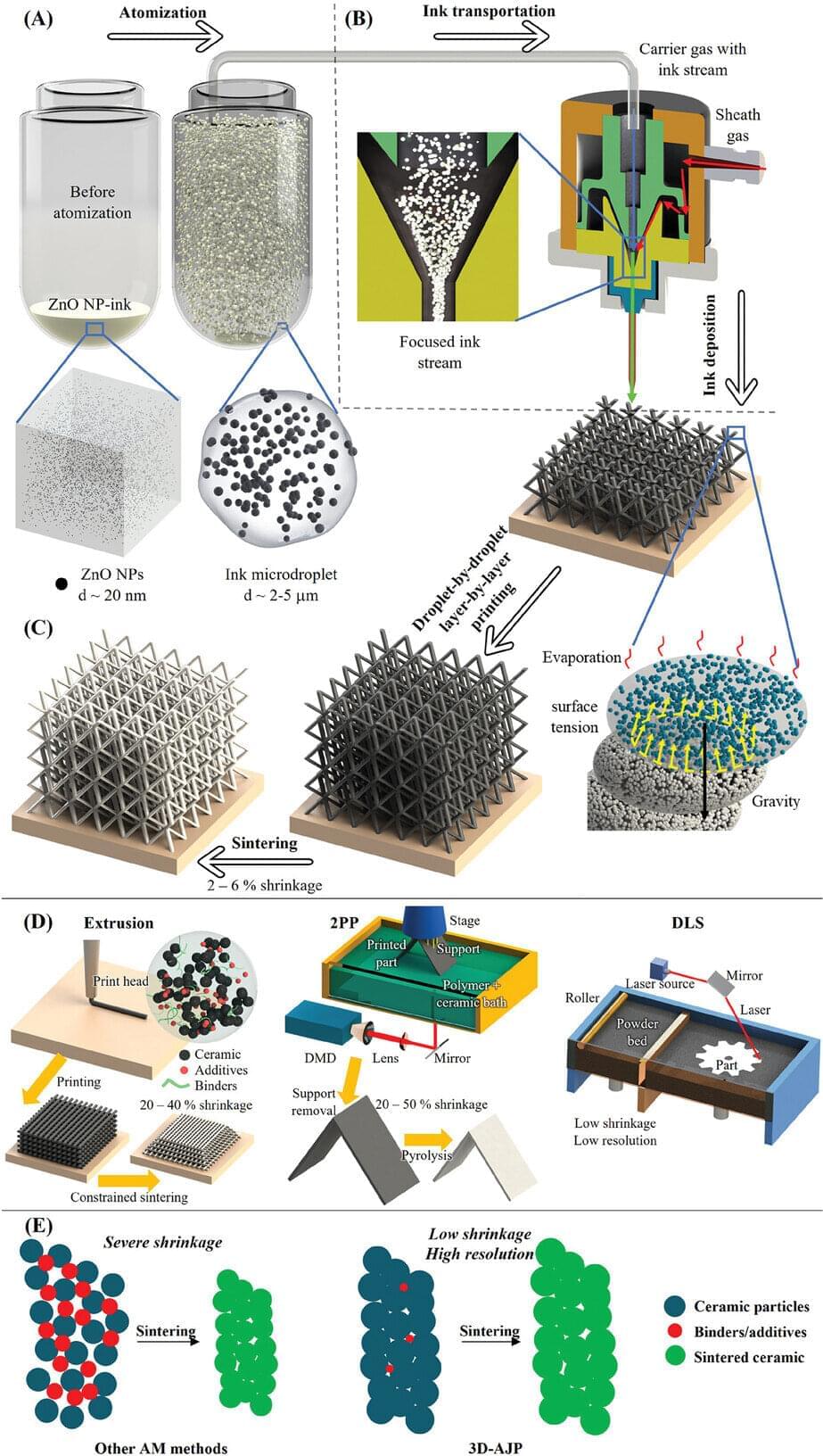
The same material from which you drink your morning coffee could transform the way scientists detect disease, purify water, and insulate space shuttles thanks to an entirely new approach to ceramic manufacturing.
Published in Advanced Science, 3D-AJP is an aerosol jet 3D nanoprinting technique that allows for the fabrication of highly complex ceramic structures that—at just 10 micrometers (a fraction of the width of human hair)—are barely visible to the naked eye. These 3D structures are made up of microscale features including pillars, spirals, and lattices that allow for controlled porosity, ultimately enabling advances in ceramic applications.
“It would be impossible to machine ceramic structures as small and as precise as these using traditional manufacturing methods,” explained Rahul Panat, professor of mechanical engineering at Carnegie Mellon University and the lead author of the study. “They would shatter.”
The small-molecule discovery could help in overcoming cell culture bottlenecks such as rapid degradation and high production costs.
Summary: Researchers have developed a geometric deep learning approach to uncover shared brain activity patterns across individuals. The method, called MARBLE, learns dynamic motifs from neural recordings and identifies common strategies used by different brains to solve the same task.
Tested on macaques and rats, MARBLE accurately decoded neural activity linked to movement and navigation, outperforming other machine learning methods. The system works by mapping neural data into high-dimensional geometric spaces, enabling pattern recognition across individuals and conditions.
Scientists used nanoparticles to introduce genetic material into plants, enabling faster and temporary crop modifications.
Scientists discovered that glass molecules shift unpredictably, reversing time at a microscopic level. This challenges our understanding of time and material science.
Mitochondrial stress disrupts insulinInsulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas, crucial for regulating blood glucose levels. It helps cells in the body absorb glucose from the bloodstream and convert it into energy or store it for future use. Insulin production and action are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. In people with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use the insulin it does produce (Type 2 diabetes), leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood. This can cause various health complications over time, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve dysfunction. Insulin therapy, where insulin is administered through injections or an insulin pump, is a common treatment for managing diabetes, particularly Type 1. The discovery of insulin in 1921 by Frederick Banting and Charles Best was a landmark in medical science, transforming diabetes from a fatal disease to a manageable condition. tabindex=0 insulin production in diabetes, but reversing the damage may restore β-cell function.
Michigan Medicine researchers have developed a SCN1B gene therapy that restores brain function and survival in mice with severe developmental epileptic encephalopathy (DEE). The therapy reduced seizure severity and increased lifespan.
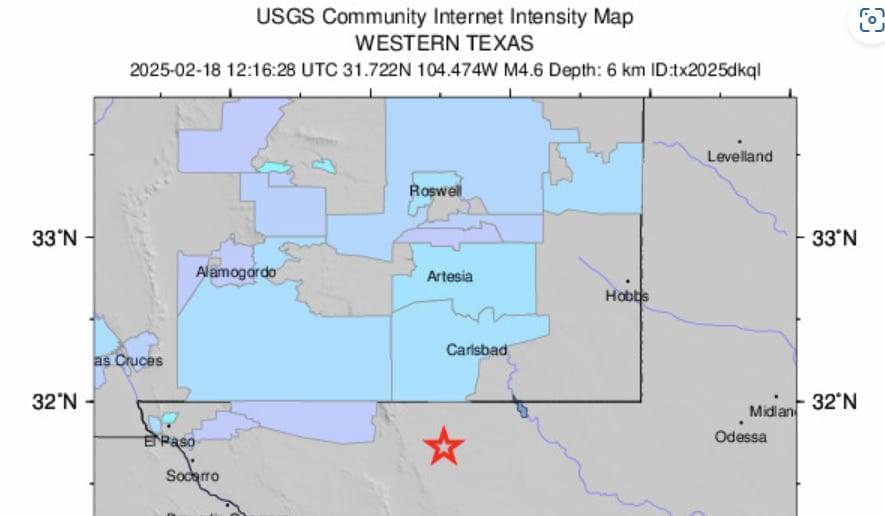
Several earthquakes rocked near the Texas-New Mexico border on Tuesday morning, the latest in a slew of quakes to hit the region.
A 4.6 magnitude earthquake happened at 5:18 a.m. MT, about 36 miles south of Whites City, New Mexico, according to the United States Geological Survey, while another 3.4 magnitude earthquake shook nearby about three hours earlier.
Another smaller earthquake — this one a 2.5 magnitude — hit the same area about 2:40 a.m. MT.