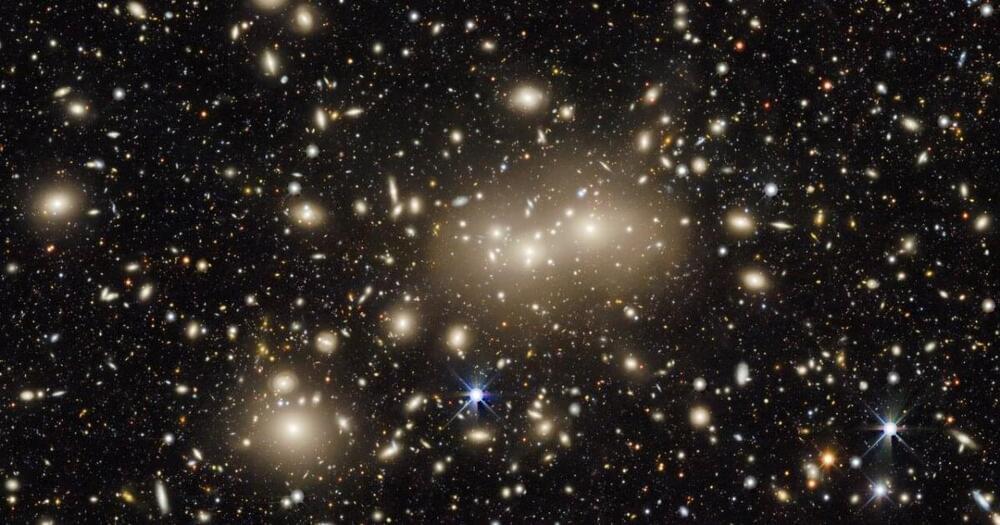
Recently an international collaboration of astronomers released the most accurate map yet of all the matter in the universe, to help to understand dark matter, and now this is being joined by the largest two-dimensional map of the entire sky, which can help in the study of dark energy. A data release from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Legacy Imaging Survey shared the results from six years of scanning almost half of the sky, totaling one petabyte of data from three different telescopes.
The reason that such large-scale data is required to study dark energy and dark matter is that these can only be detected due to their effects on ordinary matter — so researchers need to look at many galaxies to track how these otherwise unseen forces are adding mass or affecting the interaction between galaxies. This particular map was created to help scientists identify 40 million target galaxies which will be studied as part of the DESI Spectroscopic Survey.
To make the map as comprehensive as possible, the researchers included data taken in the near-infrared wavelength as well as the visible light wavelength. That is important as the light from distant galaxies appears redshifted, or shifted toward the red end of the spectrum, due to the expansion of the universe. “The addition of near-infrared wavelength data to the Legacy Survey will allow us to better calculate the redshifts of distant galaxies, or the amount of time it took light from those galaxies to reach Earth,” explained one of the researchers, Alfredo Zenteno of NSF’s NOIRLab, in a statement.