Little is as important for the future of the world, and our own lives, as how this history continues.


If you wanted to, you could access an “evil” version of OpenAI’s ChatGPT today—though it’s going to cost you. It also might not necessarily be legal depending on where you live.
However, getting access is a bit tricky. You’ll have to find the right web forums with the right users. One of those users might have a post marketing a private and powerful large language model (LLM). You’ll connect with them on an encrypted messaging service like Telegram where they’ll ask you for a few hundred dollars in cryptocurrency in exchange for the LLM.
Once you have access to it, though, you’ll be able to use it for all the things that ChatGPT or Google’s Bard prohibits you from doing: have conversations about any illicit or ethically dubious topic under the sun, learn how to cook meth or create pipe bombs, or even use it to fuel a cybercriminal enterprise by way of phishing schemes.

Geoscientists discovered a continent that had been hiding in plain sight for almost 375 years.
Historically, there’s been speculation about whether a continent known as Zealandia or Te Riu-a-Māui in the Māori language exists.
According to TN News, Zealandiais 1.89 million square miles in size. It was part of a supercontinent called Gondwana, which included most of Western Antarctica and Eastern Australia, over 500 million years ago.
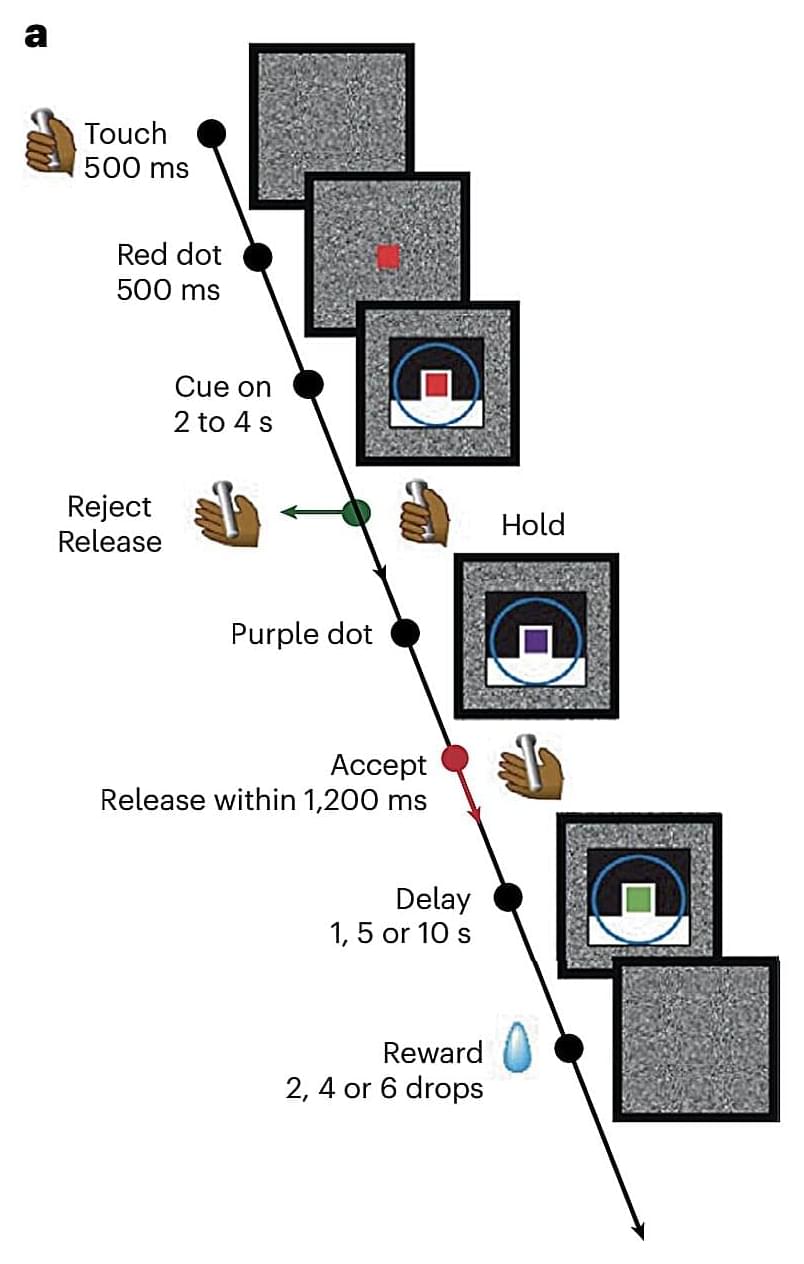
When humans make decisions, such as picking what to eat from a menu, what jumper to buy at a store, what political candidate to vote for, and so on, they might be more or less confident with their choice. If we are less confident and thus experience greater uncertainty in relation to their choice, our choices also tend to be less consistent, meaning that we will be more likely to change our mind before reaching a final decision.
While neuroscientists have been exploring the neural underpinnings decision-making for decades, many questions are still unanswered. For instance, how neural network computations support decision-making under varying levels of certainty remain poorly understood.
Researchers at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Maryland recently carried out a study on rhesus monkeys aimed at better understanding the neural network dynamics associated with decision confidence. Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, offers evidence that energy landscapes in the prefrontal cortex can predict the consistency of choices made by monkeys, which is in turn a sign of the animals’ confidence in their decisions.
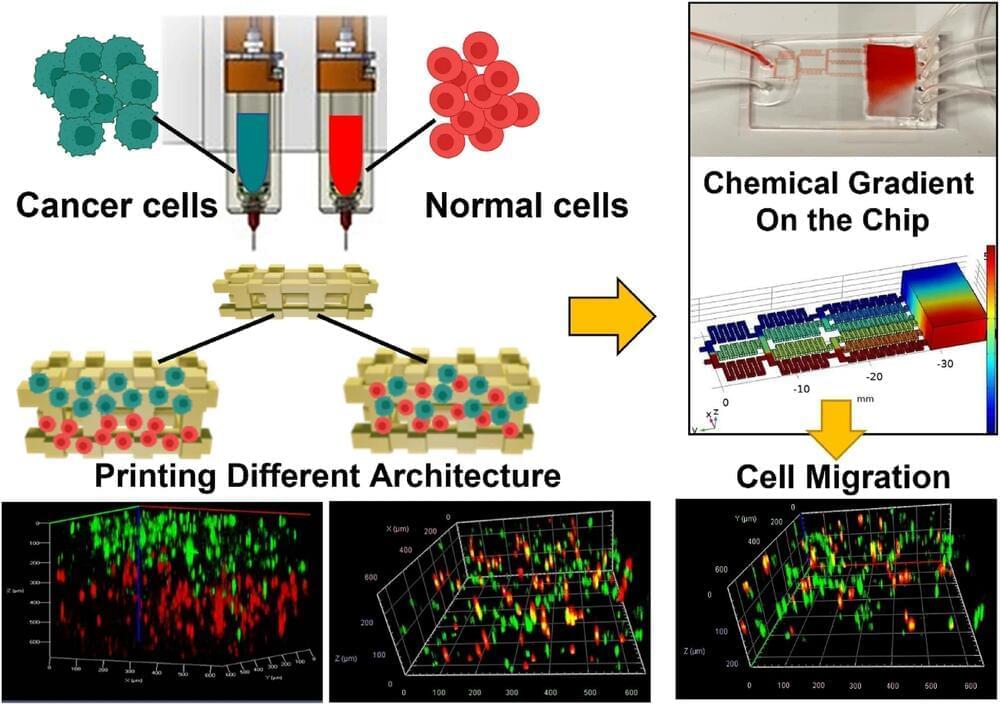
An international team of interdisciplinary researchers has successfully created a method for better 3D modeling of complex cancers. The University of Waterloo-based team combined cutting-edge bioprinting techniques with synthetic structures or microfluidic chips. The method will help lab researchers more accurately understand heterogeneous tumors: tumors with more than one kind of cancer cell, often dispersed in unpredictable patterns.
The research, “Controlled tumor heterogeneity in a co-culture system by 3D bio-printed tumor-on-chip model,” appears in Scientific Reports.
Traditionally, medical practitioners would biopsy a patient’s tumor, extract cells, and then grow them in flat petri dishes in a lab. “For 50 years, this was how biologists understood tumors,” said Nafiseh Moghimi, an applied mathematics post-doctoral researcher and the lead author of the study. “But a decade ago, repeated treatment failures in human trials made scientists realize that a 2D model does not capture the real tumor structure inside the body.”

The simulated universe theory implies that our universe, with all its galaxies, planets and life forms, is a meticulously programmed computer simulation. In this scenario, the physical laws governing our reality are simply algorithms. The experiences we have are generated by the computational processes of an immensely advanced system.
While inherently speculative, the simulated universe theory has gained attention from scientists and philosophers due to its intriguing implications. The idea has made its mark in popular culture, across movies, TV shows and books—including the 1999 film “The Matrix.”
The earliest records of the concept that reality is an illusion are from ancient Greece. There, the question “What is the nature of our reality?” posed by Plato (427 BC) and others, gave birth to idealism. Idealist ancient thinkers such as Plato considered mind and spirit as the abiding reality. Matter, they argued, was just a manifestation or illusion.
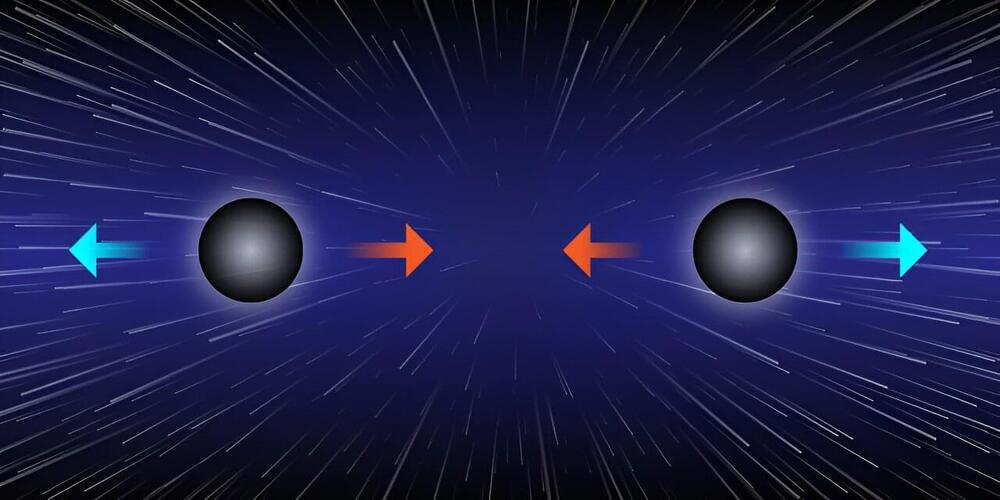
Researchers from the University of Southampton, together with colleagues from the universities of Cambridge and Barcelona, have shown it’s theoretically possible for black holes to exist in perfectly balanced pairs—held in equilibrium by a cosmological force—mimicking a single black hole.
Black holes are massive astronomical objects that have such a strong gravitational pull that nothing, not even light, can escape. They are incredibly dense. A black hole could pack the mass of the Earth into a space the size of a pea.
Conventional theories about black holes, based on Einstein’s theory of General Relativity, typically explain how static or spinning black holes can exist on their own, isolated in space. Black holes in pairs would eventually be thwarted by gravity attracting and colliding them together.

As it lay buried for two millennia, a fragment of glass gradually acquired a nanostructured surface that reflects light like a butterfly’s wings.
The ancient Roman city of Aquileia was situated close to Italy’s modern border with Slovenia. Over the centuries since its founding in 181 BCE, Aquileia suffered floods, earthquakes, sieges, and sackings. Little remains of this ancient city of 100,000 inhabitants, but archaeologists have uncovered relics from that early period. One such specimen is a glass shard discovered in 2012 on farmland in the outskirts of the modern city of Aquileia. The shard is striking in its coloration: an iridescent surface of deep blue and shiny gold atop a substrate of dark green. Now, after subjecting the shard to a string of chemical and physical tests, Giulia Guidetti of Tufts University, Massachusetts, and her collaborators have identified the origin of the shard’s appearance: a chemical transformation of the amorphous glass into a nanolayered material, a photonic crystal [1].
Glassmaking was invented independently by several Bronze Age civilizations (3300 BCE to 1,200 BCE), including those of ancient Egypt and the Indus Valley. Glass beads, vessels, and figurines remained luxury items until the Romans invented the technique of glassblowing in the first century CE. As blowing technology spread, glassware became cheaper and faster to produce in a greater variety of shapes. Items manufactured in the Roman Empire included jars for cosmetics, jugs for condiments, and cups for wine.