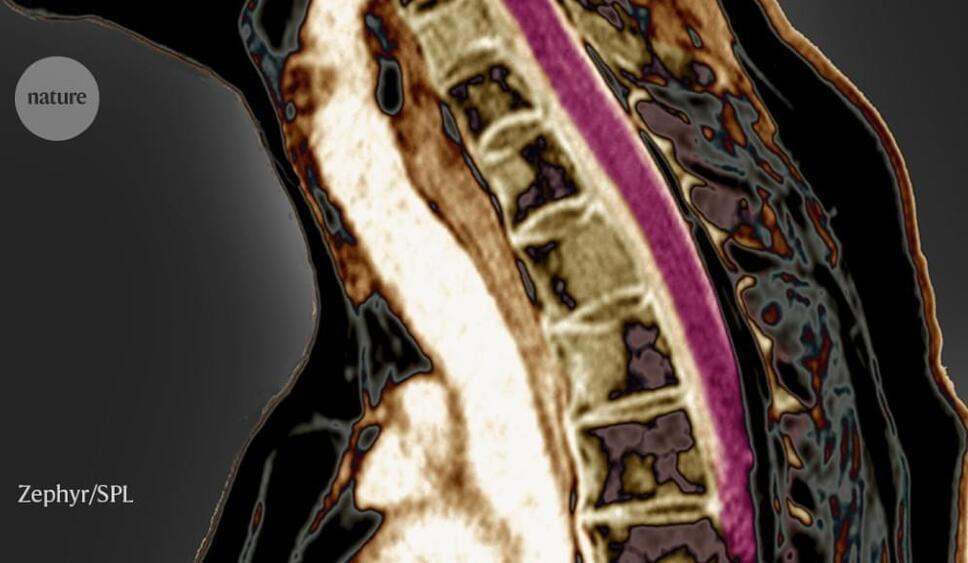
A stem cell that contributes to vertebra formation also encourages the growth of tumours that move to the backbone from elsewhere.


Quantum behavior is a strange, fragile thing that hovers on the edge of reality, between a world of possibility and a Universe of absolutes. In that mathematical haze lies the potential of quantum computing; the promise of devices that could quickly solve algorithms that would take classic computers too long to process.
For now, quantum computers are confined to cool rooms close to absolute zero (−273 degrees Celsius) where particles are less likely to tumble out of their critical quantum states.
Breaking through this temperature barrier to develop materials that still exhibit quantum properties at room temperatures has long been the goal of quantum computing. Though the low temperatures help keep the particle’s properties from collapsing out of their useful fog of possibility, the bulk and expense of the equipment limits their potential and ability to be scaled up for general use.

“In particular, the wind turbine sector uses very large quantities of a rare earth magnet that’s an alloy of neodymium, iron and boron (NdFeB). These NdFeB magnets are critical components used in PMSGs (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator) in larger onshore and offshore wind turbines”.
Extracting the rare earth magnets from end-of-life wind turbines and enabling their use in new wind turbines, both onshore and offshore
Named Re-Rewind, the partnership, partly funded by Innovate UK, aims to establish the UK’s first circular supply chain for the rare earth magnets used in wind turbines.
“From high-quality construction steel, copper and other metals to a range of rare earth elements (such as praseodymium and dysprosium), modern wind turbines contain a wealth of materials which, if they cannot be sourced from recycled channels, must be mined, leading to increased environmental impacts and resource scarcity”, the newly created partnership states.
Join this virtual presentation to learn the most innovative procedures available for treating heart disease.
Presented by: juan grau, MD, director, cardiothoracic surgery.

The API-AI nexus isn’t just for tech enthusiasts; its influence has widespread real-world implications. Consider the healthcare sector, where APIs can allow diagnostic AI algorithms to access patient medical records while adhering to privacy regulations. In the financial sector, advanced APIs can connect risk-assessment AIs to real-time market data. In education, APIs can provide the data backbone for AI algorithms designed to create personalized, adaptive learning paths.
However, this fusion of AI and APIs also raises critical questions about data privacy, ethical use and governance. As we continue to knit together more aspects of our digital world, these concerns will need to be addressed to foster a harmonious and responsible AI-API ecosystem.
We stand at the crossroads of a monumental technological paradigm shift. As AI continues to advance, APIs are evolving in parallel to unlock and amplify this potential. If you’re in the realm of digital products, the message is clear: The future is not just automated; it’s API-fied. Whether you’re a developer, a business leader or an end user, this new age promises unprecedented levels of interaction, personalization and efficiency—but it’s upon us to navigate it responsibly.

38 Terabytes of data accidentally leaked.
Article from PC Mag.
A misconfigured link accidentally leaked access to 38TB of Microsoft data, opening up the ability to inject malicious code into its AI models.
The finding comes from cloud security provider Wiz, which recently scanned the internet for exposed storage accounts. It found a software repository on Microsoft-owned GitHub dedicated to supplying open-source code and AI models for image recognition.
On the affected GitHub page, a Microsoft employee had created a URL, enabling visitors to the software repository to download AI models from an Azure storage container. “However, this URL allowed access to more than just open-source models,” Wiz said in its report. “It was configured to grant permissions on the entire storage account, exposing additional private data by mistake.”
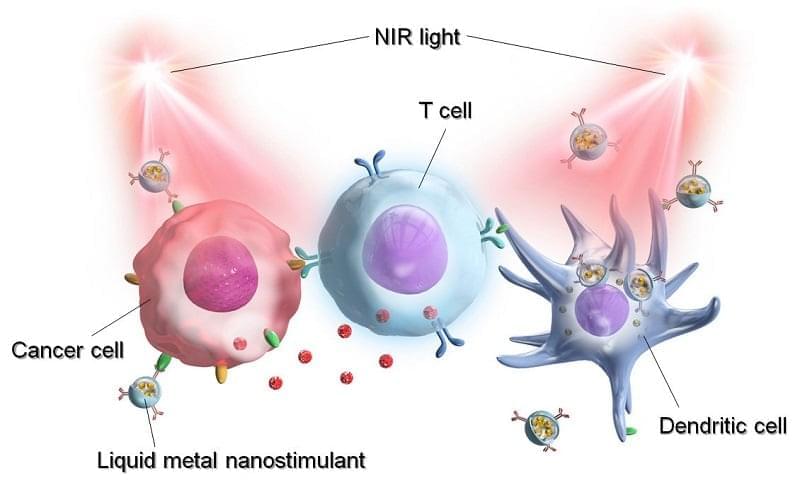
More noninvasive cancer treatments are being made:
A research group from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) developed light-activatable, liquid metal (LM) nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and treatment via photoimmunotherapy. The LM nanoparticles can target and destroy cancer cells and can be fluorescently tagged to function as reporters to identify and eliminate tumors in vivo.
Gallium (Ga)-based LM nanoparticles are promising nanoscale materials for biomedical applications due to their physicochemical properties, including flexibility, easy surface modification, efficient photothermal conversion, and high biocompatibility.
Synopsys is looking to add generative AI to its EDA tools to boost chip design productivity.
The company already uses a range of AI techniques in its tools from deep neural networks (DNNs) to recursive neural networks (RNNs). These are incorporated into the DSO.ai, VSI.ai and TSO.ai tools that have been used for well over 100 chip tapeouts.
Now the company is looking at the transformer network technologies used in generative AI (Gen-AI) to further enhance the tools says founder and retiring CEO Aart de Geus.
“We intend to harness Gen-AI capabilities into Synopsys.ai. We see this delivering further advances in design assistance, design exploration, and design generation,” said de Geus.
Scientists discover a biomarker in stroke survivors, suggesting that chemical changes after stroke can lead to depression. The findings may pave the way toward treatment.