Two mammoth underground detectors have delivered more stringent upper limits on how strongly a putative dark matter candidate interacts with normal matter.



A laser for vibrational energy, rather than for light, operating in the quantum regime could teach researchers about the interplay between spin, vibration, and dissipation in quantum mechanics.
Phonon lasers replace the light excitations (photons) that are used in a standard laser with vibrational excitations of matter (phonons). Researchers have now coaxed two ions into forming a phonon laser containing fewer than 10 phonons, placing it firmly in the quantum regime [1], whereas previous phonon lasers had at least 10,000 phonons. The researchers plan to use this quantum phonon laser as a tool to investigate the role of dissipation in the behavior of quantum systems.
Dissipation—energy leaking into or out of a system in the form of heat—is often seen as a nuisance in physics, for example, when it takes the form of air resistance and reduces the fuel efficiency of a car or an airplane. But quantum systems also exhibit dissipation, and its effects in the quantum realm are not fully understood. Jonathan Home of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) in Zurich and his colleagues wanted to investigate how two separate sources of dissipation can interact to affect the behavior of a quantum system. “A laser is the simplest quantum system we could think of” that allows such experiments, Home says.
It’s possibly the most famous question in all of science — where is everyone? Join us today for deep dive into Fermi Paradox. 🌏 Get exclusive NordVPN deal here ➵ https://NordVPN.com/coolworlds It’s risk free with Nord’s 30 day money-back guarantee!✌
The Fermi Paradox has been a topic of keen debate amongst scientists, astronomers and the rest of us for more than seven decades. We can’t resist the urge to speculate about aliens! But what is the paradox even really about? What explanations have been offered? Today, we explore this famous question, and offer a mind-shifting explanation.
Written and presented by Prof David Kipping.
→ Support our research program: https://www.coolworldslab.com/support.
→ Get Stash here! https://teespring.com/stores/cool-worlds-store.
THANK-YOU to our supporters D. Smith, M. Sloan, C. Bottaccini, D. Daughaday, A. Jones, S. Brownlee, N. Kildal, Z. Star, E. West, T. Zajonc, C. Wolfred, L. Skov, G. Benson, A. De Vaal, M. Elliott, B. Daniluk, M. Forbes, S. Vystoropskyi, S. Lee, Z. Danielson, C. Fitzgerald, C. Souter, M. Gillette, T. Jeffcoat, J. Rockett, D. Murphree, S. Hannum, T. Donkin, K. Myers, A. Schoen, K. Dabrowski, J. Black, R. Ramezankhani, J. Armstrong, K. Weber, S. Marks, L. Robinson, S. Roulier, B. Smith, G. Canterbury, J. Cassese, J. Kruger, S. Way, P. Finch, S. Applegate, L. Watson, E. Zahnle, N. Gebben, J. Bergman, E. Dessoi, J. Alexander, C. Macdonald, M. Hedlund, P. Kaup, C. Hays, W. Evans, D. Bansal, J. Curtin, J. Sturm, RAND Corp., M. Donovan, N. Corwin, M. Mangione, K. Howard, L. Deacon, G. Metts, G. Genova, R. Provost, B. Sigurjonsson, G. Fullwood, B. Walford, J. Boyd, N. De Haan, J. Gillmer, R. Williams, E. Garland, A. Leishman, A. Phan Le, R. Lovely, M. Spoto, A. Steele, M. Varenka, K. Yarbrough, A. Cornejo, D. Compos, F. Demopoulos, G. Bylinsky, J. Werner, B. Pearson, S. Thayer & T. Edris.
::References::
Go to https://brilliant.org/drbecky to get a 30-day free trial and the first 200 people will get 20% off their annual subscription. A new research study has come out claiming that to explain the massive galaxies found at huge distances in James Webb Space Telescope images, the Universe is older than we think, at 26.7 billion years (rather than 13.8 billion years old). In this video I’m diving into that study, looking at what model they used to get at that claim (a combination of the expansion of the universe and “tired light” ideas of redshift), how this impacts our best model of the Universe and the so-called “Crisis is Cosmology”, and why I’m not convinced yet!
#astronomy #JWST #cosmology.
My previous YouTube video on how JWST’s massive galaxies are no longer “impossible” — https://youtu.be/W4KH1Jw6HBI
Gupta et al. (2023; is the universe 26.7 billion years old?) — https://academic.oup.com/mnras/advance-article/doi/10.1093/m…32/7221343
Labbé et al. (2023; over-massive galaxies spotted in JWST data) — https://arxiv.org/pdf/2207.12446.pdf.
Arrabal Haro et al. (2023; z~16 candidate galaxy turns out to be z=4.9) — https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.15431.pdf.
Zwicky (1929; “tired light” hypothesis raised for first time) — https://www.pnas.org/doi/epdf/10.1073/pnas.15.10.
JWST observing schedules (with public access!): https://www.stsci.edu/jwst/science-execution/observing-schedules.
JWST data archive: https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
Twitter bot for JWST current observations: https://twitter.com/JWSTObservation.
The successful proposals in Cycle 2 (click on the proposal number and then “public PDF” to see details): https://www.stsci.edu/jwst/science-execution/approved-progra…cycle-2-go.
00:00 — Introduction: JWST’s massive galaxy problem.
In this episode, I interview Dr. Robert Sapolsky, Ph.D., Professor of Biology, Neurology & Neurosurgery at Stanford University. We discuss stress, what defines short-term versus long-term stress, and how stress can be beneficial or detrimental, depending on the context. We also discuss stress mitigation and how our sense of control over stress mitigation techniques, including exercise, determine health outcomes. Dr. Sapolsky explains some of the key effects of the hormone testosterone — how it can amplify pre-existing tendencies for aggression or sexual behavior, but that it does not produce those behaviors per se. He also explains how testosterone impacts our social hierarchies, sense of confidence, and willingness to embrace challenges of different kinds. He also explains how our behaviors and perceptions shape testosterone levels. And we discuss estrogen and the powerful role it plays in brain development, health and longevity. Finally, we discuss free will, what it means to have free will, and if we have any free will, including how knowledge alone might allow us to make better decisions for ourselves and society.
#HubermanLab #Testosterone #Stress.
Thank you to our sponsors:
ROKA — https://roka.com — use code “huberman“
InsideTracker — https://insidetracker.com/huberman.
Our Patreon page:
https://www.patreon.com/andrewhuberman.
Supplements from Thorne:
http://www.thorne.com/u/huberman.
Social:
New Patreon page! https://www.patreon.com/seanmcarroll.
Blog post: https://www.preposterousuniverse.com/podcast/2018/08/13/epis…n-nothing/
It’s fun to be in the exciting, chaotic, youthful days of the podcast, when anything goes and experimentation is the order of the day. So today’s show is something different: a solo effort, featuring just me talking without any guests to cramp my style. This won’t be the usual format, but I suspect it will happen from time to time. Feel free to chime in below on how often you think alternative formats should be part of the mix. The topic today is “Why Is There Something Rather than Nothing?”, or equivalently “Why Does the Universe Exist at All?” Heady stuff, but we’re not going to back away from the challenge.
What I have to say will roughly follow my recent paper on the subject, although in a more chatty and accessible style. It concerns ideas at the intersection of physics, philosophy, and theology, so tune in if you’re into that sort of thing.
Big news! After a number of people have asked, I have finally opened a Patreon account for people who would like to support Mindscape in some way. You can sign up to kick in a dollar or more per podcast episode, and in return you get 1) access to occasional Ask Me Anything episodes done exclusively for patrons, and 2) my undying gratitude. If the Patreon route is successful enough, I’ll forego having ads on the podcast — we’ll see how it goes.
Lecture from the 2nd mini-series (Is “God” Explanatory) from the “Philosophy of Cosmology” project. A University of Oxford and Cambridge Collaboration.
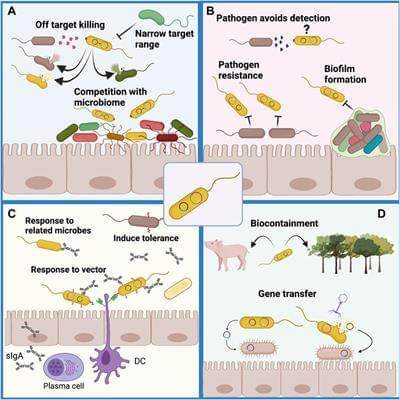
The rising prevalence of antibiotic resistant microbial pathogens presents an ominous health and economic challenge to modern society. The discovery and large-scale development of antibiotic drugs in previous decades was transformational, providing cheap, effective treatment for what would previously have been a lethal infection. As microbial strains resistant to many or even all antibiotic drug treatments have evolved, there is an urgent need for new drugs or antimicrobial treatments to control these pathogens. The ability to sequence and mine the genomes of an increasing number of microbial strains from previously unexplored environments has the potential to identify new natural product antibiotic biosynthesis pathways. This coupled with the power of synthetic biology to generate new production chassis, biosensors and “weaponized” live cell therapeutics may provide new means to combat the rapidly evolving threat of drug resistant microbial pathogens. This review focuses on the application of synthetic biology to construct probiotic strains that have been endowed with functionalities allowing them to identify, compete with and in some cases kill microbial pathogens as well as stimulate host immunity. Weaponized probiotics may have the greatest potential for use against pathogens that infect the gastrointestinal tract: Vibrio cholerae, Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium perfringens and Clostridioides difficile. The potential benefits of engineered probiotics are highlighted along with the challenges that must still be met before these intriguing and exciting new therapeutic tools can be widely deployed.
The discovery and application of antibiotic drugs is among the most significant accomplishments of medical science. Alexander Fleming’s discovery of penicillin (Fleming, 1929) and subsequent discovery and development of multiple classes of natural product antibiotics have been transformational to modern society. These compounds have yielded cheap and effective treatments for diseases caused by common bacterial infections that would previously have proven fatal. The advent of effective antibiotic drugs has made it possible to survive complex surgical procedures like open heart surgery and organ transplants and extended the average human life-span (Riley, 2005; Kaviani et al., 2020). The benefits of readily available antibiotic drugs have extended into agriculture and aquaculture, making it possible to increase productivity of farmed animals (Park et al., 1994; Patel et al., 2020).