“Aging reversal is something that’s been proven about eight different ways in animals,” geneticist George Church says. So when will humans get to turn back t…
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
How LISA — A Gravitational Wave Observatory in Space — Will Transform Our Cosmic Understanding
LISA, a collaborative mission between ESA and NASA, aims to detect gravitational waves from space, offering new insights into the cosmos through advanced technology and international cooperation.
The first space-based observatory designed to detect gravitational waves has passed a major review and will proceed to the construction of flight hardware. On January 25, ESA (European Space Agency), announced the formal adoption of LISA, the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna, to its mission lineup, with launch slated for the mid-2030s. ESA leads the mission, with NASA serving as a collaborative partner.
NASA’s Role and Mission Collaboration.

Revolutionizing Physics With a Game-Changing Topological Approach
Innovative research introduces a practical, model-free method for exploring topological properties in materials, enhancing the scope and efficiency of topological studies.
The branch of mathematics known as topology has become a cornerstone of modern physics thanks to the remarkable – and above all reliable – properties it can impart to a material or system. Unfortunately, identifying topological systems, or even designing new ones, is generally a tedious process that requires exactly matching the physical system to a mathematical model.
Researchers at the University of Amsterdam and the École Normale Supérieure of Lyon have demonstrated a model-free method for identifying topology, enabling the discovery of new topological materials using a purely experimental approach.
Debate simmers over when doctors should declare brain death
Benjamin Franklin famously wrote: “In this world nothing can be said to be certain, except death and taxes.” While that may still be true, there’s a controversy simmering today about one of the ways doctors declare people to be dead.
Bioethicists, doctors and lawyers are weighing whether to redefine how someone should be declared dead. A change in criteria for brain death could have wide-ranging implications for patients’ care.

Can AI Be Controlled?
Summary: Dr. Roman V. Yampolskiy, an AI Safety expert, warns of the unprecedented risks associated with artificial intelligence in his forthcoming book, AI: Unexplainable, Unpredictable, Uncontrollable. Through an extensive review, Yampolskiy reveals a lack of evidence proving AI can be safely controlled, pointing out the potential for AI to cause existential catastrophes.
He argues that the inherent unpredictability and advanced autonomy of AI systems pose significant challenges to ensuring their safety and alignment with human values. The book emphasizes the urgent need for increased research and development in AI safety measures to mitigate these risks, advocating for a balanced approach that prioritizes human control and understanding.
Colonizing Jupiter
Jupiter and its moon are a rarely considered prospect for colonization, but potentially the ripest opportunity for it in the solar system. In this episode of the Outward Bound series we will examine the options for colonizing each of Jupiter’s primary moons and even discuss ways to colonize the giant planet itself.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: / colonizing-jupiter.
Cover Art by Jakub Grygier: https://www.artstation.com/artist/jak…
Graphics Team:
Edward Nardella.
Jarred Eagley.
Justin Dixon.
Jeremy Jozwik.
Katie Byrne.
Kris Holland.
Misho Yordanov.
Murat Mamkegh.
Pierre Demet.
Sergio Botero.
Stefan Blandin.
Script Editing:
Andy Popescu.
Connor Hogan.
Edward Nardella.
Eustratius Graham.
Gregory Leal.
Jefferson Eagley.
Keith Blockus.
Luca de Rosa.
Mark Warburton.
Michael Gusevsky.
Mitch Armstrong.
MolbOrg.
Naomi Kern.
Philip Baldock.
Sigmund Kopperud.
Tiffany Penner.
Music:
Markus Junnikkala, \
Colonizing Ceres
Today we’ll look at colonizing Ceres and asteroid mining, farming in space, and a potential distant future of a developed asteroid belt.
Visit our sponsor, Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/IsaacArthur/
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version:
/ colonizing-ceres.
Episode’s Narration-only version: / colonizing-ceres-narration-only.
Credits: outward bound: colonizing ceres. 141 season 4 episode 26
Writers.
Isaac Arthur.
Editors.


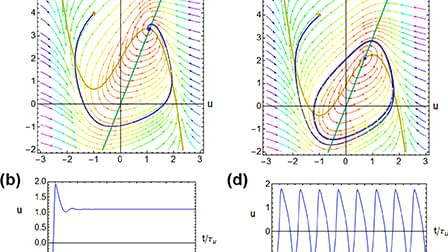
Device physics recipe to make spiking neurons
Divice recipe for making spiking artificial neurons.
Neurons, which are made of biological tissue, exhibit cognitive properties that can be replicated in various material substrates. To create brain-inspired computational artificial systems, we can construct microscopic electronic neurons that mimic natural systems. In this paper, we discuss the essential material and device properties needed for a spiking neuron, which can be characterized using impedance spectroscopy and small perturbation equivalent circuit elements. We find that the minimal neuron system requires a capacitor, a chemical inductor, and a negative resistance. These components can be integrated naturally in the physical response of the device, instead of built from separate circuit elements. We identify the structural conditions for smooth oscillations that depend on certain dynamics of a conducting system with internal state variables. These state variables can be of diverse physical nature, such as properties of fluids, electronic solids, or ionic organic materials, implying that functional neurons can be built in various ways. We highlight the importance of detecting the Hopf bifurcation, a critical point in achieving spiking behavior, through spectral features of the impedance. To this end, we provide a systematic method of analysis in terms of the critical characteristic frequencies that can be obtained from impedance methods. Thus, we propose a methodology to quantify the physical and material properties of devices to produce the dynamic properties of neurons necessary for specific sensory-cognitive tasks. By replicating the essential properties of biological neurons in electronic systems, it may be possible to create brain-inspired computational systems with enhanced capabilities in information processing, pattern recognition, and learning. Additionally, understanding the physical and material properties of neurons can contribute to our knowledge of how biological neurons function and interact in complex neural networks. Overall, this paper presents a novel approach toward building brain-inspired artificial systems and provides insight into the important material and device considerations for achieving spiking behavior in electronic neurons.