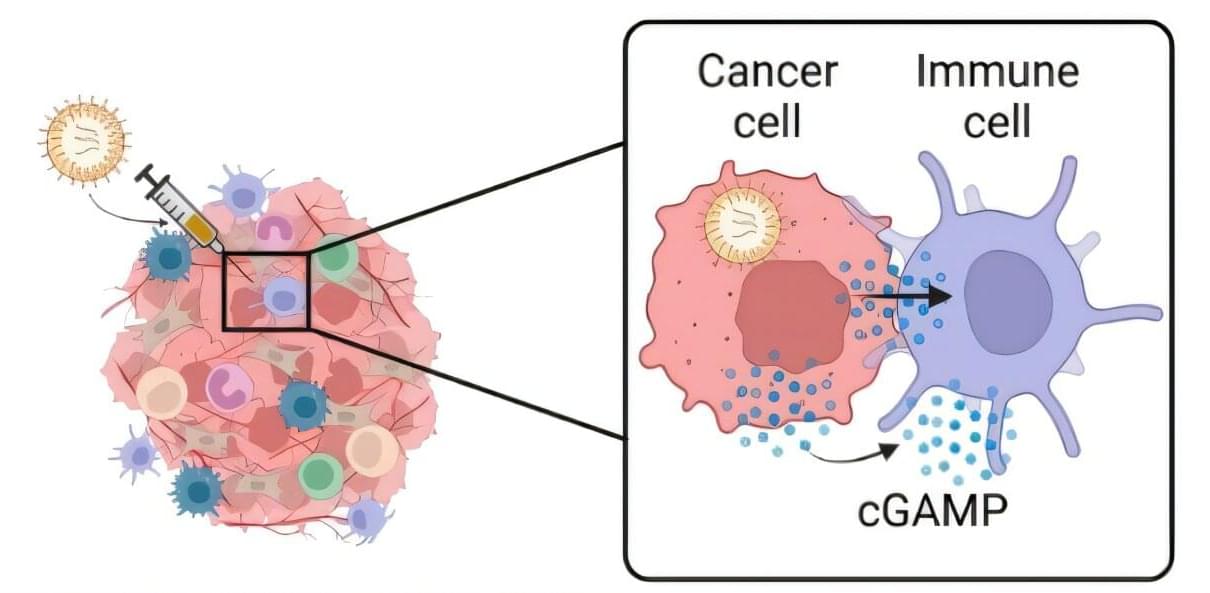
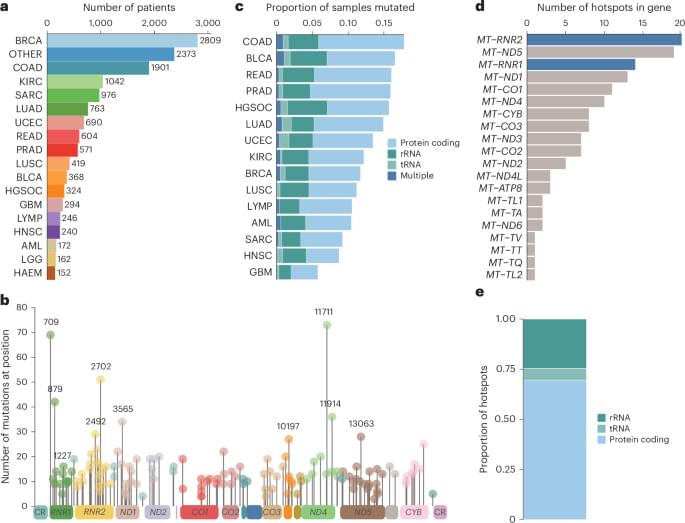
To study selection for somatic single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in tumor mtDNA, we identified somatic mtDNA variants across primary tumors from the GEL cohort (n = 14,106). The sheer magnitude of the sample size in this dataset, in conjunction with the high coverage depth of mtDNA reads (mean = 15,919×), enabled high-confidence identification of mtDNA variants to tumor heteroplasmies of 5%. In total, we identified 18,104 SNVs and 2,222 indels (Supplementary Table 1), consistent with previously reported estimates of approximately one somatic mutation in every two tumors1,2,3. The identified mutations exhibited a strand-specific mutation signature, with a predominant occurrence of CT mutations on the heavy strand and TC on the light strand in the non-control region that was reversed in the control region2 (Extended Data Fig. 1a, b). These mutations occur largely independently of known nuclear driver mutations, with the exception of a co-occurrence of TP53 mutation and mtDNA mutations in breast cancer (Q = 0.031, odds ratio (OR) = 1.43, chi-squared test) (Extended Data Fig. 2a and Supplementary Table 4).
Although the landscape of hotspot mutations in nuclear-DNA-encoded genes is relatively well described, a lack of statistical power has impeded an analogous, comprehensive analysis in mtDNA16,17. To do so, we applied a hotspot detection algorithm that identified mtDNA loci demonstrating a mutation burden in excess of the expected background mutational processes in mtDNA (Methods). In total, we recovered 138 unique statistically significant SNV hotspots (Q 0.05) across 21 tumor lineages (Fig. 1a, b and Supplementary Table 2) and seven indel hotspots occurring at homopolymeric sites in complex I genes, as previously described by our group (Extended Data Fig. 2b and Supplementary Table 3). SNV hotspots affected diverse genetic elements, including protein-coding genes (n = 96 hotspots, 12 of 13 distinct genes), tRNA genes (n = 8 hotspots, 6 of 22 distinct genes) and rRNA genes (n = 34 hotspots, 2 of 2 genes) (Fig. 1b, c, e).