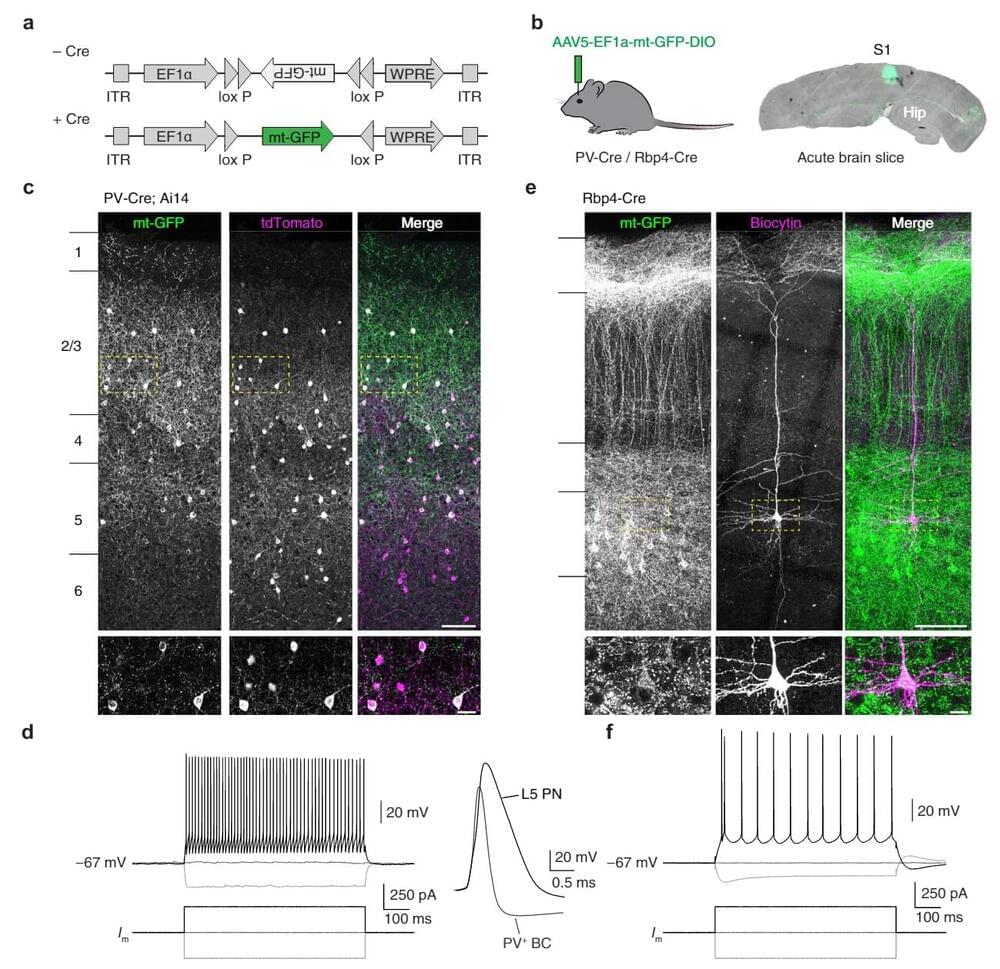
Researchers at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience have discovered that the energy management of inhibitory brain cells is different than that of excitatory cells in our brain. Why is that the case and what is the link with multiple sclerosis?
Brain cells are connected to each other by axons, the parts of the neuron that transmit electrical signals. To do this efficiently, axons are wrapped in myelin, a lipid-rich material which increases the speed at which electrical pulses are conducted. The importance of myelin becomes apparent in diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), where myelin is broken down, which has detrimental effects on brain function.
As a result of myelin loss, the conduction of electrical signals is disrupted, which also means that the energy costs of this process become much higher.