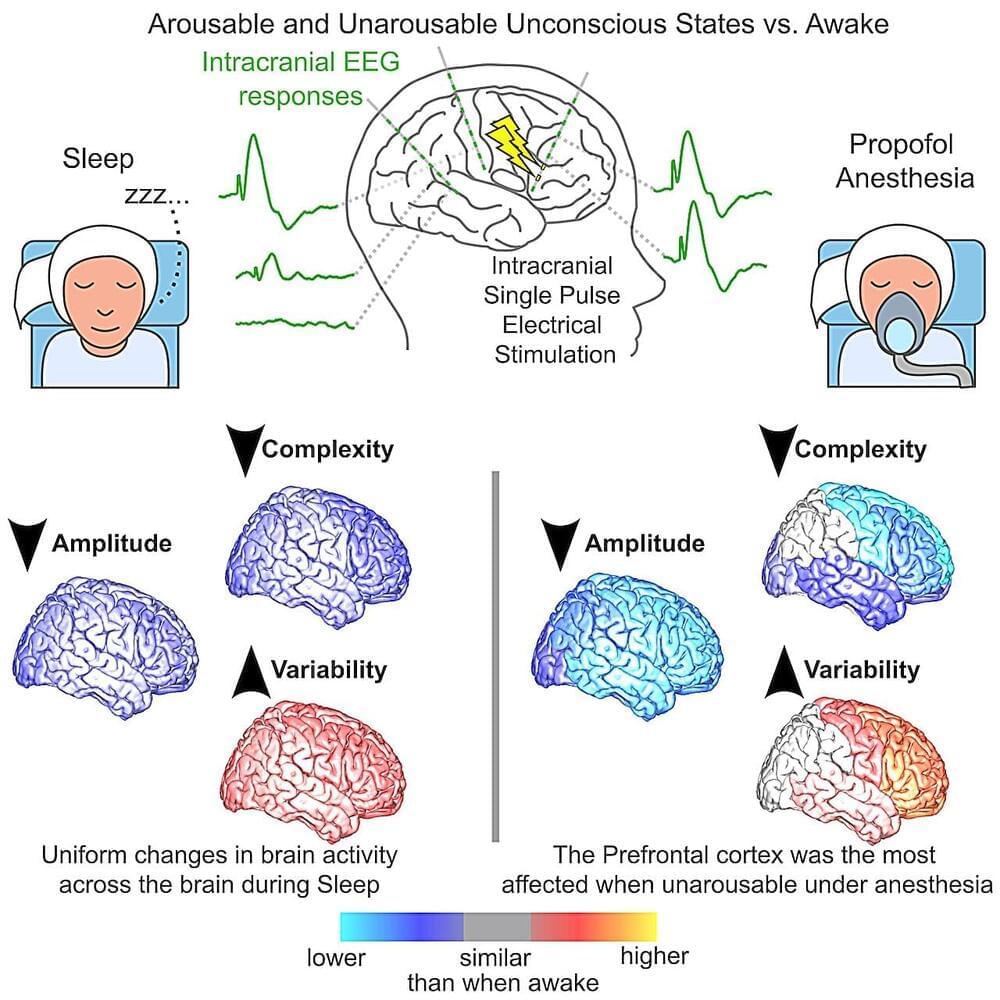
Despite substantial work, we are still unsure which brain regions are involved and how they are impacted when consciousness is disrupted.
States of unconsciousness, such as those that occur during sleep or while under the effect of anesthesia, have been the focus of countless past neuroscience studies. While these works have identified some brain regions that are active and inactive when humans are unconscious, the precise contribution of each of these regions to consciousness remains largely unclear.
Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding the activity of different regions of the cortex, the outer layer of the mammalian brain, during different states of unconsciousness, namely sleep and general anesthesia. Their paper, published in Neuron, identifies distinct cortical networks that are engaged during different states of unconsciousness.
“We have always been interested in trying to understand better how neuronal activity in the brain gives rise to consciousness,” Dr. Rina Zelmann, the lead researcher for the study, told Medical Xpress. “This is a huge and difficult question to answer. In this project, we started with seemingly simple questions, such as: What happens in the human brain when we are unconscious? And, what happens when we cannot be awakened?”