Oct 12, 2024
Comet likely last seen when Neanderthals walked Earth could soon dazzle in the night sky
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: energy, space
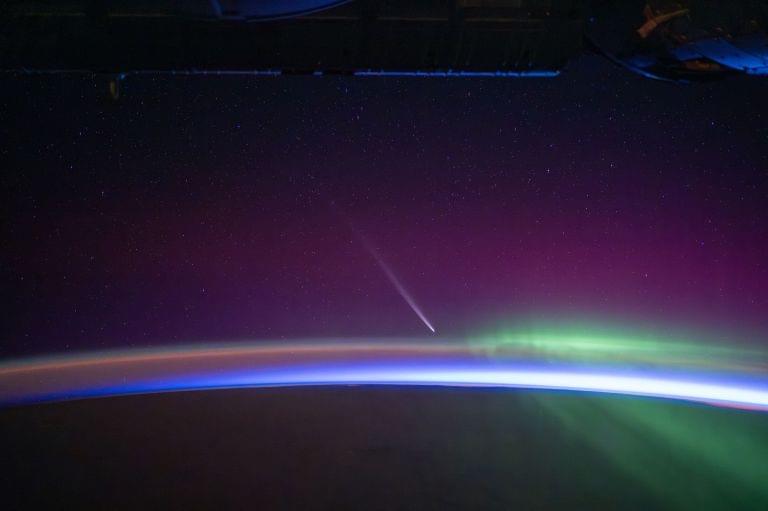
A recently discovered comet, known as C/2023 A3 Tsuchinshan–ATLAS, will make its closest approach of Earth on Saturday. Sky-gazers won’t want to miss the event since it may be the last time the comet will be seen in the night sky for another 80,000 years.
The comet successfully reached perihelion, its closest point to the sun in its orbital path around the parent star, on September 27, and was visible for those in the Southern Hemisphere in September and early October. Now, the icy body is on its way out of the inner solar system and will be visible to those in the Northern Hemisphere in mid-October through early November, according to NASA.