Most children receiving radiation therapy for cancer can hold still without anesthesia if they watch videos during the treatment, a study of a technique developed at Stanford Medicine found.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
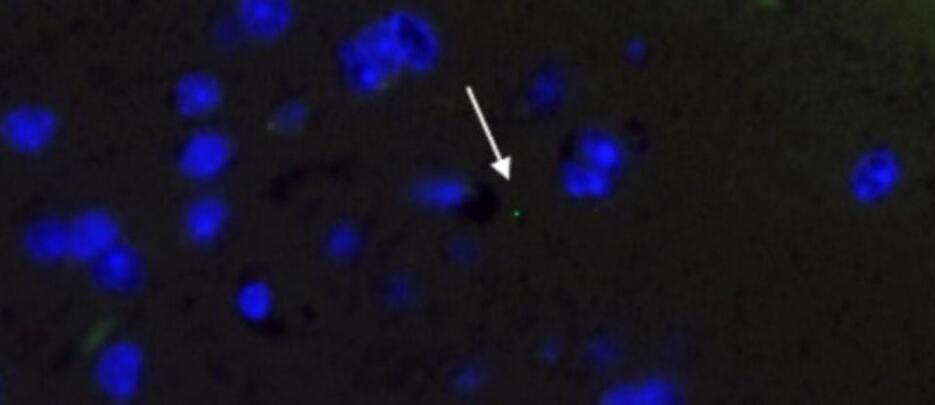
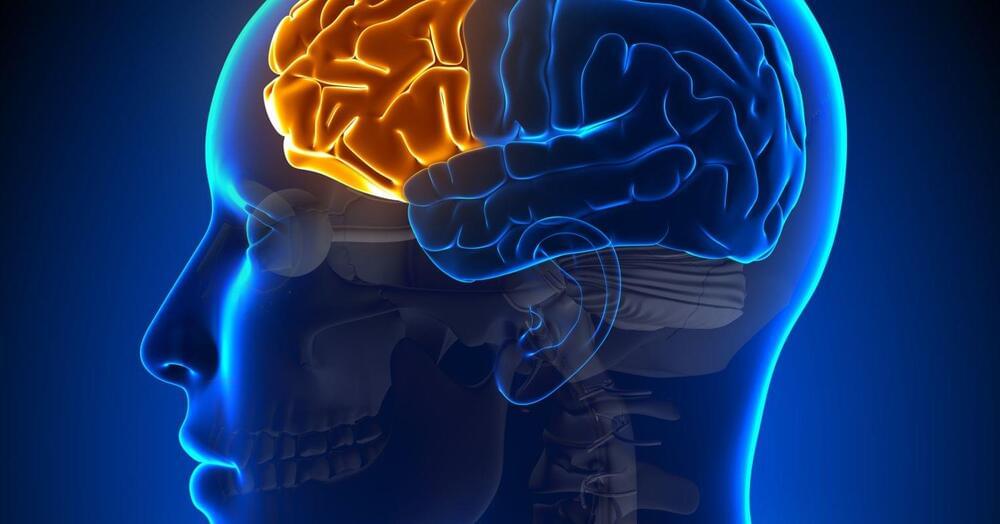
Microplastics Infiltrate Every Organ, Including Brain, Study in Mice Shows
Scientists investigating the possible health effects of microplastics have uncovered some disturbing initial results in an experiment based on mice.
When old and young rodents drank microscopic fragments of plastic suspended in their water over the course of three weeks, researchers at the University of Rhode Island found traces of the pollutants had accumulated in every organ of the tiny mammal’s body, including the brain.
The presence of these microplastics was also accompanied by behavioral changes akin to dementia in humans, as well as changes to immune markers in the liver and brain.
The AI-assistant wars heat up with Claude Pro, a new ChatGPT Plus rival
On Thursday, AI-maker and OpenAI competitor Anthropic launched Claude Pro, a subscription-based version of its Claude.ai web-based AI assistant, which functions similarly to ChatGPT. It’s available for $20/month in the US or 18 pounds/month in the UK, and it promises five-times-higher usage limits, priority access to Claude during high-traffic periods, and early access to new features as they emerge.
Like ChatGPT, Claude Pro can compose text, summarize, do analysis, solve logic puzzles, and more.
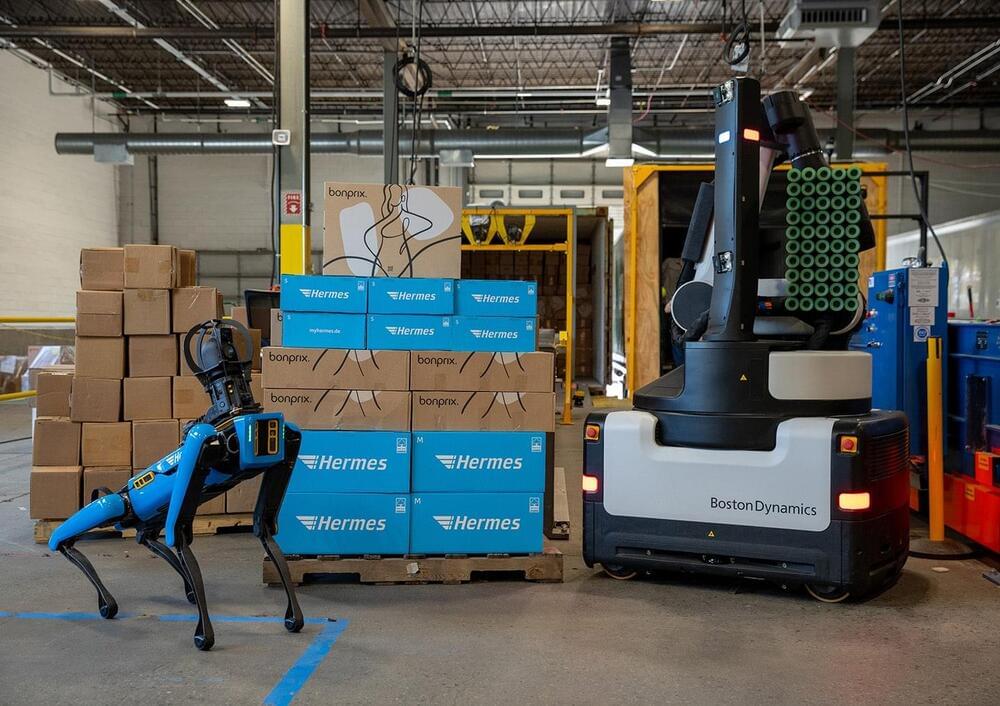

Otto Group Teams Up with Boston Dynamics to Strengthen Logistics Operations
Strategic agreement calls for fleet of Boston Dynamics robots to be deployed across more than 20 facilities over the next two years, to position retailer for the future.
Hamburg, Germany / Waltham, MA, USA – September 11, 2023 – The Otto Group, one of the world’s largest e-commerce retailers, has signed a strategic agreement with Boston Dynamics, the global leader in mobile robotics, to continue automating its logistics operations. The plan is to deploy Boston Dynamics’ Spot® robots in more than 10 and Stretch™ robots in more than 20 of the group’s facilities over the next two years, beginning with Hermes Fulfilment. The deployment supports Otto Group’s efforts to improve safety, increase operational efficiency and address labor shortages for specific types of warehouse work and the agreement marks the first time both of Boston Dynamics’ commercially available robots will be deployed together at enterprise scale.
Under the terms of the agreement, Spot, the four-legged mobile robot from Boston Dynamics, will support tunnel inspections and predictive maintenance activities for operations equipment, including thermal monitoring, analog gauge reading and acoustic detection of pressurized air and gas leaks. The Spot fleet will also run autonomous missions, collecting data for machine learning models to support tasks like fire exit egress monitoring and detecting slight changes in storage racks to keep Otto Group’s warehouses even safer. In addition, the Otto Group will be utilizing Stretch, Boston Dynamics’ box-moving robot designed for warehouse applications. Stretch will begin unloading containers at 10 facilities next year, with the goal of having all sites operational by the end of 2025. Stretch, which is particularly useful for unloading heavy packages in the container sector, will provide technological support for physically demanding activities.
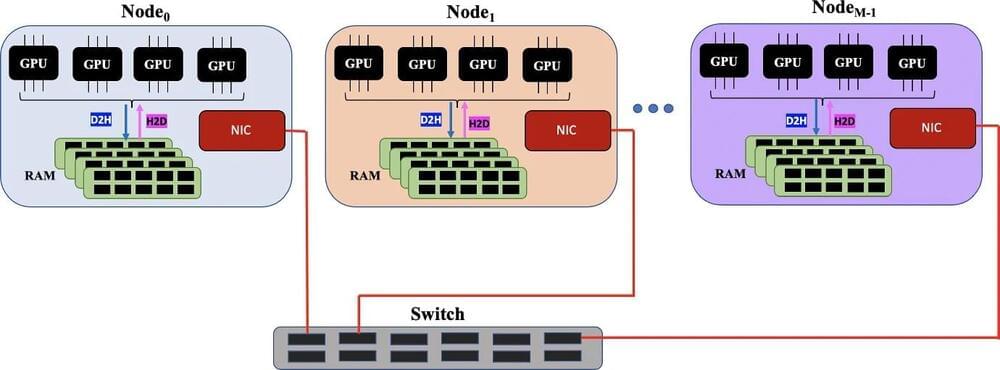
Machine learning masters massive data sets
A machine-learning algorithm demonstrated the capability to process data that exceeds a computer’s available memory by identifying a massive data set’s key features and dividing them into manageable batches that don’t choke computer hardware. Developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory, the algorithm set a world record for factorizing huge data sets during a test run on Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Summit, the world’s fifth-fastest supercomputer.
Equally efficient on laptops and supercomputers, the highly scalable algorithm solves hardware bottlenecks that prevent processing information from data-rich applications in cancer research, satellite imagery, social media networks, national security science and earthquake research, to name just a few.
“We developed an ‘out-of-memory’ implementation of the non-negative matrix factorization method that allows you to factorize larger data sets than previously possible on a given hardware,” said Ismael Boureima, a computational physicist at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Boureima is first author of the paper in The Journal of Supercomputing on the record-breaking algorithm.
UBIK — Take As Directed!
The ultimate answer to the supply chain issue.
A school project for motion graphics, put together several of the product advertisements found in Philip K Dick’s 1969 sci-fi novel into a full 1m commercial. Aimed for surrealism.
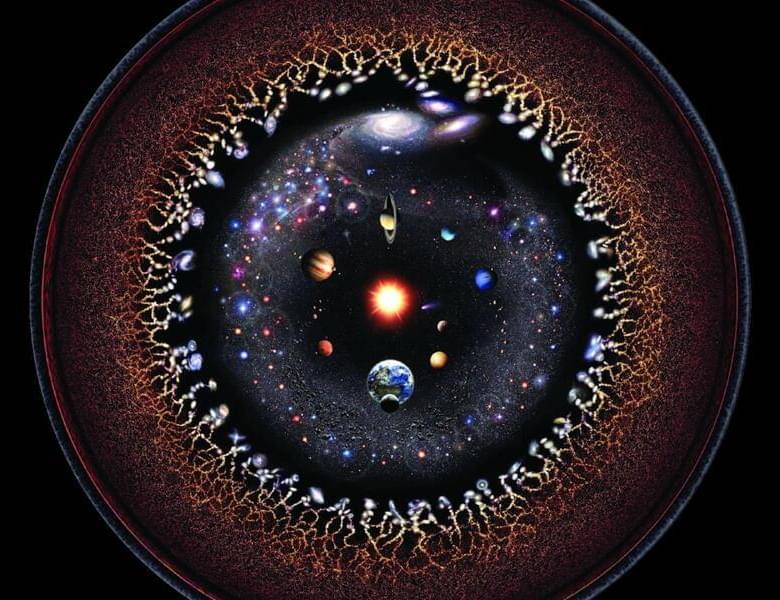
The case for a small universe
The universe is big, as Douglas Adams would say.
The most distant light we can see is the cosmic microwave background (CMB), which has taken more than 13 billion years to reach us. This marks the edge of the observable universe, and while you might think that means the universe is 26 billion light-years across, thanks to cosmic expansion it is now closer to 46 billion light-years across. By any measure, this is pretty darn big. But most cosmologists think the universe is much larger than our observable corner of it. That what we can see is a small part of an unimaginably vast, if not infinite creation. However, a new paper published on the arXiv preprint server argues that the observable universe is mostly all there is.
In other words, on a cosmic scale, the universe is quite small.
How x-ray vision is becoming a reality | Tara Boroushaki | TEDxMIT Salon
This talk is about how you can use wireless signals and fuse them with vision and other sensing modalities through AI algorithms to give humans and robots X-ray vision to see objects hidden inside boxes or behind other object.
Tara Boroushaki is a Ph.D student at MIT. Her research focuses on fusing radio frequency (RF) sensing with vision through artificial intelligence. She designs algorithms and builds systems that leverage such fusion to enable capabilities that were not feasible before in applications spanning augmented reality, virtual reality, robotics, smart homes, and smart manufacturing. This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.