A system that detects forces and interprets which stimuli have the potential to cause harm could imbue robots with a sense akin to pain.
By Alex Wilkins
A system that detects forces and interprets which stimuli have the potential to cause harm could imbue robots with a sense akin to pain.
By Alex Wilkins
PBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http://to.pbs.org/DonateSPACE
Sign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!
/ pbsspacetime.
If we ever want to simulate a universe, we should probably learn to simulate even a single atomic nucleus. But it’s taken some of the most incredible ingenuity of the past half-century to figure out how that out. All so that today I can teach you how to simulate a very very small universe.
Check out the Space Time Merch Store.
https://www.pbsspacetime.com/shop.
Sign up for the mailing list to get episode notifications and hear special announcements!
https://mailchi.mp/1a6eb8f2717d/space… the Entire Space Time Library Here: https://search.pbsspacetime.com/ Hosted by Matt O’Dowd Written by Euan McLean & Matt O’Dowd Post Production by Leonardo Scholzer, Yago Ballarini, Pedro Osinski, Adriano Leal & Stephanie Faria GFX Visualizations: Ajay Manuel Directed by Andrew Kornhaber Associate Producer: Bahar Gholipour Executive Producers: Eric Brown & Andrew Kornhaber Executives in Charge (PBS): Adam Dylewski, Maribel Lopez Director of Programming (PBS): Gabrielle Ewing Spacetime is produced by Kornhaber Brown for PBS Digital Studios. This program is produced by Kornhaber Brown, which is solely responsible for its content. © 2022 PBS. All rights reserved. End Credits Music by J.R.S. Schattenberg: / multidroideka Special Thanks to Our Patreon Supporters Big Bang Supporters Steffen Bendel Gautam Shine NullBlox. ZachryWilsn Adam Hillier Bryce Fort Peter Barrett David Neumann Charlie Leo Koguan Ahmad Jodeh Alexander Tamas Morgan Hough Amy Hickman Juan Benet Vinnie Falco Fabrice Eap Mark Rosenthal David Nicklas Quasar Supporters Glenn Sugden Dr. Sujasha Gupta Vaka Dr. Vikram Reddy Vaka Alex Kern Ethan Cohen Stephen Wilcox Christina Oegren xaexyz Mark Heising Hank S Hypernova Supporters john ibes Vyce Ailour Brandon Paddock Oneamazinguy Ken S Gregory Forfa Kirk Honour Mark Evans drollere Joe Moreira Marc Armstrong Scott Gorlick Paul Stehr-Green Russell Pope Ben Delo Scott Gray Антон Кочков John R. Slavik Mathew Donal Botkin John Pollock Edmund Fokschaner Joseph Salomone chuck zegar Jordan Young John Hofmann Daniel Muzquiz Gamma Ray Burst Supporters Kane Holbrook Bradley S. Isenbek Jason Bowen John Yaraee Ross Story teng guo Mason Dillon Harsh Khandhadia Thomas Tarler bsgbryan Sean McCaul Carsten Quinlan Susan Albee Frank Walker Matt Q WhizBangery MHL SHS Terje Vold Anatoliy Nagornyy comboy Andre Stechert Paul Wood Kent Durham jim bartosh Nubble Scott R Calkins The Mad Mechanic Ellis Hall John H. Austin, Jr. Diana S Ben Campbell Faraz Khan Almog Cohen Alex Edwards Ádám Kettinger MD3 Endre Pech Daniel Jennings Cameron Sampson Geoffrey Clarion Darren Duncan Russ Creech Jeremy Reed Eric Webster David Johnston Web Browser Michael Barton Mr T Andrew Mann Isaac Suttell Devon Rosenthal Oliver Flanagan Bleys Goodson Robert Walter Bruce B Mirik Gogri Mark Delagasse Mark Daniel Cohen Nickolas Andrew Freeman Shane Calimlim Tybie Fitzhugh Robert Ilardi Eric Kiebler Craig Stonaha Graydon Goss Frederic Simon Tonyface John Robinson A G David Neal justahat John Funai Tristan Bradley Jenkins Kyle Hofer Daniel Stříbrný Luaan Cody Thomas Dougherty King Zeckendorff Dan Warren Patrick Sutton John Griffith Daniel Lyons DFaulk Kevin Warne.
Search the Entire Space Time Library Here: https://search.pbsspacetime.com/
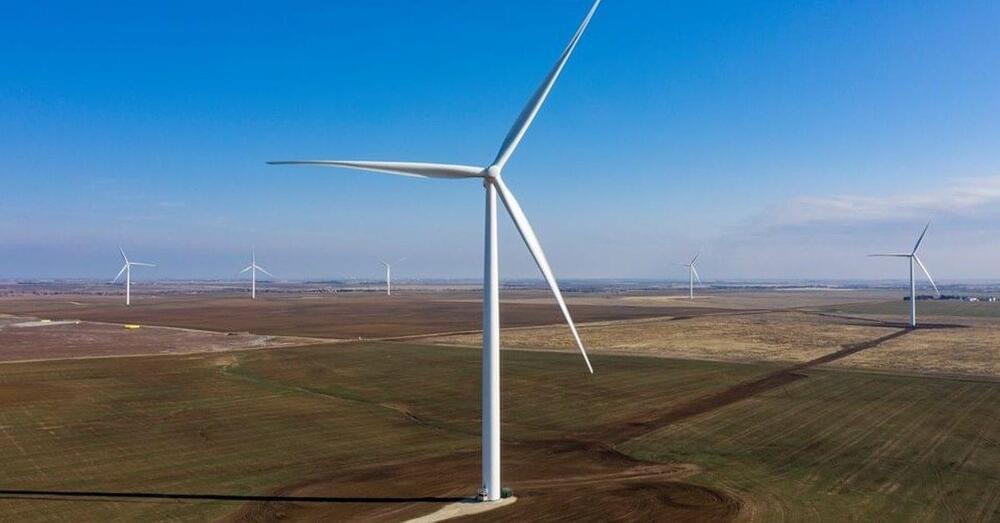

When two new Montana wind farms come online, the state will have more nameplate capacity in wind than in coal.
Nameplate capacity is the maximum rated output in megawatts when a source of power operates in optimal conditions.
According to US Energy Information Administration (EIA) data, Montana coal plants provided 1,631 megawatts (MW) of nameplate capacity in October. In the same period, Montana’s wind capacity provided 1,479 megawatts.

The AI gold rush has brought many market opportunities to the space tech sector, said Zainab Qasim, investor at Seraphim.
“AI’s impact on existing tech used in space will no doubt become more prevalent over the coming years allowing faster research and development execution and smarter insights for end customers,” she said.
AI plays a “heavy hand” in the development of future climate and space technologies, said Jeff Crusey, partner at early-stage fund 7percent Ventures, adding that it has “dramatically improved the efficiency of models, improving logistics, fuel savings, and ultimately the environment.”



Teleportation of quantum states promises to play a central role in securing the information superhighway of tomorrow.
In spite of the headway that’s been made, the process remains slow and kind of clunky. That could change, with scientists using a new process that could efficiently teleport states of light to form an image using a single pair of entangled photons.
The team, from South Africa, Germany, and Spain, is hopeful that the innovation may help build the secure networks of the future: if the key data isn’t transmitted, then it can’t be stolen.
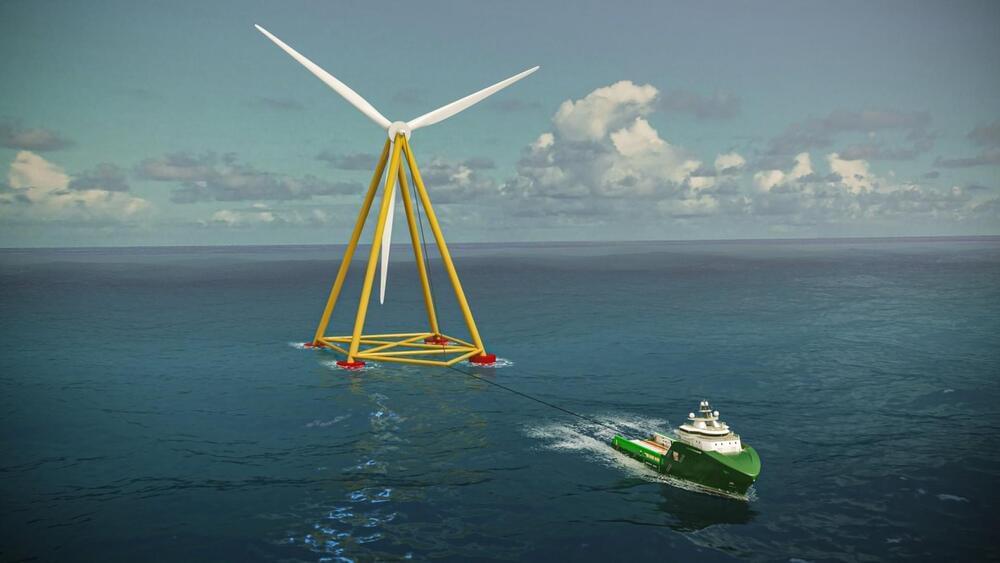

An innovative floating offshore wind turbine prototype was launched in New Bedford, Massachusetts this week. Instead of a single anchor tower, the approach uses a pyramid base that can also passively orient itself in the direction of the blowing wind.
As wind turbines get bigger and sweep larger areas in a single rotation, wind farms move offshore to gain maximum advantage from powerful sea winds. Over the years, the costs of wind-based energy have been plummeting, but as wind farms are set up farther into the sea, the costs and time required to set up new wind farms are bound to increase.

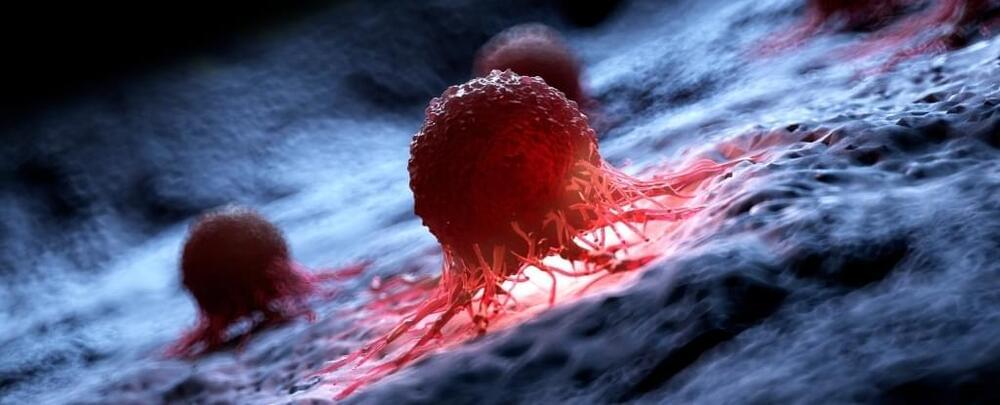
Scientists have discovered a new way to destroy cancer cells. Stimulating aminocyanine molecules with near-infrared light caused them to vibrate in sync, enough to break apart the membranes of cancer cells.
Aminocyanine molecules are already used in bioimaging as synthetic dyes. Commonly used in low doses to detect cancer, they stay stable in water and are very good at attaching themselves to the outside of cells.
The research team from Rice University, Texas A&M University, and the University of Texas, says the new approach is a marked improvement over another kind of cancer-killing molecular machine previously developed, called Feringa-type motors, which could also break the structures of problematic cells.