For decades, researchers have sought ways to precisely manipulate and identify individual molecules like DNA in liquid environments. Such capabilities could revolutionize areas ranging from disease diagnosis to drug development. However, the randomness of molecular movements in fluids has hindered progress.
Now, scientists from Shenzhen University and the Chinese University of Hong Kong report promising advances in optical tweezing techniques that allow exquisite control over nanoscale biological particles (Light: Science & Applications, “CRISPR-powered optothermal nanotweezers: Diverse bio-nanoparticle manipulation and single nucleotide identification”).
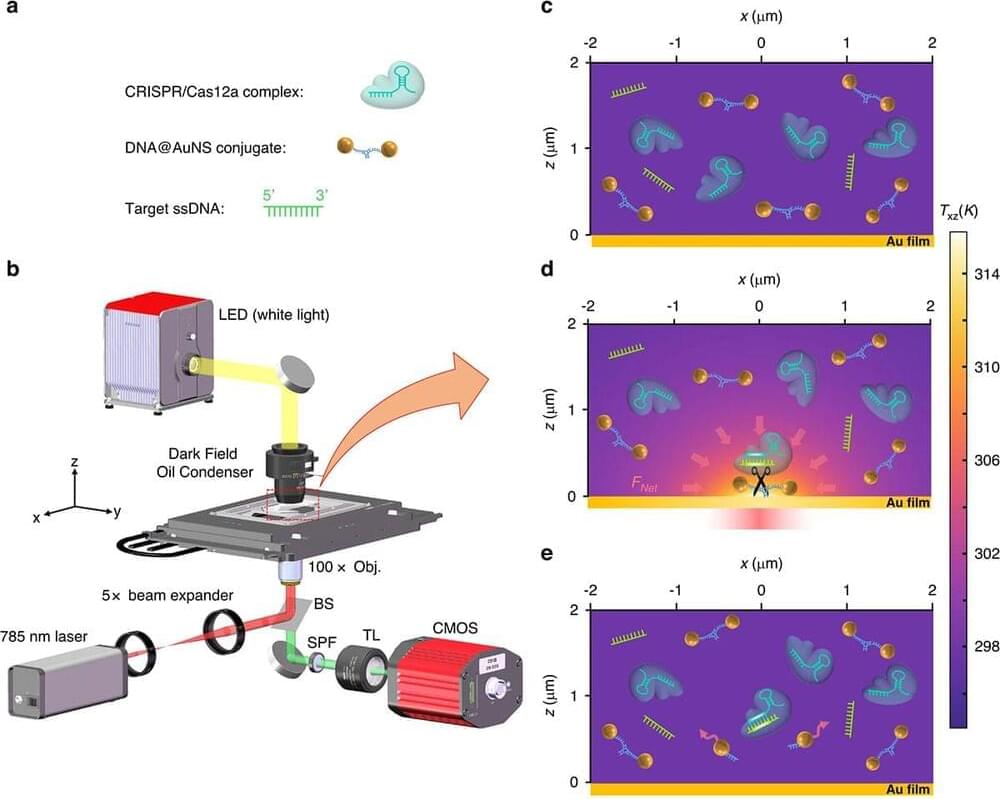
A The diagrammatic sketch of the three components in the solution: DNA@AuNS conjugate, CRISPR/Cas12a complex, and target ssDNA. b Optical setup, the BS, SPF, and TL are beam splitter, short pass filter, and tube lens (f = 200 mm), respectively. Additional details of the setup are provided in the Materials and Methods section. c Dispersion of the three components in the solution without optical heating. d Optothermal net force induced migration and DNA@AuNS conjugate cleavage upon optical heating, the heating laser power is 0.5 mW. e Observation of the cleavage after the optical heating is switched off. (© Light: Science & Applications) (click on image to enlarge)