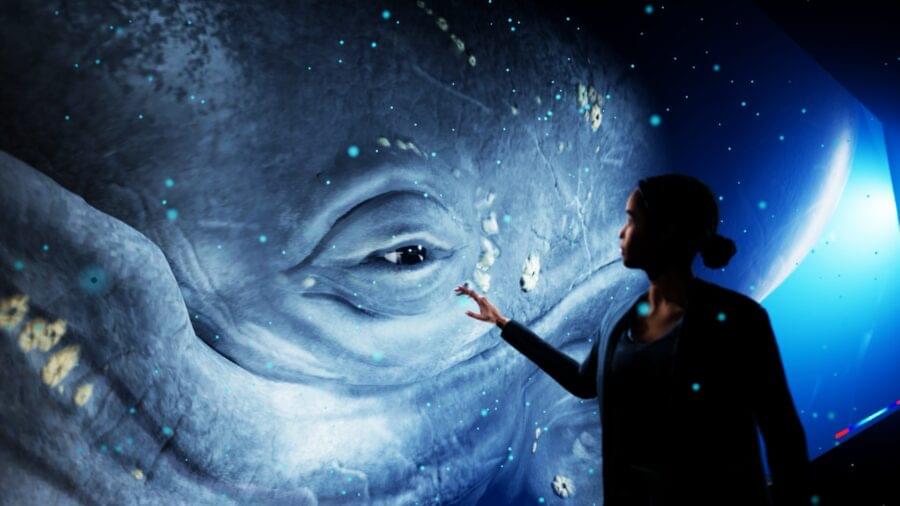
The number of Star Trek sci-fi technology that ultimately became real-life tech never ceases to amaze. The series inspired the development of touchscreens, communicators became mobile phones, PAADs became tablets, replicators became 3D printing, and now holodecks are becoming virtual and augmented realities (VRs and ARs). And while fully immersive environments like the holodeck still remain in the realm of sci-fi, a recent report from BBC on a hologram zoo indicates that the future isn’t so far-fetched when it comes to immersive holographic.
The holograms use a new depth technology that not only makes the animals seem big but makes them visible as 3D objects rather than suspended 2D images.
According to the report, the visitors of Australia’s Hologram Zoo, which opened earlier this year, can dodge stampeding elephants, peer into the gaping jaws of a hippopotamus, pet-friendly giraffes, and witness more than 50 lifelike displays from dinosaurs to gorillas—all crafted from concentrated beams of light.