Powerful tech companies keep LLMs like GPT-4 shrouded in secrecy. But a new wave of open-source LLMs is giving the power of chatbots to the people.
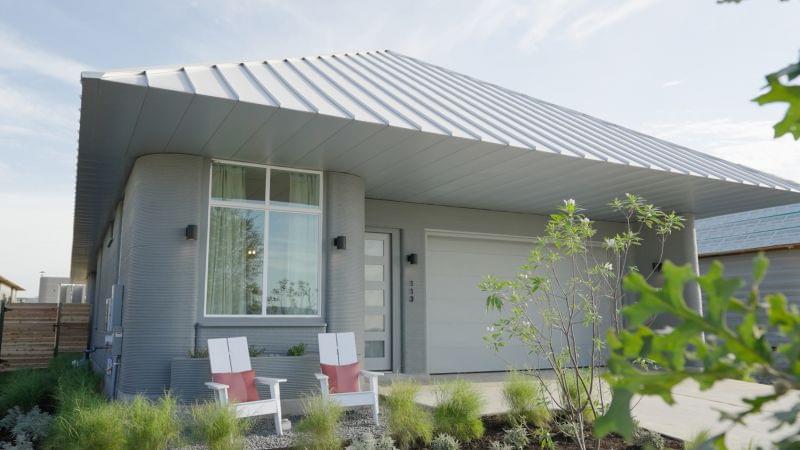



The world’s largest community of 3D-printed homes is being built in Texas — and the neighborhood just unveiled its first completed house.
With walls “printed” using a concrete-based material, the single-story structure is the first of 100 such homes set to welcome residents starting September.
The community is part of a wider development in Georgetown, Texas called Wolf Ranch. It’s located about 30 miles north of Austin, the state capital, and is a collaboration between Texas construction firm ICON, homebuilding company Lennar and Danish architecture practice Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG).


More often than not, studies of human biology are conducted when the body is under duress from infection or disease. Now, as part of a larger effort to delineate what “healthy” looks like, two Stanford Medicine teams have unfurled detailed molecular maps of healthy human intestinal and placental tissues. The maps, which capture cell types, cell quantity and other cellular nuances, are just two of a collection of maps that will establish a cellular baseline for the majority of the human body, including where cells in certain tissues congregate, how tissues develop during pregnancy and how cell-to-cell interactions drive human biology.
The studies, which published in Nature on July 19, are part of a larger effort spearheaded by the Human Biomolecular Atlas Program — called HuBMAP — funded by the National Institutes of Health. It aims to fill gaps in our knowledge of how the human body works when it’s in tip-top shape. Dozens of teams from the United States and Europe contribute to the HuBMAP consortium.
“In research, we have a habit of studying things that are abnormal without really understanding what normal looks like,” said Michael Angelo, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of pathology who is also the co-chair of the HuBMAP steering committee. “That’s created a big gap in our knowledge. HuBMAP is the only effort that is systematically focusing on the spatial architecture of these tissues.”

The rich world is ageing fast. How can societies afford the looming costs of caring for their growing elderly populations? film supported by @mission.winnow.
00:00 The wealthy world is ageing.
01:17 Japan’s elderly population.
02:11 The problems of an ageing world.
04:01 Reinventing old age.
05:48 Unlocking the potential of older years.
07:09 Reforming social care.
08:20 A community-based approach.
11:08 A fundamental shift is needed.
Read our special report on ageing and the economics of longevity here: https://econ.st/3EwnCV3
Sign up to The Economist’s daily newsletter to keep up to date with our latest stories: https://econ.st/3gJBH8D
Getting to grips with longevity: https://econ.st/3DBJU6k.
A small Japanese city shrinks with dignity: https://econ.st/3dBDgT2

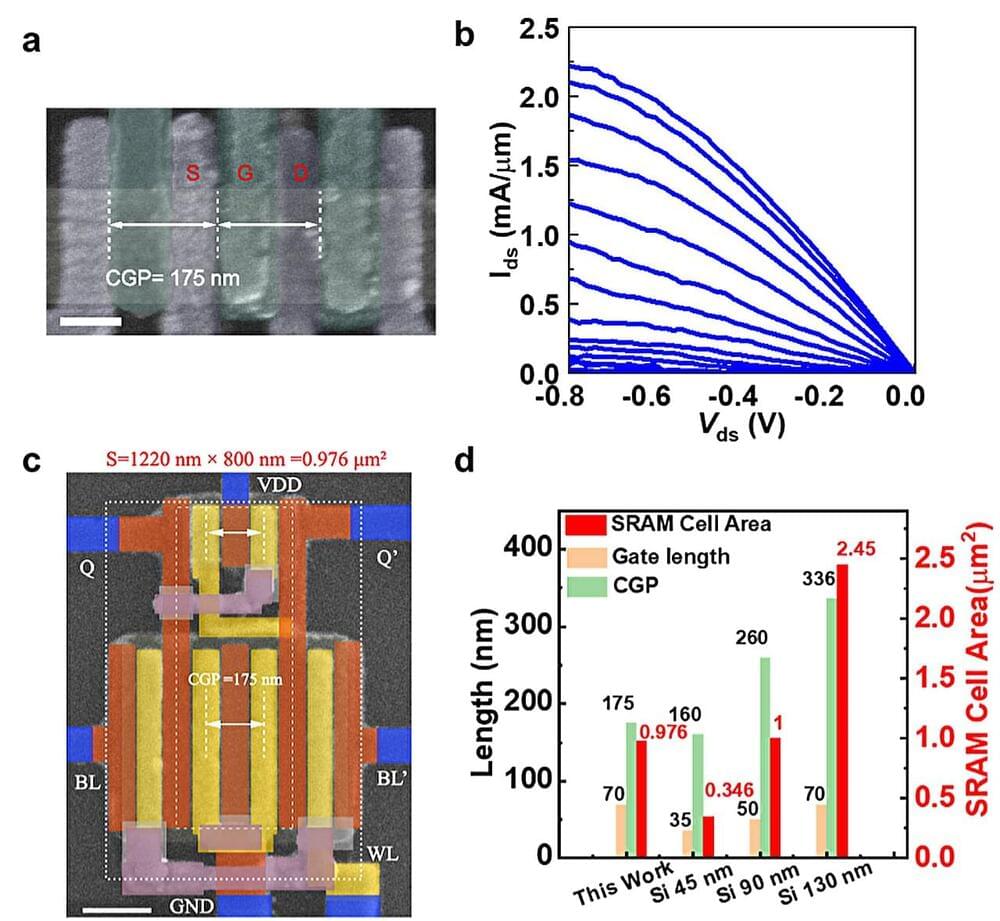
Carbon nanotubes, large cylindrical molecules composed of hybridized carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal structure, recently attracted significant attention among electronics engineers. Due to their geometric configuration and advantageous electronic properties, these unique molecules could be used to create smaller field-effect transistors (FETs) that exhibit high energy efficiencies.
FETs based on carbon nanotubes have the potential to outperform smaller transistors based on silicon, yet their advantage in real-world implementations has yet to be conclusively demonstrated. A recent paper by researchers at Peking University and other institutes in China, published in Nature Electronics, outlines the realization of FETs based on carbon nanotubes that can be scaled to the same size of a 10 nm silicon technology node.
“Recent progress in achieving wafer-scale high density semiconducting carbon nanotube arrays brough us one step closer to the practical use of carbon nanotubes in CMOS circuits,” Zhiyong Zhang, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “However, previous research efforts have mainly focused on the scaling of channel or gate length of carbon nanotube transistors while keeping large contact dimensions, which cannot be accepted for high density CMOS circuits in practical applications.