Quantum technologies, a wide range of devices that operate by leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics, could significantly outperform classical devices on some tasks. Physicists and engineers worldwide have thus been working hard to achieve this long-sought “quantum advantage” over classical computing approaches.
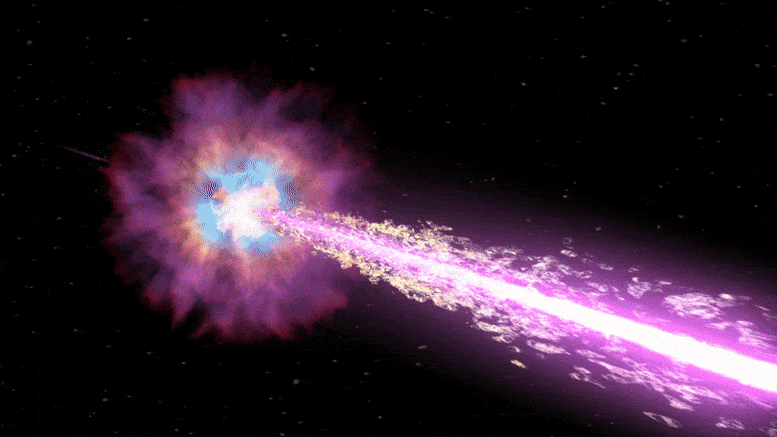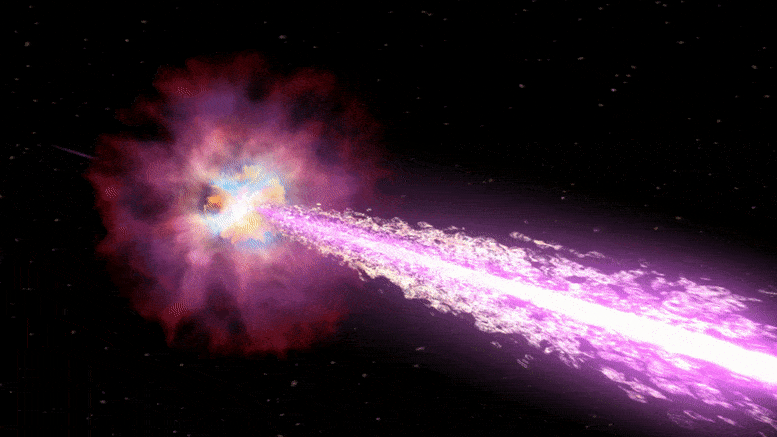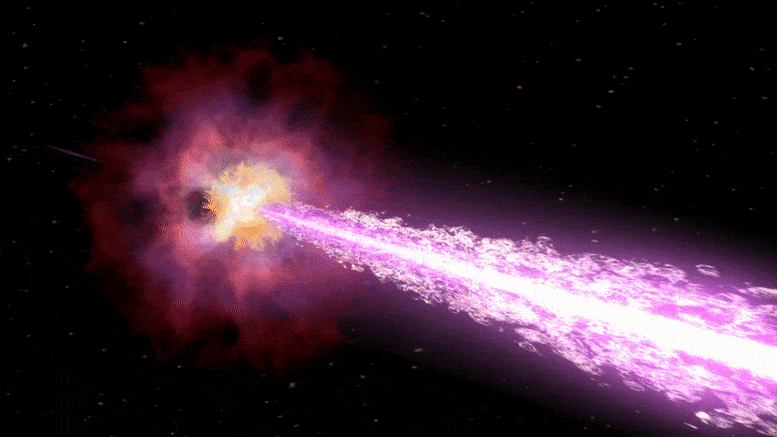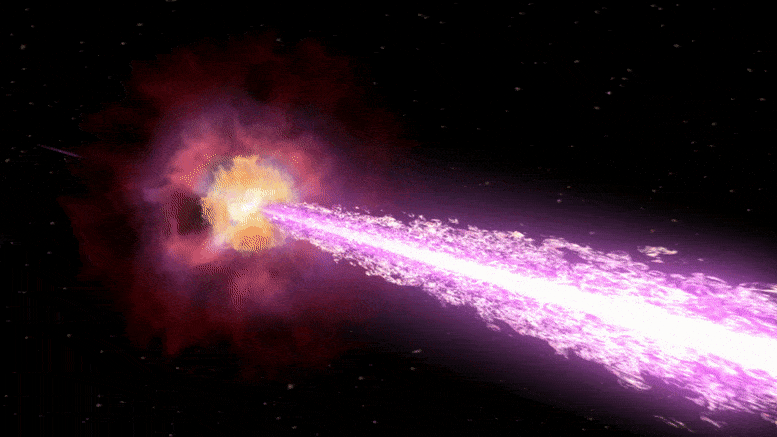
A research team at Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon, CNRS recently developed a quantum radar that could significantly outperform all existing radars based on classical approaches. This new radar, introduced in a paper published in Nature Physics, concurrently measures an entangled probe and the idler microwave photon states occurring once this probe reflects from target objects, merging with thermal noise.
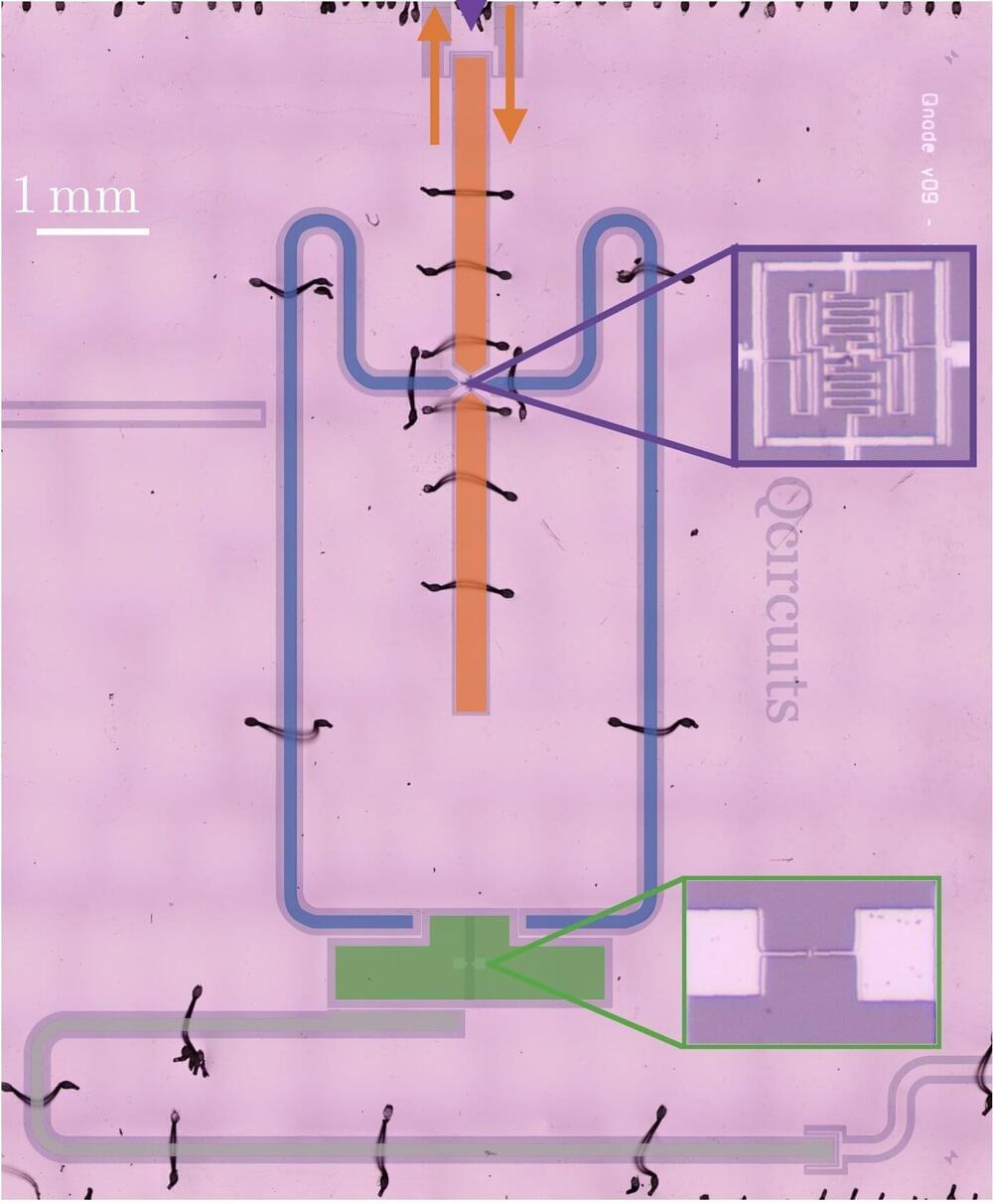
“We invented a superconducting circuit in 2020 that was able, among other things, to generate entanglement, store and manipulate microwave quantum states and count the number of photons in a microwave field,” Benjamin Huard, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “We then realized that it had all the features we needed to tackle one of the biggest challenges in microwave quantum metrology: demonstrating a quantum advantage in radar sensing.”