@SpaceX has launched its eighth Falcon 9 mission of November, as it heads towards its first 10-launch month and conceivably its first 100-launch year.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Nobel Prize in Phyiscs 2023
Pierre Agostini, Ferenc Krausz and Anne L’Huillier share the 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics for experiments that “have given humanity new tools for exploring the world of electrons inside atoms and molecules.” A more succinct description is that they have given us attosecond physics.
Attosecond physics is the science of the exceedingly, extremely, exceptionally [insert your own hyperbolic adverb here] fast. To put it into context, L’Huillier’s first call from the Nobel Prize’s Adam Smith after she received the news took 3 minutes 48 seconds, or-1 attoseconds. Her first heartbeat during that call lasted a second, or a billion billion attoseconds. Almost defying a description, an attosecond is an unfathomably tiny amount of time. But it happens to be the natural timescale of the near-instantaneous dance of electrons.
Being able to gain a glimpse into the incredibly tiny scale of electrons in the incredibly fast attosecond regime opens the door to directly measuring, and perhaps even controlling, quantum processes. And this, in turn, offers huge potential to advance research, not only in quantum physics but also in biology, chemistry, medicine, electronics and many more areas important to science and society.
Virgin Galactic sets dates for first commercial space flights
After multiple delays, billionaire Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic is finally ready to begin commercial space flights — and you can snag a ticket for $450,000.
The background: In June 2021, Virgin Galactic became the first spaceline to secure permission from the FAA for commercial space flights, suggesting that it was pulling ahead of rivals Blue Origin and SpaceX in the space tourism arena.
While both of those companies planned to use rockets to send crewed capsules into space, Virgin Galactic’s idea was to put people in a spaceplane — a vehicle that can fly through Earth’s atmosphere like a plane, but also navigate space like a spacecraft.
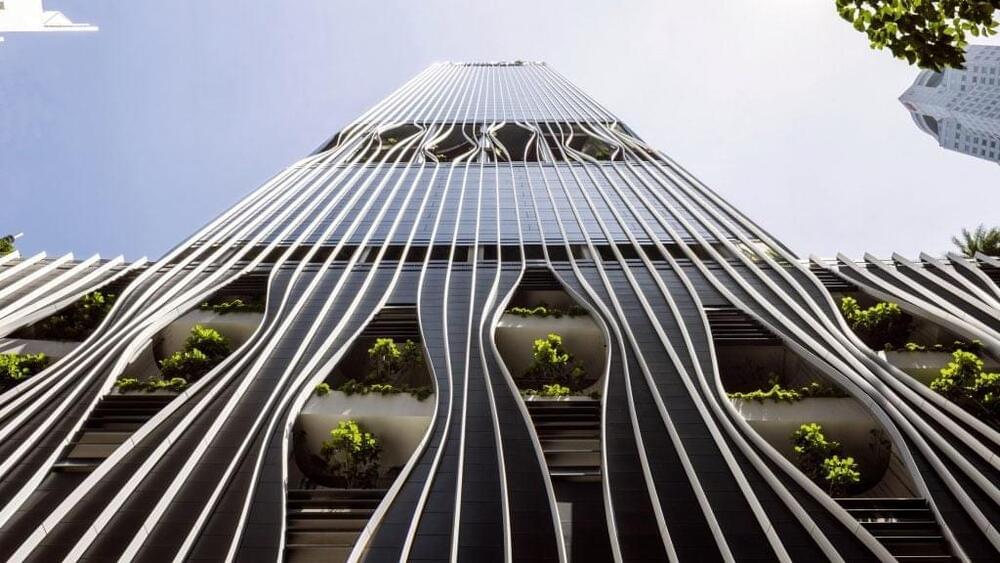

Seven of the latest skyscrapers designed by BIG
Following the completion of The Spiral in New York, we take a look at seven of the latest skyscrapers designed by its architect, Danish studio BIG, along with a “landscaper”
From CapitaSpring in Singapore to O-Tower in China, a mix of recently completed projects and others still under construction make up the list of towers by the studio, which was founded in 2005 by Danish architect Bjarke Ingels.
Common threads throughout the projects are the incorporation of greenery to bring occupants closer to nature and unusual forms that challenge traditional boxy skyscrapers that dominate many city skylines.

Coinbase CEO to OpenAI Board: You Just “Torched $80B of Value”
Less than 48 hours after Sam Altman was fired from OpenAI, Brian Armstrong, the CEO of Coinbase made a post highlighting some of the impact his departure might cause the ChatGPT creator.
Armstrong eulogized Sam Altman for taking OpenAI’s valuation to $80 billion, a massive worth he believe the company has just ‘torched by ousting the tech veteran.
Coinbase CEO Suspects Foul Play
The Promise Of Stem Cells In Aging Research | Dr Elena Seranova Interview Series Ep3
In particular I like the 3D modeling segment.
Here Dr Seranova talks about stem cell use in helping with research into diseases of aging, particularly generating organiods of the brain by growing them from stem cells.
Some links are affiliate links so we will earn a commission when they are used to purchase products.
NMN Bio 10% off all products https://tinyurl.com/2af2v2fw Code ModernHealthSpan10 in link.
Renue By Science 10% : Code MHS NMN https://tinyurl.com/3wr8pr3t.
ProHealth 15% discount Code MODERN : https://prohealth.pxf.io/zNOPoW
NMN http://prohealth.pxf.io/JzQaER
NOVOS Core & Boost https://novos.sjv.io/QyWP7o code 5OFFMHS
DoNotAge 10% discount code MHS https://tinyurl.com/6dbvhv87
☕If you would like to support our channel, we’d love a coffee…thank you! _https://www.buymeacoffee.com/mhealthspan_
Nuchido Time+ 20% discount of first purchase with code MODERN20 https://nuchido.com/MODERN
*Insidetracker* 20% discount Code MODERN20 _https://insidetracker.sjv.io/NkbP7V_
*Bulletproof* 15% off with coupon code: HEALTHSPAN15: _https://tinyurl.com/4npjk5vp_
*SiPhox Health* 20% Code MODERN blood test (only in US & Canada) _https://siphoxhealth.com/discount/modern_
*Delavie Sciences* 10% Code Modern Age Defying Serum https://tinyurl.com/yp2jmhy8 Eye Refresh https://tinyurl.com/mt8knv3s.
*OmegaQuant* 5% discount Code MODERN _https://omegaquant.com/shop/_
Dr. Seranova is a serial entrepreneur, holds an MSc in Translational Neuroscience from the University of Sheffield and a PhD in Stem Cell Biology and Autophagy from the University of Birmingham, UK.
Inflection AI unveils Inflection-2, surpassing Google and Meta in AI performance
Inflection AI just announced Inflection-2, a HUGE new 175 billion parameter language model.
Capabilities exceed Google and Meta’s top models and “is very close” to catching GPT-4.
The CEO also said the company’s next model will be 10x larger in six months.
Inflection AI, the innovative startup behind the conversational chatbot Pi, has recently unveiled a new AI model, Inflection-2, claiming superior performance over popular models developed by Google and Meta. According to a recent Forbes report, this new model is rapidly gaining attention for its potential to rival OpenAI’s GPT-4.
Inflection-2 has demonstrated impressive results, outperforming Google’s PaLM Large 2 and Meta’s LLaMA 2 in various standard benchmarks. According to Inflection AI, their model is the most efficient of its size, only trailing behind OpenAI’s larger GPT-4 model.
Inflection AI’s vision for the future


Tesla open sources all design and engineering of original Roadster
Tesla has open-sourced all of the design and engineering of the original Roadster, CEO Elon Musk announced today, and plenty of people are wondering if the timing of the release has anything to do with the next-gen Roadster that is now several years behind schedule.
Tesla has opened everything from Owner’s Manuals to Circuits and Connectors for the original Roadster, which was the automaker’s first project fifteen years ago in 2008.
The vehicle was essentially a fundraising campaign for Tesla as it fought to keep its doors open and transform the passenger vehicle industry. It almost bankrupted the company, but now, everything that was developed for Tesla’s initial EV project is available for anyone to take a look at.
AI Experts Warn 46% Of All Aussie Jobs Could Be Automated By 2030
AI can be used to make our lives easier, but it is also a frightening tool that could see many of us out of a job – at least according to some experts.
Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Engineering (ATSE) CEO Kylie Walker told The Canberra Times AI could replace anywhere between 25 and 46 percent of all Aussie jobs by 2030.
Walker, and a group of 13 other AI experts, called for a $1 billion national artificial intelligence initiative in a new report to push out more than 100,000 digitally skilled workers over the next decade.