Super-agers have the memory and focus on people decades younger. A neurologist said he’s on track to be one with a brain-boosting daily routine.


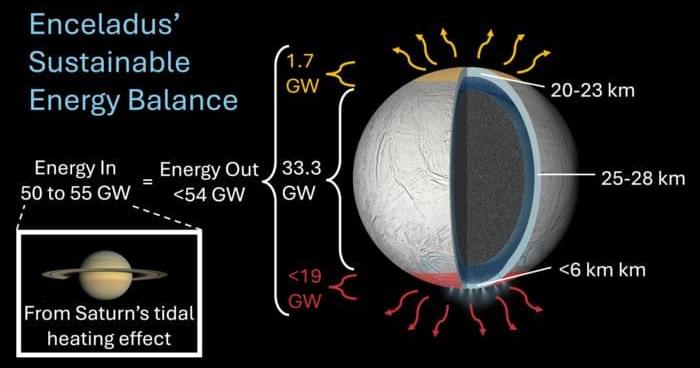
A new study led by researchers from Oxford University, Southwest Research Institute and the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona has provided the first evidence of significant heat flow at Enceladus’s north pole, overturning previous assumptions that heat loss was confined to its active south pole.
This finding confirms that the icy moon is emitting far more heat than would be expected if it were simply a passive body, strengthening the case that it could support life.
The research is published in the journal Science Advances.
Scientists may have uncovered a surprising new weapon in the fight against diabetes: the fruit of an ancient desert plant. Known as Nitraria roborowskii Kom, this resilient shrub has long been used in traditional medicine but has only recently gained scientific attention. In modern experiments, its fruit extract displayed a remarkable ability to reverse insulin resistance and restore healthy metabolism in diabetic mice.
The results went far beyond stabilizing blood sugar. Researchers found that the extract also corrected lipid imbalances and reduced oxidative stress, two major complications of diabetes. These effects were linked to the activation of a key cellular signaling pathway that helps regulate metabolism. Taken together, the findings suggest a powerful new direction for developing safer, more natural treatments for diabetes, one of the world’s most common chronic diseases.
As the number of people living with diabetes continues to climb, potentially reaching 750 million by 2045, scientists are urgently seeking better ways to manage the condition. Current medications can treat symptoms but often fail to tackle the root causes of metabolic dysfunction and may cause side effects over time. This challenge has driven researchers to reexamine traditional medicines in search of untapped therapeutic compounds.

If you read my last post, you may have had the same reaction as the legendary fintech blogger Chris Skinner. On the blog entitled “Fintechs New Power Couple: AI and Trust, he politely corrected, ” AI, trust and DLT sir” as a comment on my post.
As soon as I read his input I knew he was right. I had to write a follow up post, to correct my glaring omission. As there are three forces converging here rather than two, I will update the title to make it both more contemporary, and more accurate at the same time…
Fintech’s New Power Throuple is the convergence of AI, Trust, and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
If I drew a diagram of the relationships between the three different factors I would put it in the form of a triangle. From my viewpoint Trust would hold the uppermost position, with Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence occupying the two lower positions.
They are kind of the technology layer that makes that makes Trust possible.
As Trust isn’t a technology — or is it? 🤔
(https://fintechconfidential-newsletter.beehiiv.com/p/m2020-a…-payments)
Dr. Cody shows takes a look Graph Theory related to Brain Circuitry and Neurofeedback.
►►►Muse Headband 15% off Discount (applied at checkout): https://choosemuse.com/codyrallmd.
►►►Want to connect with a Myndlift Neurocoach? $60 off with this link: https://signup.myndlift.com/subscription. Enter CODYRALL at checkout.
►►► GET YOUR FREE MEDITATION GUIDE HERE: https://bit.ly/2XIRDNa.
►►► INSTAGRAM (Behind The Scenes with Cody Rall MD): https://www.instagram.com/codyrall_techforpsych/
Cody Rall, M.D., is a United States Navy trained Psychiatrist who specializes in neurotechnology wearables. He is a co-founder of Stanford Brainstorm, the world’s first academic laboratory dedicated to transforming brain health through entrepreneurship.
Dr. Rall also served as a board member of the psychiatry innovation lab, an annual national competition at the American Psychiatric Association that works as an incubator for groups developing technological solutions to problems in mental health care. He is the founder of Techforpsych, a media and relations company that covers advancements in technology related to neuroscience.
To apply for Dr. Cody’s Brain Circuit Training program head to this link: https://www.techforpsych.com/coaching



AI has emerged as a pivotal tool in redefining TBI rehabilitation, bridging gaps in traditional care with innovative, data-driven approaches. While its potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, outcome prediction, and individualized therapy is evident, challenges such as bias in datasets and ethical implications must be addressed. Continued research and multidisciplinary collaboration will be key to harnessing AI’s full potential, ensuring equitable access and optimizing recovery outcomes for TBI patients.
Overall, the integration of AI in TBI rehabilitation presents numerous opportunities to advance patient care and enhance the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.