The discovery made using NASA’s powerful space telescope brings scientists a step closer to determining if the salty water oceans of Europa could support life.



An international research team led by scientists in the Center for Genetic Epidemiology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center has singled out mutations in 11 genes that are associated with aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
These findings come from the largest-scale prostate cancer study ever exploring the exome—that is, the key sections of the genetic code that contain the instructions to make proteins. The scientists analyzed samples from about 17,500 prostate cancer patients.
Today, oncologists customize care for certain individuals with aggressive prostate cancer with help from genetic tests. The results can inform treatment, as one class of targeted therapies has proved effective against some inherited prostate cancers. Test findings also can lead to genetic screening among patients’ family members, so they have the chance to take measures that reduce risk and to work with their doctors to be more vigilant in early detection.
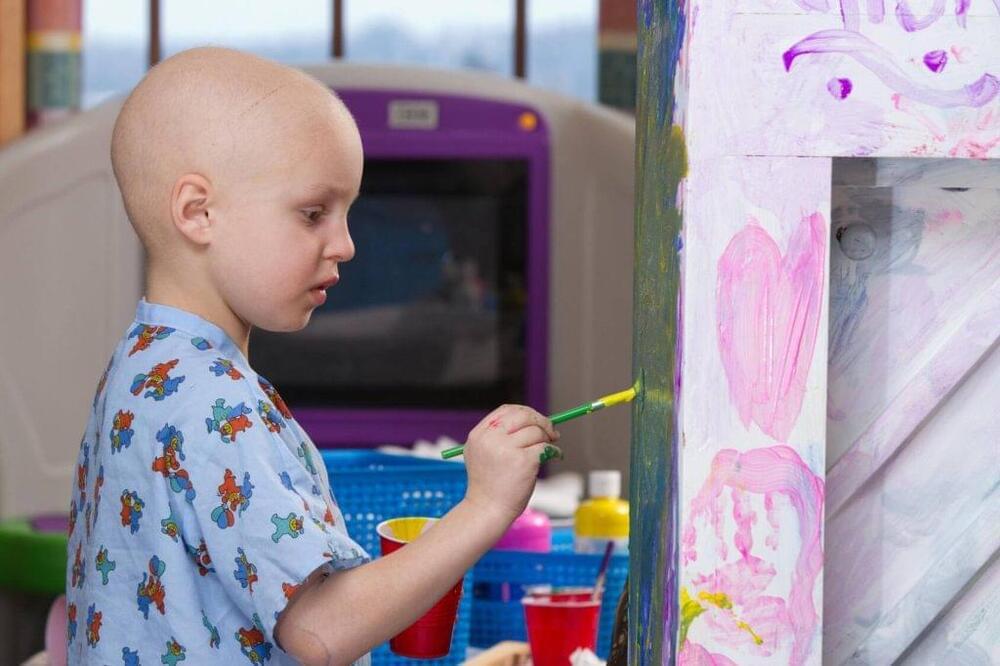

The types of cancer that occur in children often are different from those in adults. Childhood cancers usually are not linked to lifestyle or environmental risk factors, as is often the case in adults. Nonetheless, cancer is the second-leading cause of death in children 1 to 14 years old, according to the American Cancer Society. Nearly 10,000 children in the U.S. under the age of 15 will be diagnosed with cancer in 2023, and about 1,000 children are expected to die of the disease.
September is Childhood Cancer Awareness Month, which makes this a good time to learn about three of the most common types of cancer in children: acute lymphocytic leukemia, neuroblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It’s the most common type of cancer in children, and treatments result in a good chance for a cure. Acute lymphocytic leukemia also can occur in adults, though the chance of a cure is greatly reduced.

‘They’re not announcing like, ‘We have created a model that does a particular thing.’ Instead, they’re saying ‘We are planning to create a resource that is going to be available for biologists to create new models,’ Carpenter said.
The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, the couple’s LLC, told The Register that they plan to have their product running by 2024. The company also declined to tell the Register how much it’ll have to spend to make its product.
It could be a hefty bill, considering that the computer parts it wants to use are in high demand and low supply, The Register reported.
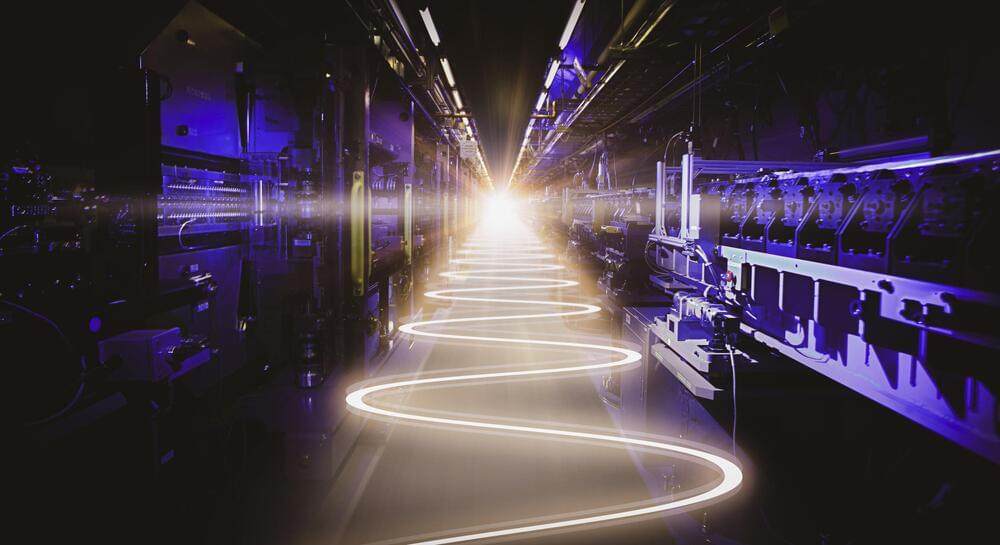

The newly upgraded Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory successfully produced its first X-rays, and researchers around the world are already lined up to kick off an ambitious science program.
The upgrade, called LCLS-II, creates unparalleled capabilities that will usher in a new era in research with X-rays.
Scientists will be able to examine the details of quantum materials with unprecedented resolution to drive new forms of computing and communications; reveal unpredictable and fleeting chemical events to teach us how to create more sustainable industries and clean energy technologies; study how biological molecules carry out life’s functions to develop new types of pharmaceuticals; and study the world on the fastest timescales to open up entirely new fields of scientific investigation.
Year 2022 😗😁
During the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (or IEDM), Intel claimed that by 2030, there would be circuits with transistor counts of a trillion, roughly ten times the number of transistors currently available on modern CPUs.
At the meeting, Intel’s Components Research Group laid down its prediction for the future of circuits manufacturing (via sweclockers) and how new packaging technologies and materials will allow chipmakers to build chips with 10x the transistor density, keeping in Moore’s Law.
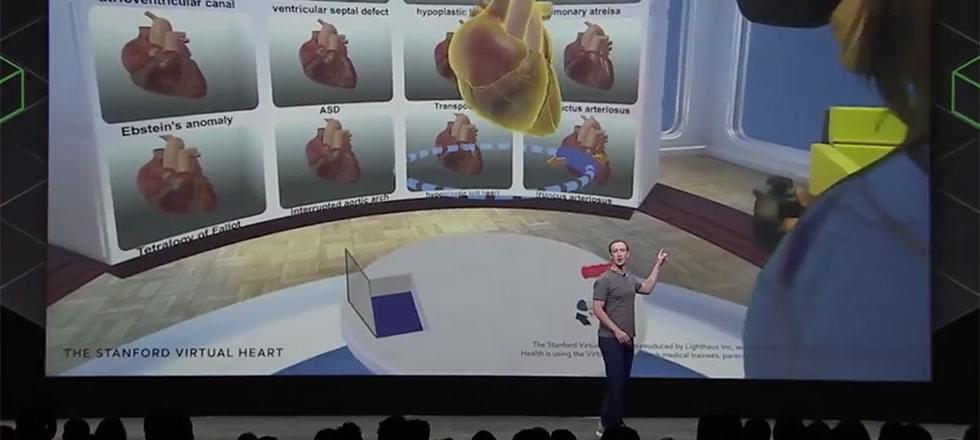
Pediatric specialists at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital Stanford are implementing innovative uses for immersive virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies to advance patient care and improve the patient experience.
Through the hospital’s CHARIOT program, Packard Children’s is one of the only hospitals in the world to have VR available on every unit to help engage and distract patients undergoing a range of hospital procedures. Within the Betty Irene Moore Children’s Heart Center, three unique VR projects are influencing medical education for congenital heart defects, preparing patients for procedures and aiding surgeons in the operating room. And for patients and providers looking to learn more about some of the therapies offered within our Fetal and Pregnancy Health Program, a new VR simulation helps them understand the treatments at a much closer level.
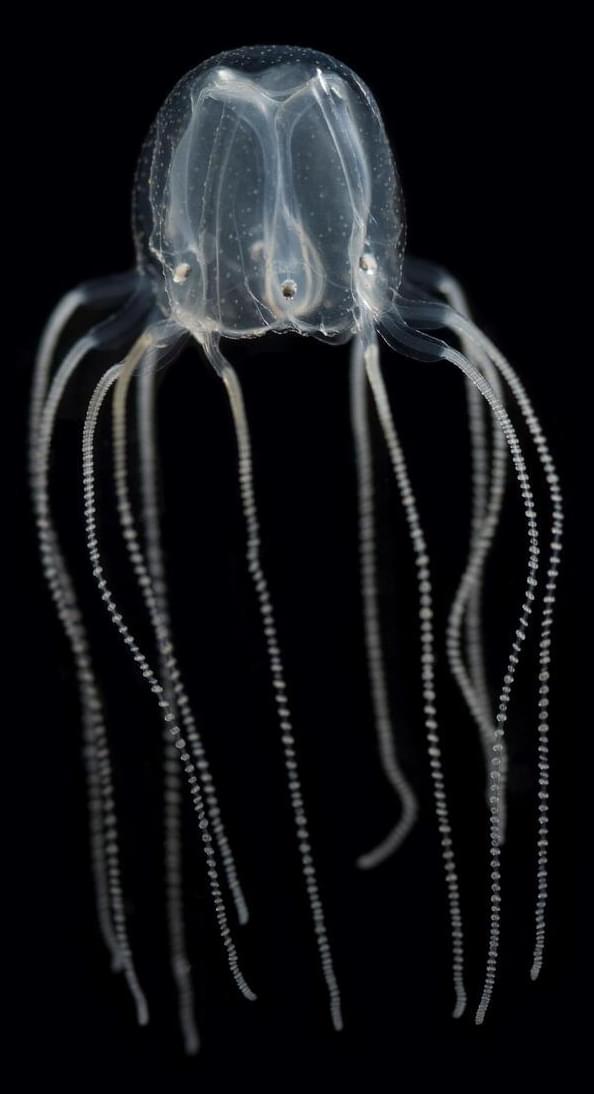


Jellyfish are more advanced than once thought. A new study from the University of Copenhagen has demonstrated that Caribbean box jellyfish can learn at a much more complex level than ever imagined—despite only having one thousand nerve cells and no centralized brain. The finding changes our fundamental understanding of the brain and could enlighten us about our own mysterious brains.
After more than 500 million years on Earth, the immense evolutionary success of jellyfish is undeniable. Still, we’ve always thought of them as simple creatures with very limited learning abilities.
The prevailing opinion is that more advanced nervous systems equate with more advanced learning potential in animals. Jellyfish and their relatives, collectively known as cnidarians, are considered to be the earliest living animals to develop nervous systems and to have fairly simple nervous systems and no centralized brain.
Discovering And Developing Medicines To Keep You Biologically Young — Dr. Marco Quarta, Ph.D. — Co-Founder and CEO, Rubedo Life Sciences; CEO, Phaedon Institute.
Dr. Marco Quarta, Ph.D. is Co-Founder and CEO of Rubedo Life Sciences (https://www.rubedolife.com/), a biopharmaceutical company developing a broad portfolio of innovative therapies engineered to target cells which drive chronic age-related diseases. The company’s proprietary ALEMBIC™ drug discovery platform has engineered novel first-in-class small molecules designed to selectively target senescent cells, which play a key role in the progression of pulmonary, dermatological, oncological, neurodegenerative, fibrotic and other chronic disorders.
Dr. Quarta received his doctorate degree in Biotechnology from the University of Bologna and a Ph.D. in Neuroscience from the University of Padua. He completed a post-doc in Aging and Stem cell Biology in the lab of Prof. Thomas Rando at Stanford University and continued his work at Stanford directing a research team at the Center for Tissue Regeneration, Repair, and Restoration at the VA Hospital in Palo Alto, CA. While there, he established a translational program in regenerative medicine. He has over 35 publications and patents in the field of aging, stem cells, regenerative medicine, and rejuvenation.
Dr. Quarta also co-founded Wetware Concepts, Young European Biotech Network (YEBN), and Turn Biotechnology, and served as an executive board member of the European Federation of Biotechnologies. He currently sits on the advisory board of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) Calpoly Bridge program, and the advisory board at the Center for Healthcare Innovation. He is a member of the Paul F Glenn Center for the Biology of Aging Studies at Stanford University, one of the most prestigious institutions supporting the science of aging.
Dr. Quarta also serves as CEO and President for the Board of Directors of The Phaedon Institute (https://www.phaedon.institute/), a think-tank organization that operates with the mission of supporting and enabling effective and sustainable growth in the field of aging and longevity sciences.