Researchers are working to unlock the immense potential of terahertz waves for applications ranging from medical imaging to wireless communications. However, efficiently controlling the polarization state of these high-frequency electromagnetic waves has remained an enduring challenge.
Conventional approaches relying on natural birefringent crystals or dielectric waveplates are hampered by narrow operational bandwidths, bulky hardware, and susceptibility to damage. These limitations have throttled progress towards commercially viable terahertz systems that fully exploit the information encoded in electromagnetic wave polarization.
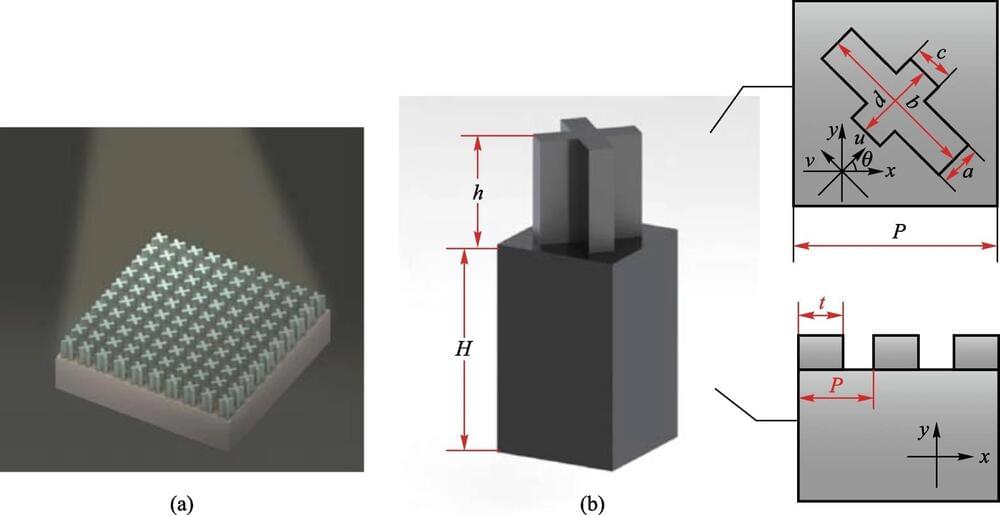
Recent advances in metamaterials – artificial structures engineered with properties unattainable in nature – have brought fresh hope. Carefully designed metamaterial arrays allow researchers to overcome the constraints of natural materials and exercise unprecedented control over terahertz wave propagation.