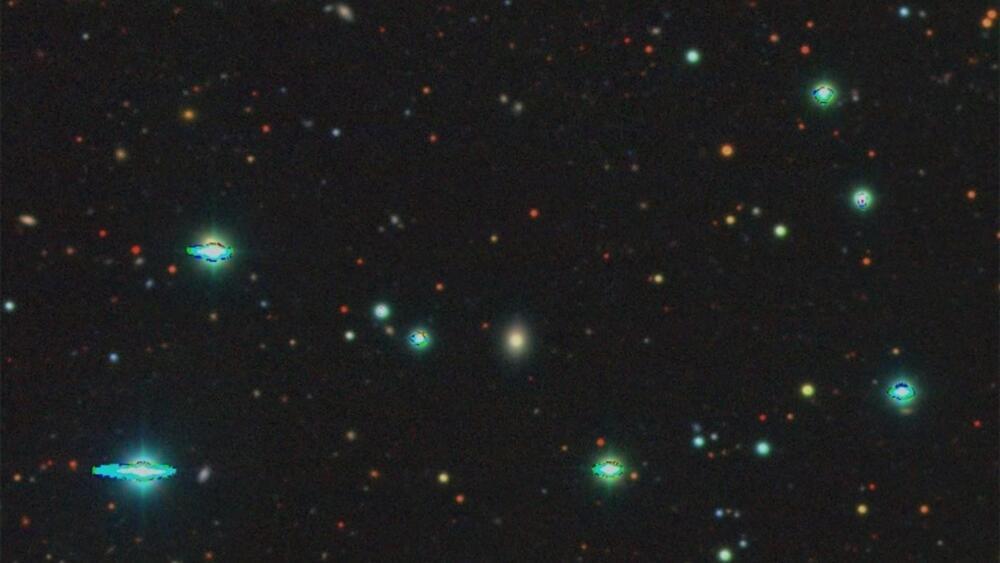
Vera C. Rubin Observatory will help shed light on the dark universe.
The upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory will help astronomers better understand two perplexing phenomena: dark energy and dark matter. Dark energy, which accounts for 68 percent of the universe, is an enigmatic factor responsible for the observed rapid expansion of the universe. Dark matter, which comprises 27 percent of all matter, has gravitational pull but does not interact with light, therefore remaining hidden.
Together, these mysterious components form what scientists refer to as the dark universe.
RubinObs/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. Pinto.
Dark energy, which accounts for 68 percent of the universe, is an enigmatic factor responsible for the observed rapid expansion of the universe. Dark matter, which comprises 27 percent of all matter, has gravitational pull but does not interact with light, therefore remaining hidden.