Join the discussion on this paper page.



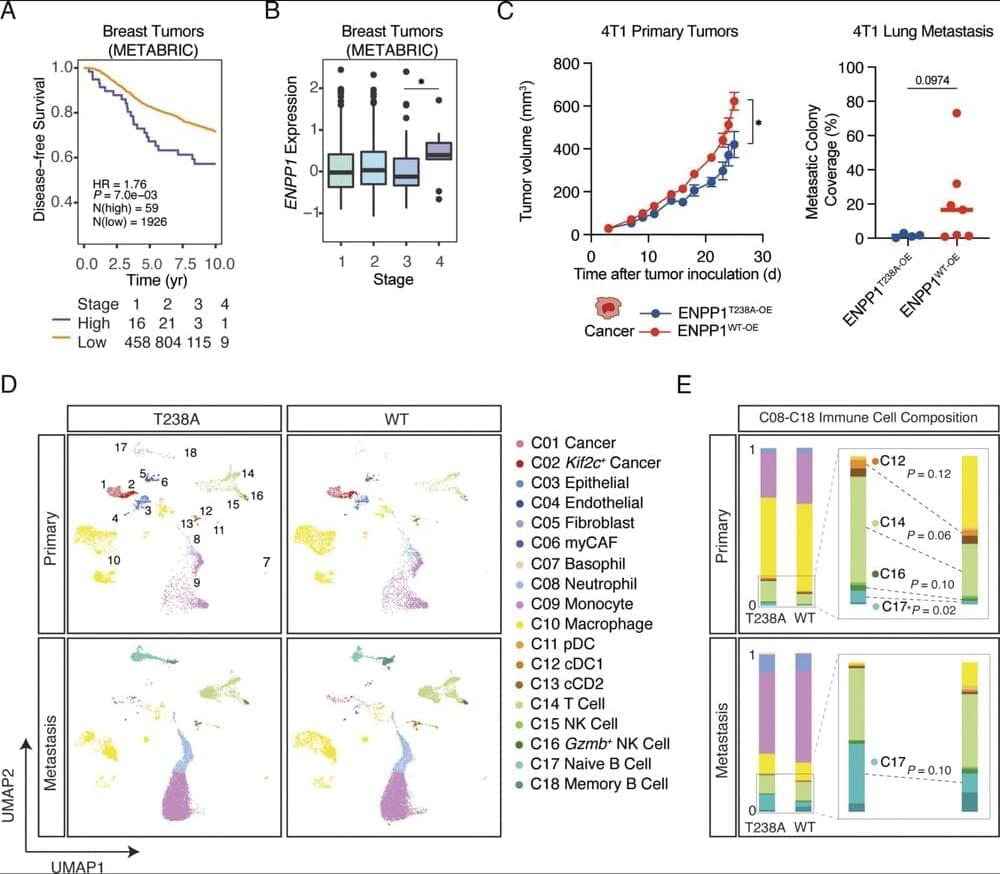

What changes in cells lead to breast cancer? Scientists now have access to the world’s most comprehensive atlas of healthy breast tissue to help answer this question. 7 years in the making, the Human Breast Cell Atlas is helping scientists better understand breast cancer and other diseases to find new treatments.
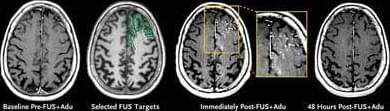
In three patients with Alzheimer’s disease, focused ultrasound was applied with aducanumab therapy. Reduction in amyloid was greater in treated regions than in matched contralateral regions over 6 months. Read the full report:
Original Article from The New England Journal of Medicine — Ultrasound Blood–Brain Barrier Opening and Aducanumab in Alzheimer’s Disease.
This morning in breaking news, Brett Adcock CEO of Figure Robotics, dropped a mind-blowing demo showing that their Figure 1 robot can now do end-to-end AI training. This demo of the bot now able to make coffee is just one of many applications that they are promising the bot can do. Robotics expert Dr. Scott Walter does a comparison with Tesla Bot and Google’s Mobile ALOHA Scott Walter is an Aerospace Engineer with a Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering and has co-founded two robotics companies Follow Scott on X @GoingBallistic5 Get Free TESLA Milestone Tables M.

Hmmm I wonder if this can lead to allergies and inflammation. I googled it. Yes it can lead to allergies. Maybe that’s why I can’t drink coffee anymore or Earl Grey Tea. Another Google search says it can lead to inflammation which causes a lot of health problems.
You may think that artificial sweeteners can help you lose some weight, but a new study finds they are no good for your gut’s microbiome.
People who use aspartame (Equal), sucralose (Splenda), saccharin (Sweet’N Low), or stevia leaf extract tended to have intestinal bacteria colonies that differed significantly from those of people who didn’t use sugar substitutes, researchers found.
They had less rich colonies of bacteria in their small intestines or, even worse, higher levels of bacteria that churn out harmful toxins.

“Rather than seeing the organization as a machine, we need to see it as a collection of clever apes.” Psychologist Robin Dunbar’s latest book argues companies are social groups that can’t be perfected like a machine.
What is it about working life that can make us feel so alienated and isolated, and what can we do to prevent it? In The Social Brain: The Psychology of Successful Groups, the evolutionary psychologist Robin Dunbar joins forces with Tracey Camilleri and Samantha Rockey, associate fellows at Oxford’s Saïd Business School, to apply Dunbar’s own scientific discoveries about human cooperation to our work lives. The idea is that, in order to perform our jobs more effectively, we need to go with, and at times go against, the grain of human nature. The authors home in on what makes us best work together, given the central importance of groups throughout our evolutionary history.
Dunbar spent the better part of two decades, starting in the 1970s, studying wild monkeys in Africa to understand why some species develop their own societies. His close contact with our primate cousins gave him a new perspective from which to approach questions about human nature, and that led him, in 1998, to propose the “social brain hypothesis”—the idea that keeping track of who’s who, and cooperating effectively, takes considerable brain power.
Eli Lilly & Novartis are entering a strategic research collaboration with Isomorphic Labs to use state-of-the-art AI technologies—including the next-gen model of #AlphaFold—to discover novel small molecule therapeutics for select biological targets.
We are reimagining the entire drug discovery process from first principles with an AI-first approach.

Dementia and stroke often have devastating consequences, so patients want to know what they can do to protect themselves against these diseases. A team of clinicians in partnership with patients developed a Brain Care Score (BCS) based on modifiable risk factors identified in past epidemiological studies. In the BCS, weights are assigned to four physical components (i.e., blood pressure, glycosylated hemoglobin, cholesterol, and body-mass index), to five lifestyle elements (i.e., nutrition, alcohol intake, smoking, aerobic activities, and sleep), and to three social factors (i.e., stress, relationships, and purpose in life). Lower scores on the BCS (range, 0–19) predict higher risk.
The team then validated whether the BCS predicted new dementia or stroke in the U.K. Biobank cohort, which consisted of 398,900 people (age range at baseline, 40–69). During average follow-up of nearly 13 years, new dementia or stroke occurred in ≈3% of the cohort. The BCS identified people who were at highest risk for these outcomes. For example, among those who were younger than 50 at baseline, a 5-point higher score predicted 59% lower risk for dementia and 48% lower risk for stroke.
This score could be computed automatically from information already in electronic health records and used to identify risk factors and to engage patients in modifying those risk factors. Whether such scoring would actually lead to lower incidences of dementia and stroke remains to be seen.