Brain-computer interface technology is moving fast and Silicon Valley is moving in. Will we all soon be typing with our minds?



If “junk” DNA goes toxic, does that suggest it had an original normal function? See the conclusion of this new paper, “Native functions of short tandem repeats” (emphasis added):
Historically, repetitive elements within human genomes have been viewed as mostly unregulated ‘junk DNA’ that is not under selective evolutionary pressure. As such expansions of these repetitive elements are unfortunate accidents which become apparent and important only when they elicit highly penetrant and syndromic human diseases. Consistent with this line of reasoning, the field of REDs [Repetitive Element Diseases] has largely focused on emergent toxic mechanisms as drivers of disease only in the setting of large STR [Short Tandem Repeats] expansions rather than considering their pathology as alterations in the native functions played by these repeats in their normal genomic contexts. Here, we propose re-framing the discussion around repetitive elements in general — and STRs in particular — within human genomes.
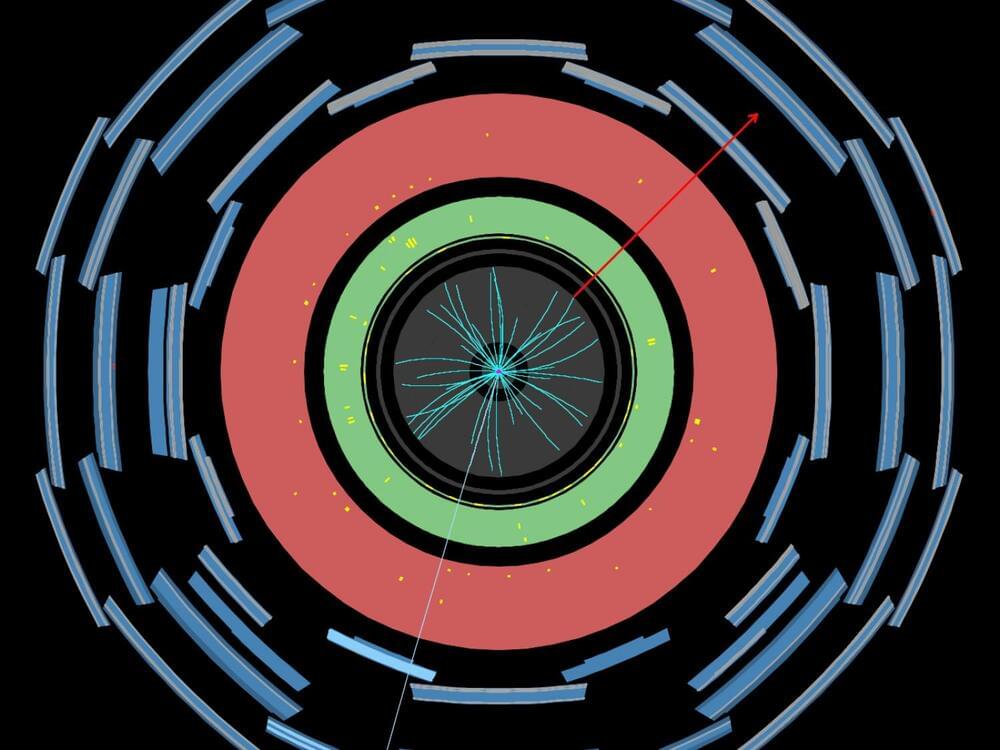
For the past 40 years, the W boson has been making headlines. In the 1980s, the announcement of its discovery helped confirm the theory of the electroweak interaction – a unified description of electromagnetic and weak forces. Today, measurements of its mass (mW) are testing the consistency of the Standard Model it helped to form. Figure 1: The measured value of the W-boson mass is compared to other published results. The vertical bands show the Standard Model prediction, and the horizontal bands and lines show the statistical and total uncertainties of the published results. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) The W-boson mass is closely related to the masses of nature’s heaviest particles, including the top quark and the Higgs boson. However, if additional heavy particles exist, the mass might deviate from the Standard Model prediction. By comparing direct measurements of the W-boson mass to theoretical calculations, physicists are looking for deviations that could be an indicator of new phenomena. To be sufficiently sensitive to such deviations, mass measurements need to have amazingly small uncertainties, of the order of 0.01%. In 2017, the ATLAS Collaboration at CERN published the LHC’s first measurement of the W-boson mass, giving a value of 80,370 MeV with an uncertainty of 19 MeV. At the time, this measurement was the most precise single-experiment result, and was in agreement with the Standard Model prediction and all other experimental results. Last year, the CDF Collaboration at Fermilab published an even more precise measurement of the W-boson mass, analysing the full dataset provided by the Tevatron collider. With a value of 80,434 MeV and an uncertainty of 9 MeV it differed significantly from the Standard Model prediction and from the other experimental results. In a new preliminary result released today, the ATLAS Collaboration reports an improved re-analysis of its initial W-boson mass measurement. ATLAS finds mW to be 80,360 MeV, with an uncertainty of just 16 MeV. The measured value is 10 MeV lower than the previous ATLAS result and is in agreement with the Standard Model. The ATLAS Collaboration has measured the W boson mass to be 80,360 MeV with an uncertainty of 16 MeV – in agreement with the Standard Model. Figure 2: The 68% and 95% confidence-level contours of the indirect determination of the W-boson and top-quark mass from the global electroweak fit are compared to the 68% and 95% confidence-level contours of the ATLAS measurements of the W-boson and top-quark masses. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) For this new analysis, ATLAS physicists revisited its data collected in 2011 at a centre-of-mass energy of 7 TeV (corresponding to 4.6 fb-1, also used in ATLAS’ previous measurement). Researchers employed improved statistical methods and refinements in the treatment of the data, enabling them to reduce the uncertainty of their mass measurement by more than 15%. Researchers focused on collision events where the W boson decays into an electron or a muon (leptons), and a corresponding neutrino. The W-boson mass was then determined by fitting the kinematic distributions of the decay leptons in simulation to the data. The main difference between the 2017 and the new measurement is in the method used to perform these fits. While the previous measurement used the available data solely to determine the W-boson mass, with systematic uncertainties added after the fact, the new measurement simultaneously adjusts the systematic uncertainties together with the W-boson mass. This improvement reduced several systematic uncertainties, particularly those related to the theoretical modelling of W-boson production and decay. The W-boson transverse momentum distribution has as much of an influence on the lepton-decay distributions as the W-boson mass itself – and is therefore an important source of uncertainty. As the resolution of the 2011 data was too poor to verify the modelling of this distribution in detail, researchers instead used data recorded in 2017 during a special, low-luminosity proton-proton run at a centre-of-mass energy of 5 TeV. They found the data agreed with predicted distributions, thus validating the model. Also crucial to the measurement were the parton distribution functions (PDFs) of the proton, which model the relative momenta of its quark and gluon constituents. PDFs incorporate a multitude of data from different particle physics experiments. Since the previous measurement, these sets have been refined by including more data. The new ATLAS measurement evaluated the dependence of the measured W-boson mass on PDFs sets considering these more recent versions. Future measurements of the W-boson mass are expected by other LHC experiments, as well as further studies by ATLAS using data samples recorded in different pile-up conditions and at different centre-of-mass energies. These will provide independent evaluations of the experimental results obtained so far. About the event display in the banner: Display of a candidate W→μν event using proton-proton collisions at 7 TeV centre-of-mass energy at the LHC. Starting from the centre of the ATLAS detector, the reconstructed tracks of the charged particles in the Inner Detector (ID) are shown as cyan lines. The energy deposits in the electromagnetic (the green layer) and hadronic (the red layer) calorimeters are shown as yellow boxes. The identified muon is shown with its reconstructed track (blue line) passing through the muon chambers (blue layers). The muon has a transverse momentum of pT=36 GeV, whereas the missing transverse energy (red arrow) is 35 GeV and corresponds to the muon neutrino energy. The transverse mass of the W boson candidate is 71 GeV. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Explore the interactive event display Dynamic view of a candidate W→μν event using proton-proton collisions at 7 TeV centre-of-mass energy at the LHC. Starting from the centre of the ATLAS detector, the reconstructed tracks of the charged particles in the Inner Detector (ID) are shown as red lines. The energy deposits in the calorimeters are shown as yellow boxes. The identified muon is shown as a longer red dashed line. The missing transverse momentum is shown by a green dashed line. Learn more Improved W boson Mass Measurement using 7 TeV Proton-Proton Collisions with the ATLAS Detector (ATLAS-CONF-2023–004) Improved ATLAS result weighs in on the W boson, CERN Press Release, March 2023 Moriond EW 2023 presentation by Matthias Schott: EWK highlights from ATLAS High-precision measurement of the W boson mass with the CDF II detector (Science, Vol 376, Issue 6589) Briefing to previous W boson mass measurement, Physics Briefing, December 2016 First high-precision measurement of the mass of the W boson at the LHC, CERN Press Release, February 2018.
For a while now, we’ve known there’s a complex interplay between our hormones, guts, and mental health, but untangling the most relevant connections within our bodies has proved challenging.
New research has found a single enzyme that links all three, and its presence may be responsible for depression in some women during their reproductive years.
Wuhan University medical researcher Di Li and colleagues compared the blood serum of 91 women aged between 18 and 45 years with depression and 98 without. Incredibly, those with depression had almost half the serum levels of estradiol – the primary form of estrogen our bodies use during our fertile years.
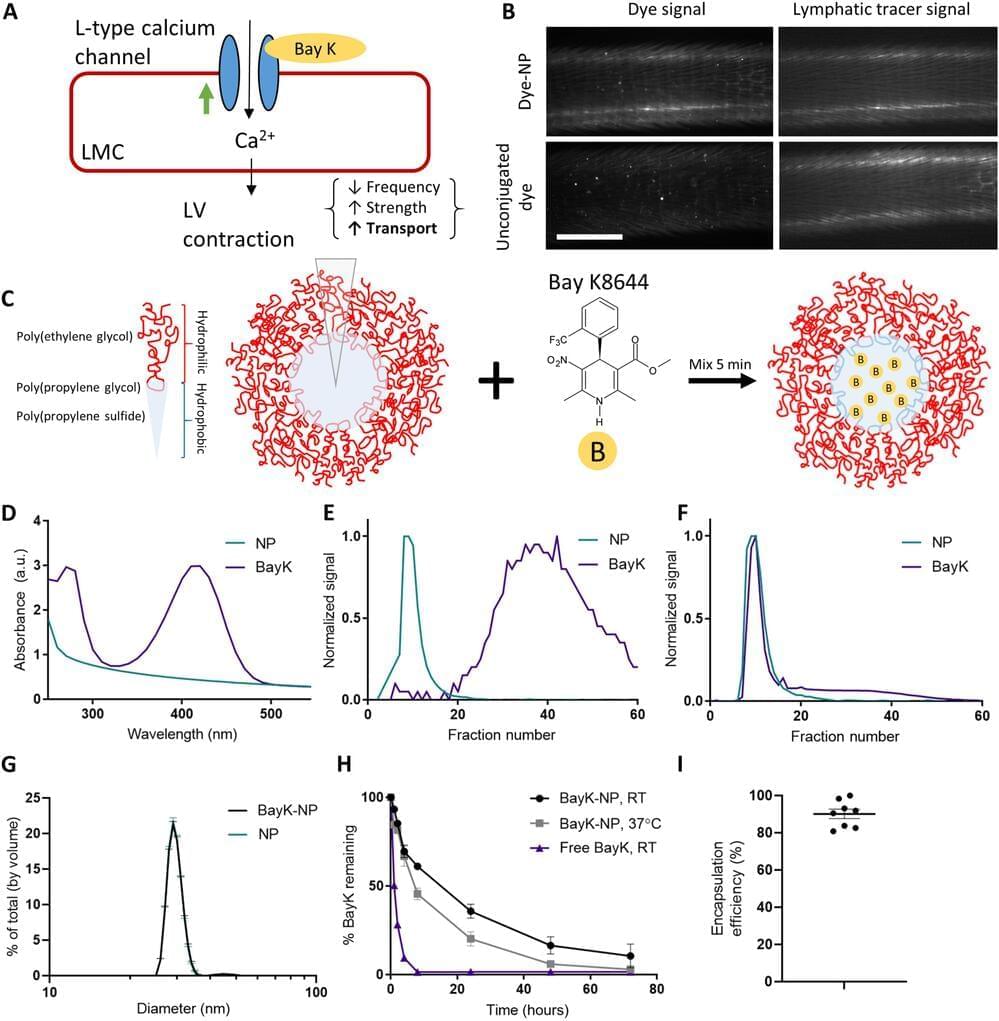
The human body is made up of thousands of tiny lymphatic vessels that ferry white blood cells and proteins around the body, like a superhighway of the immune system. It’s remarkably efficient, but if damaged from injury or cancer treatment, the whole system starts to fail. The resulting fluid retention and swelling, called lymphedema, isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s also irreversible.
When lymphatic vessels fail, typically their ability to pump out the fluid is compromised. Georgia Institute of Technology researchers have developed a new treatment using nanoparticles that can repair lymphatic vessel pumping. Traditionally, researchers in the field have tried to regrow lymphatic vessels, but repairing the pumping action is a unique approach.
“With many patients, the challenge is that the lymphatic vessels that still exist in the patient aren’t working. So it’s not that you need to grow new vessels that you can think of as tubes, it’s that you need to get the tubes to work, which for lymphatic vessels means to pump,” said Brandon Dixon, a professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering. “That’s where our approach is really different. It delivers a drug to help lymphatic vessels pump using a nanoparticle that can drain into the diseased vessels themselves.”


“AlphaFold was a huge advance in protein structure prediction. We were inspired by the advances they made, which led to a whole new wave of using deep learning,” said Professor David Baker, a biochemist and computational biologist at the University of Washington.
“The advantage of ESMFold is that it is very fast, and so can be used to predict the structures of a larger set of proteins than AlphaFold, albeit with slightly lower accuracy, similar to that of RoseTTAFold,” Dr. Baker said, referring to a tool that emerged from his lab in 2021.
DeepMind open-sourced the code for AlphaFold2, making it freely available to the community. Nearly all proteins known to science—about 214 million—can be looked up in the public AlphaFold Protein Structure Database. Meta’s ESM Metagenomic Atlas includes 617 million proteins.
Researchers at Yale have for the first time, using a process known as quantum error correction, substantially extended the lifetime of a quantum bit—a long-sought-after goal and one of the trickiest challenges in the field of quantum physics.
Led by Yale’s Michael Devoret, the experiment proves—decades after its theoretical foundations were proposed—that quantum error correction works in practice. Quantum error correction is a process designed to keep quantum information intact for a period of time longer than if the same information were stored in hardware components without any correction.
The results were published March 22 in Nature.
The technology I want to talk about today is something out of this world, but also a bit controversial There is a startup in Australia who are actually growing live human neurons and then integrating it into traditional computer chips… mind-blowing stuff!
My Gear:
Camera Sony Alpha 7 III: https://amzn.to/3dmv2O6
Lens Sony 50mm F1.8: https://amzn.to/3weJoJo.
Mic Sennheiser: https://amzn.to/3IKW5Ax.
Music from my videos: https://www.epidemicsound.com/referral/908oe4
Support me on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/AnastasiInTech
A leading neuroscientist claims that a pong-playing clump of about a million neurons is “sentient”. What does that mean? Why did they teach a lab-grown brain to play pong? To study biological self-organization at the root of life, intelligence, and consciousness. And, according to their website, “to see what happens.”
CORRECTIONS/Clarifications:
- The cells aren’t directly frozen in liquid nitrogen — they are put in vials and stored in liquid nitrogen: https://www.atcc.org/products/pcs-201-010
- The sentience of some invertebrates, like octopuses, is generally agreed upon. Prominent scientists affirmed non-human consciousness in the Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness: https://philiplow.foundation/consciousness/
DISCLAIMER: The explanations in this video are those proposed by the researchers, or my opinion. We are far from understanding how brains, or even neurons, work. The free energy principle is one of many potential explanations.
Support the channel: https://www.patreon.com/IhmCurious.
Footage from Cortical Labs: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=neV3aZtTgVM
NASJAQ’s interview with founder Hon Weng Chong: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y1R5k5QWPsY
Cortical Labs website: https://corticallabs.com.
Full paper on DishBrain: https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(22)00806-6