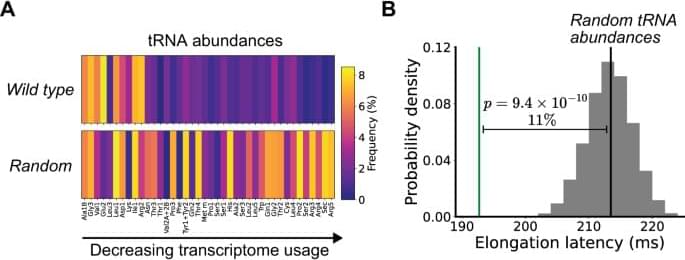
Mature fields of engineering use physics-based models to design systems that work reliably the first time. Here the authors show how a similar approach can be used to design and build a cellular-scale system, protein synthesis, from scratch.




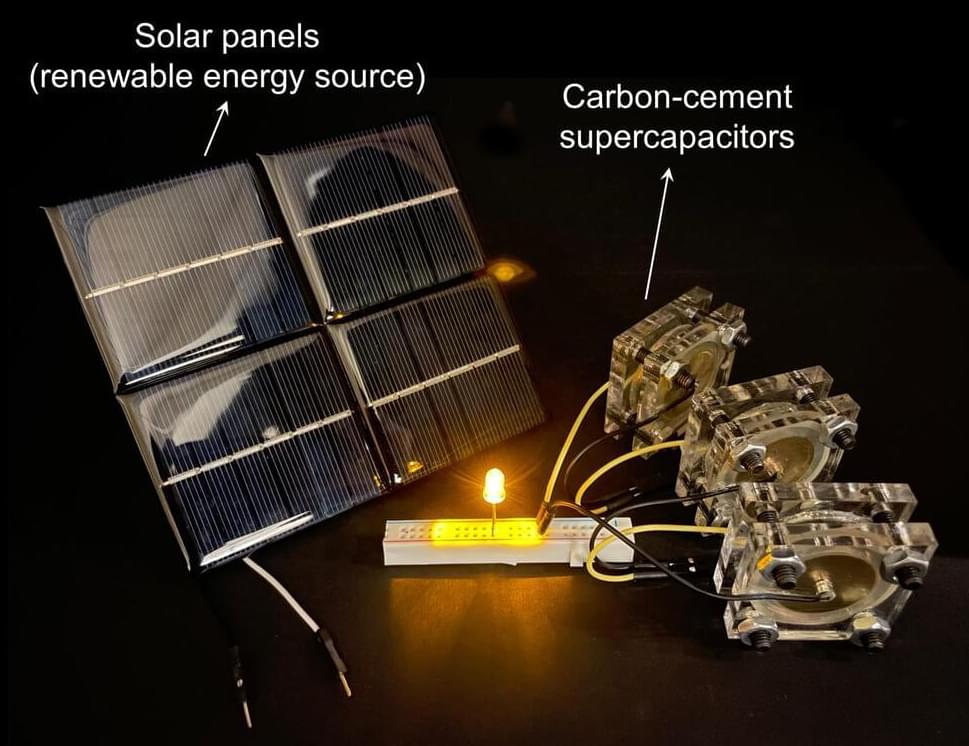
Two of humanity’s most ubiquitous historical materials, cement and carbon black (which resembles very fine charcoal), may form the basis for a novel, low-cost energy storage system, according to a new study. The technology could facilitate the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and tidal power by allowing energy networks to remain stable despite fluctuations in renewable energy supply.
The two materials, the researchers found, can be combined with water to make a supercapacitor—an alternative to batteries—that could provide storage of electrical energy.
As an example, the MIT researchers who developed the system say that their supercapacitor could eventually be incorporated into the concrete foundation of a house, where it could store a full day’s worth of energy while adding little (or no) to the cost of the foundation and still providing the needed structural strength. The researchers also envision a concrete roadway that could provide contactless recharging for electric cars as they travel over that road.
Using conventional testing techniques, it can be challenging—sometimes impossible—to detect harmful contaminants such as nano-plastics, air pollutants and microbes in living organisms and natural materials. These contaminants are sometimes found in such tiny quantities that tests are unable to reliably pick them up.
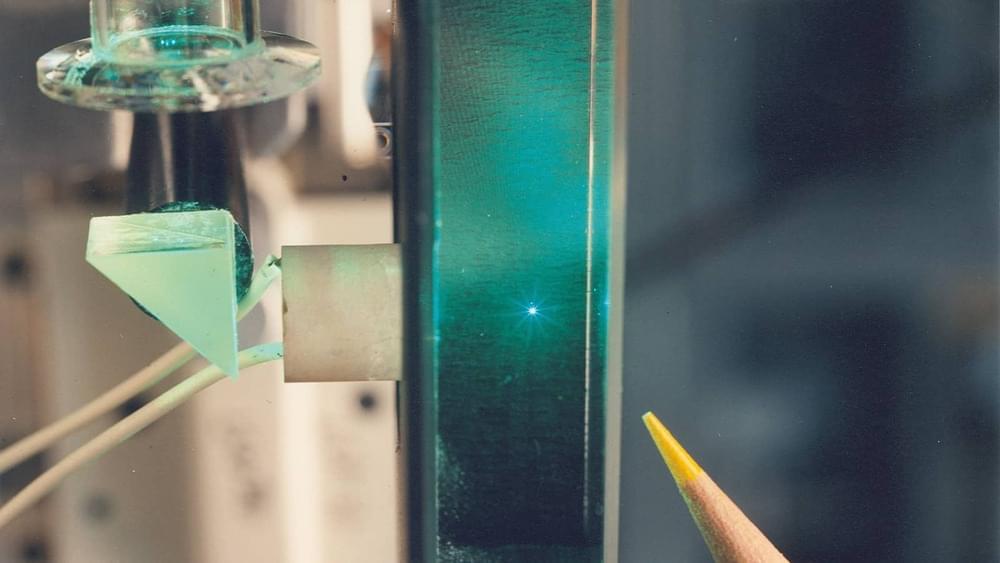
This may soon change, however. Emerging nanotechnology (based on a “twisted” state of light) promises to make it easier to identify the chemical composition of impurities and their geometrical shape in samples of air, liquid and live tissue.
An international team of scientists led by physicists at the University of Bath is contributing toward this technology, which may pave the way to new environmental monitoring methods and advanced medicines. Their work is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
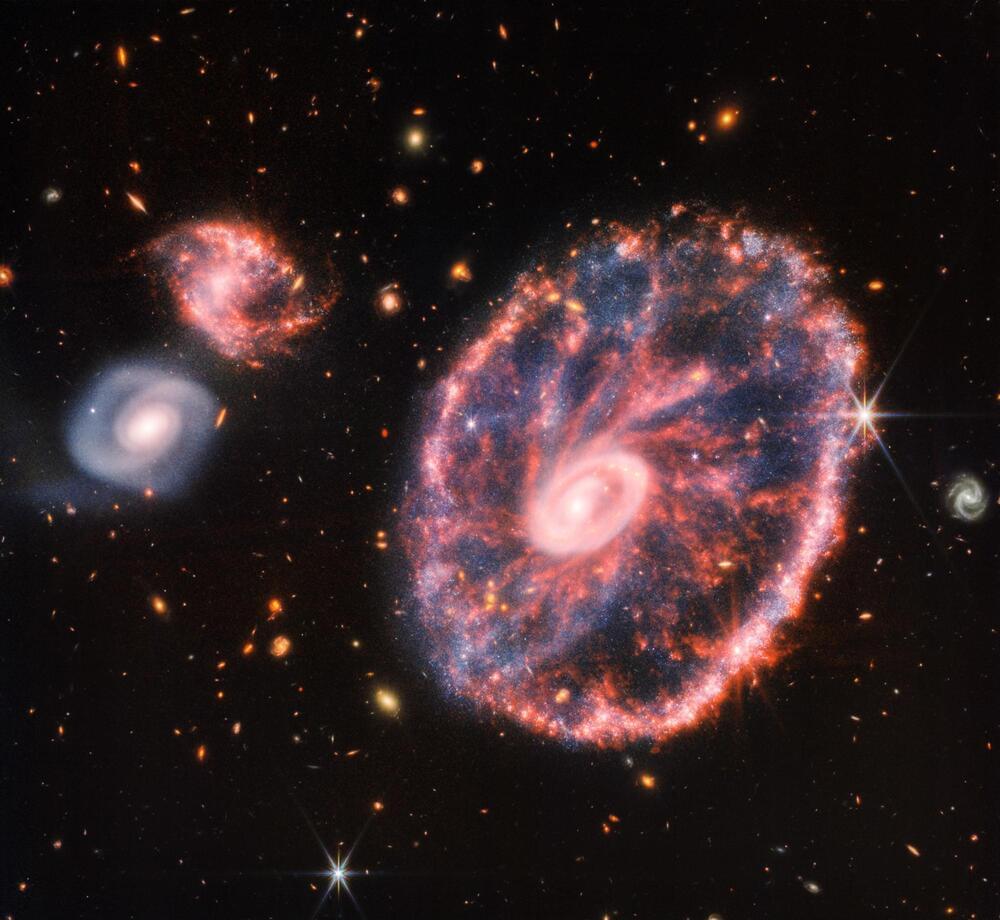

As the James Webb Space Telescope enters its second year of capturing images of the depths of space, it has already revealed a treasure trove of beauty from around the universe, both near and far from home.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was launched on Christmas Day in 2021, and sent back its first batch of images on July 12, 2022, making this July its functional birthday.
This telescope, now situated around 1 million miles from Earth as it photographs the cosmos, is the successor space telescope to Hubble, designed to peer far back into the universe’s history and study the earliest stars and galaxies.

The works will be sent in commercial shipments in tandem with NASA’s Artemis missions.
Adam Schrader, July 31, 2023.
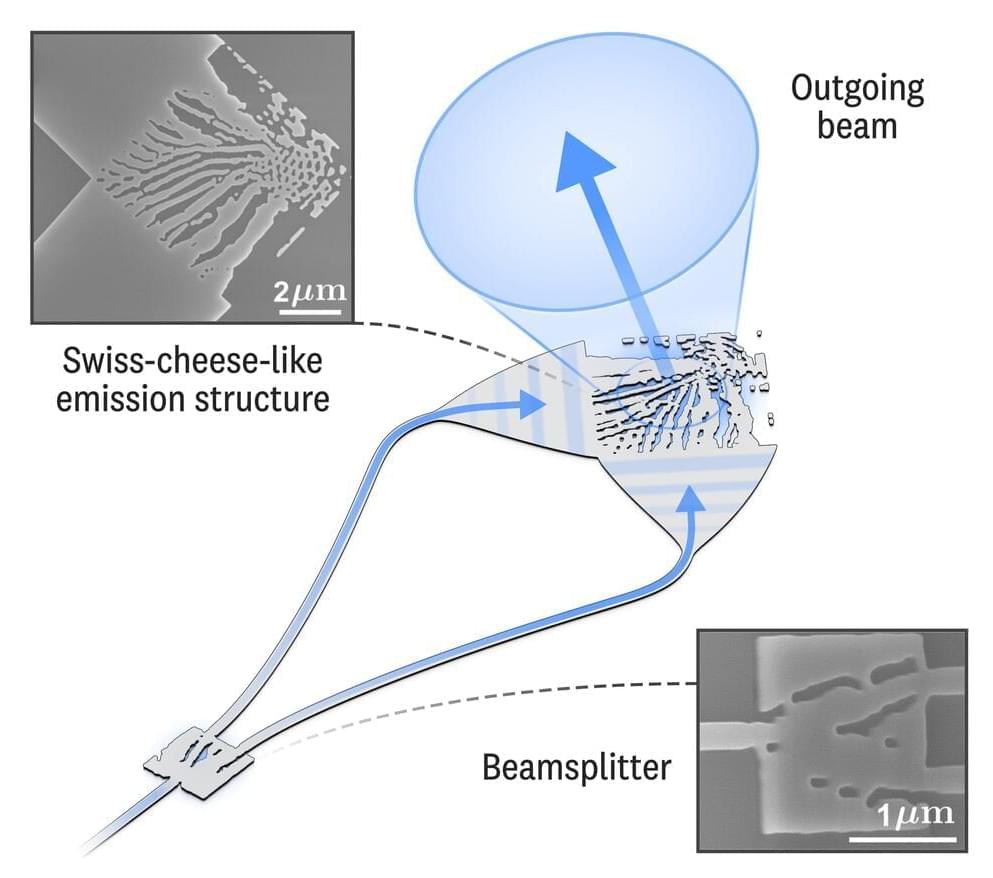
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have devised a photonic circuit on a chip that transforms a single incoming beam of laser light into a panoply of new beams, each with a host of different optical properties.
The newly generated beams—which retain the frequency of the original beam—simultaneously exit the circuit at different locations along the chip. That allows scientists and engineers to select the specific characteristics of one or more beams needed for a particular application.
Precision shaping and controlling beams of visible light are critical for diagnosing and studying human diseases, trapping atoms that form the basis of the world’s most accurate clocks, quantum computing, and many other quantum-based technologies.