From wearable electronics to microscopic sensors to telemedicine, new advances like graphene and supercapacitors are already here.
Americans endlessly chatter about what to eat. Low fat, high protein, vegan, ketogenic — but what about electronic? Since the turn of the 21st century, a dedicated group of scientists, engineers, and technologists has been trying to create edible electronics, not necessarily for human nutrition, but rather for medical purposes.
Electronic devices composed of digestible materials that gradually break down in the body over a matter of days could precisely deliver medication inside the body and measure drug uptake. They could monitor symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders and the gut microbiome. They could allow doctors to remotely observe patients’ internal health without a visit to the hospital, further enhancing the telehealth revolution and allowing more people access to healthcare.
As in physics, paradoxes in biology really are just unsolved puzzles. Enter Peto’s paradox. Biologist Richard Peto noticed in the 1970s that mice had a much higher rate of cancer than humans do, which doesn’t make any sense. Humans have over 1,000 times as many cells as mice, and cancer is simply a rogue cell that goes on multiplying out of control. One would expect humans to be more likely to get cancer than smaller creatures such as mice. This paradox occurs across all species, too: blue whales are much less likely to get cancer than humans, even though they have many more cells in their bodies.
Fermi paradox
Named after physicist superstar Enrico Fermi, the Fermi paradox is the contradiction between how likely alien life is in the universe and its apparent absence. Considering the billions of stars in the galaxy like the sun, the many Earth-like planets that must be orbiting some of those stars, the likelihood that some of those planets developed life, the likelihood that some of that life is as intelligent or more intelligent than humanity, the galaxy should be teeming with alien civilizations. This absence led Fermi to pose the question, “Where is everybody?” Some answers to that question are unfortunately a little disturbing.
Erik Verlinde has been compared to Einstein for completely rethinking the nature of gravity.
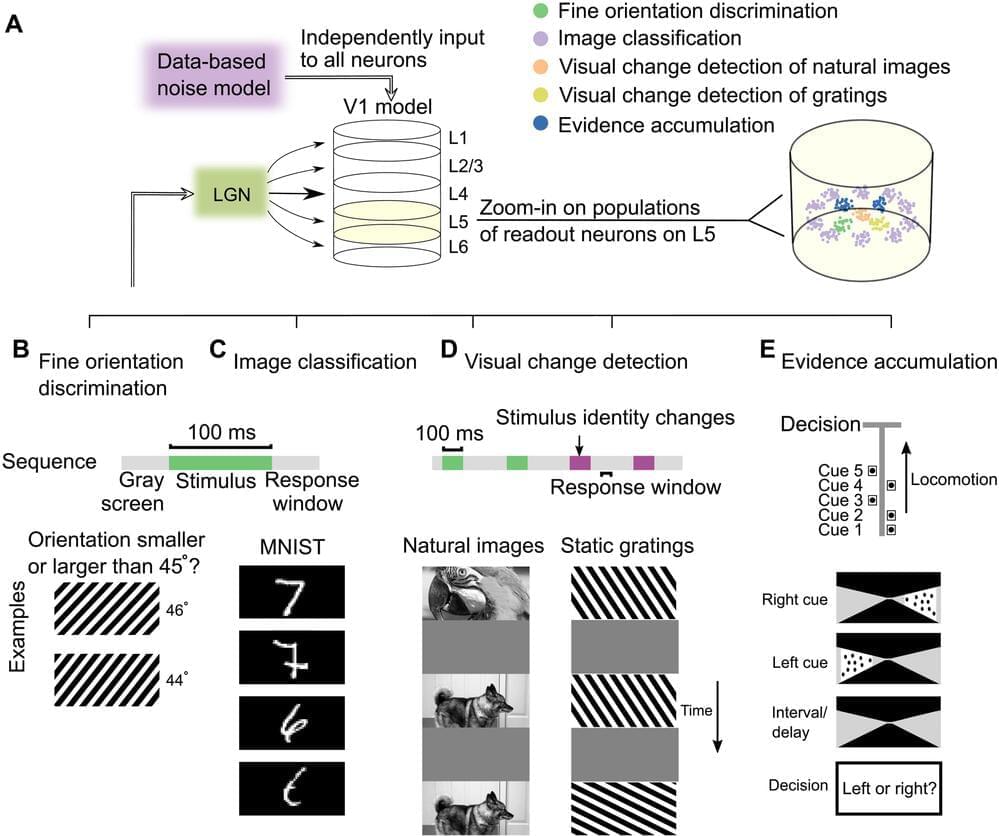
Human Brain Project researchers have trained a large-scale model of the primary visual cortex of the mouse to solve visual tasks in a highly robust way. The model provides the basis for a new generation of neural network models. Due to their versatility and energy-efficient processing, these models can contribute to advances in neuromorphic computing.
Modeling the brain can have a massive impact on artificial intelligence (AI): Since the brain processes images in a much more energy-efficient way than artificial networks, scientists take inspiration from neuroscience to create neural networks that function similarly to the biological ones to significantly save energy.
In that sense, brain-inspired neural networks are likely to have an impact on future technology, by serving as blueprints for visual processing in more energy-efficient neuromorphic hardware. Now, a study by Human Brain Project (HBP) researchers from the Graz University of Technology (Austria) showed how a large data-based model can reproduce a number of the brain’s visual processing capabilities in a versatile and accurate way. The results were published in the journal Science Advances.
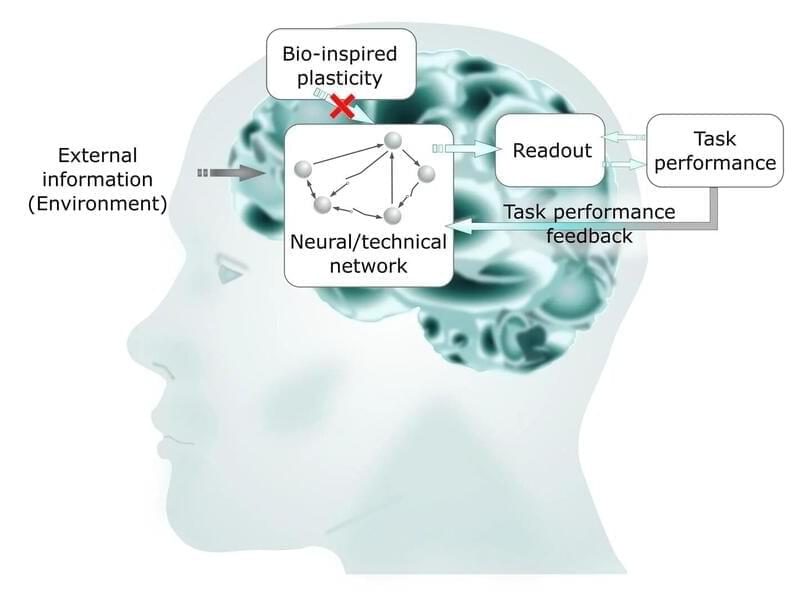
With mathematical modeling, a research team has now succeeded in better understanding how the optimal working state of the human brain, called criticality, is achieved. Their results mean an important step toward biologically-inspired information processing and new, highly efficient computer technologies and have been published in Scientific Reports.
“In particular tasks, supercomputers are better than humans, for example in the field of artificial intelligence. But they can’t manage the variety of tasks in everyday life —driving a car first, then making music and telling a story at a get-together in the evening,” explains Hermann Kohlstedt, professor of nanoelectronics. Moreover, today’s computers and smartphones still consume an enormous amount of energy.
“These are no sustainable technologies—while our brain consumes just 25 watts in everyday life,” Kohlstedt continues. The aim of their interdisciplinary research network, “Neurotronics: Bio-inspired Information Pathways,” is therefore to develop new electronic components for more energy-efficient computer architectures. For this purpose, the alliance of engineering, life and natural sciences investigates how the human brain is working and how that has developed.
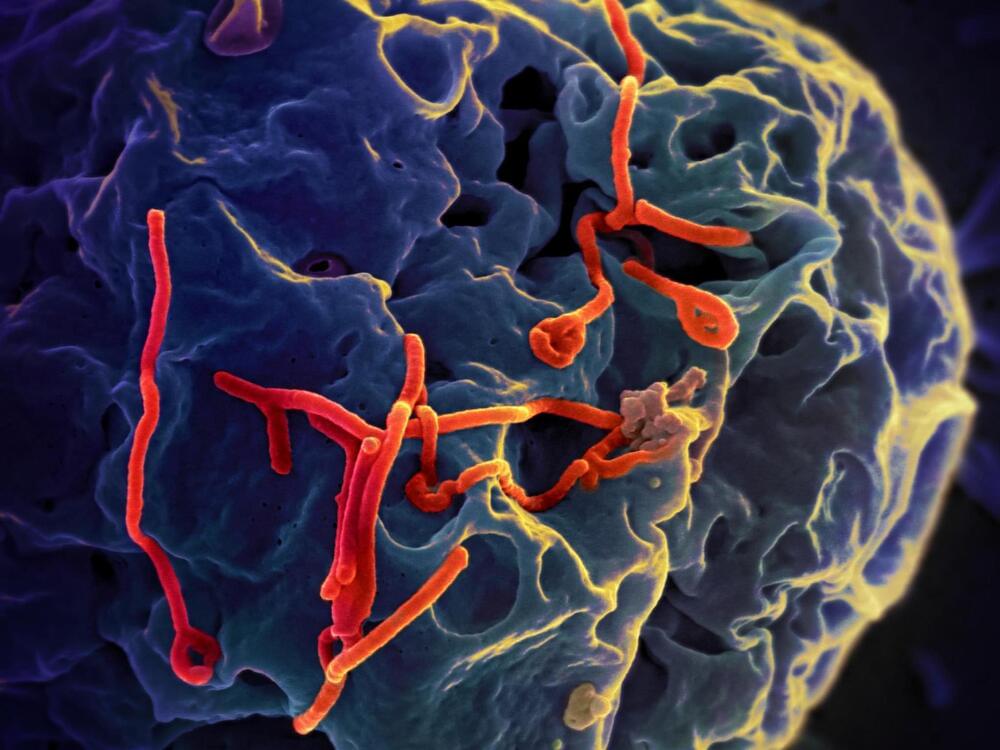
Several proteins have been identified in hosts that interact with Ebola virus and primarily function to inhibit the production of viral genetic material in cells and prevent Ebola virus infection, according to a study led by the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University.
Zaire ebolavirus or Ebola virus, an RNA virus pathogen that belongs to the filovirus family, causes outbreaks of severe disease in humans. This public health threat has produced outbreaks where reported case fatality rates ranged up to 90 percent.
The West Africa Ebola virus epidemic from 2013–2016 resulted in more than 28,000 infections and more than 11,000 deaths. Four outbreaks occurred in the Democratic Republic of Congo from 2017–2021 and Ebola virus reemerged in Guinea in 2021.
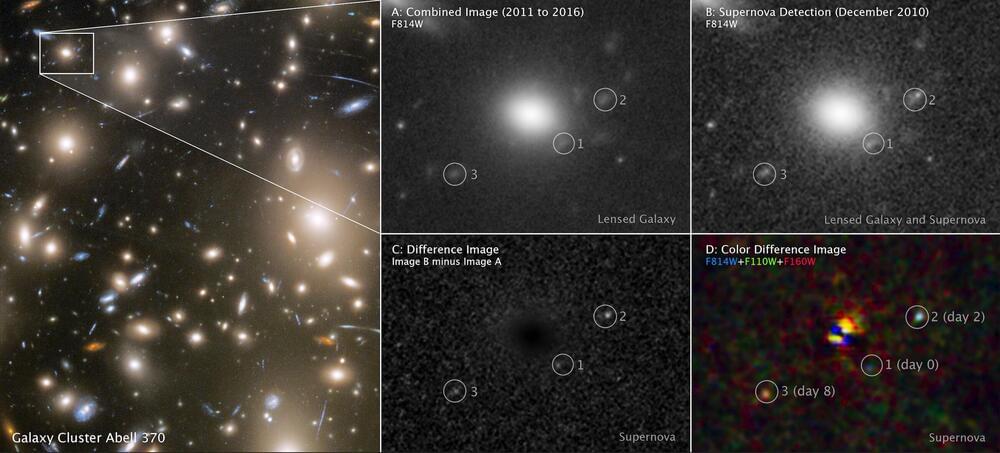
An international research team led by the University of Minnesota Twin Cities has measured the size of a star dating back 2 billion years after the Big Bang, or more than 11 billion years ago. Detailed images show the exploding star cooling and could help scientists learn more about the stars and galaxies present in the early universe. The paper is published in Nature.
“This is the first detailed look at a supernova at a much earlier epoch of the universe’s evolution,” said Patrick Kelly, a lead author of the paper and an associate professor in the University of Minnesota School of Physics and Astronomy. “It’s very exciting because we can learn in detail about an individual star when the universe was less than a fifth of its current age, and begin to understand if the stars that existed many billions of years ago are different from the ones nearby.”
The red supergiant in question was about 500 times larger than the sun, and it’s located at redshift three, which is about 60 times farther away than any other supernova observed in this detail.
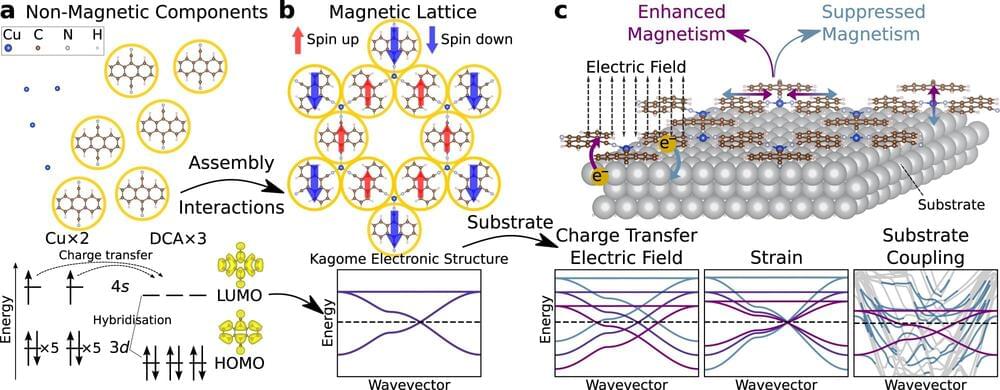
A new study at Monash University illustrates how substrates affect strong electronic interactions in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks.
Materials with strong electronic interactions can have applications in energy-efficient electronics. When these materials are placed on a substrate, their electronic properties are changed by charge transfer, strain, and hybridization.
The study also shows that electric fields and applied strain could be used to “switch” interacting phases such as magnetism on and off, allowing potential applications in future energy-efficient electronics.
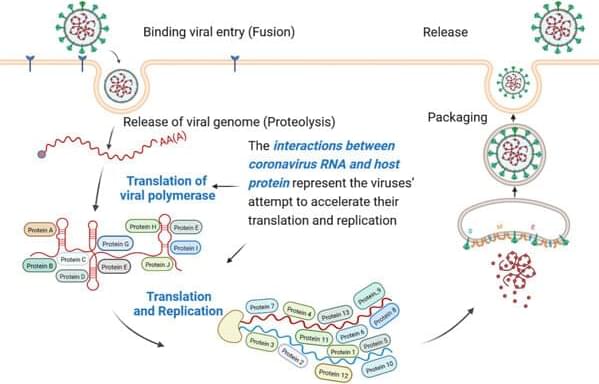
Coronaviruses have brought about three massive outbreaks in the past two decades. Each step of its life cycle invariably depends on the interactions among virus and host molecules. The interaction between virus RNA and host protein (IVRHP) is unique compared to other virus-host molecular interactions, and has emerged to be a very hot topic in recent studies.
These studies provide essential information for a deeper understanding of IVRHP, which represents not only an attempt by viruses to promote their translation/replication, but also the host’s endeavor to combat viral pathogenicity. In other words, there is an urgent need to have a panorama of coronavirus RNA-Host protein interactions, which will then aid in the discovery of new antiviral therapies.
On October 6, 2022, Prof. Zhu Feng from College of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Zhejiang University, Prof. Han Lianyi from College of Life Sciences in Fudan University and Prof. Lin Tao from College of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Hangzhou Normal University published an article titled “CovInter: Interaction Data between Coronavirus RNAs and Host Proteins” in Nucleic Acids Research.