And other low pressure rail & maglev systems offer the possibility of ultra-fast and ultra-cheap transport on and off of Earth. Watch my exclusive video Topopolis: The Eternal River: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: Vacuum Trains Episode 435a; February 25, 2024 Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Editors: Konstantin Sokerin Merv Johnson II Graphics: Allen DeMoura Apogii.uk Ian “LITE” Long Jarred Eagley Justin Dixon Katie Byrne Ken York Phil Swan Real Courte Sergio Botero Udo Schroeter Music Courtesy of: Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Physicists Discover Evidence of Time Being Reversible in Glass
Time’s inexorable march might well wait for no one, but a new experiment by researchers at the Technical University of Darmstadt in Germany and Roskilde University in Denmark shows how in some materials it might occasionally shuffle.
An investigation into the way substances like glass age has uncovered the first physical evidence of a material-based measure of time being reversible.
For the most part the laws of physics care little about time’s arrow. Flip an equation describing the movement of an object and you can easily calculate where it started. We describe such laws as time reversible.
Birch Planets: Galaxy-Sized Worlds
So called Dyson megaphere.
Birch Planets are enormous hypothetical Megastructures which would have more living area than every planet in our galaxy combined, and are even larger than Dyson Spheres. Mega Earths: https://youtu.be/ioKidcpkZN0 To find out more about megastructures, see the Megastructure Compendium: https://youtu.be/1xt13dn74wc Produced, Written & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Graphics by: Jeremy Jozwik, Ken York Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator
Mega Earths
A look at creating artificial planets, ones vastly bigger than Earth, or potentially even an entire solar system.
Visit our sponsor, Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/IsaacArthur/
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: / mega-earths.
Cover Art by Jakub Grygier: https://www.artstation.com/artist/jak…
Graphics Team:
Edward Nardella.
Jarred Eagley.
Justin Dixon.
Katie Byrne.
Kris Holland of Mafic Stufios: www.maficstudios.com.
Misho Yordanov.
Pierre Demet.
Sergio Botero: https://www.artstation.com/sboterod?f…
Stefan Blandin.
Script Editing:
Andy Popescu.
Connor Hogan.
Edward Nardella.
Eustratius Graham.
Gregory Leal.
Jefferson Eagley.
Luca de Rosa.
Mark Warburton.
Michael Gusevsky.
Mitch Armstrong.
MolbOrg.
Naomi Kern.
Philip Baldock.
Sigmund Kopperud.
Tiffany Penner.
Music:
Markus Junnikkala, \

Risk Factors for Young-Onset Dementia
Investigators identified 15 factors that affect risk for young-onset dementia.
Limited data are available on risk factors for young-onset dementia. In this study, researchers assessed 39 potential risk factors for young-onset dementia from data in the UK Biobank. Participants 65 years of age or older without a dementia diagnosis were included in the analysis. Potential risk factors were grouped into sociodemographic factors, genetic factors, lifestyle factors, environmental factors, blood marker factors, cardiometabolic factors, psychiatric factors, and other risk factors.
Among 359,052 participants, the mean age at baseline was 55 years and 55% were women. There were 485 incident all-cause young-onset dementia cases after a mean follow-up of 8 years. Incident young-onset dementia increased with age and was more common in men. Fewer years of formal education, lower socioeconomic status, the presence of two apolipoprotein E ℇ4 alleles, no alcohol use, alcohol use disorder, social isolation, vitamin D deficiency (1 mg/dL), lower handgrip strength, hearing impairment, orthostatic hypotension, stroke, diabetes, heart disease, and depression were associated with higher risk for young-onset dementia in fully adjusted models. Men with diabetes were more likely to have young-onset dementia than men without diabetes, and women with high C-reactive protein were more likely to have young-onset dementia than women with low C-reactive protein levels.
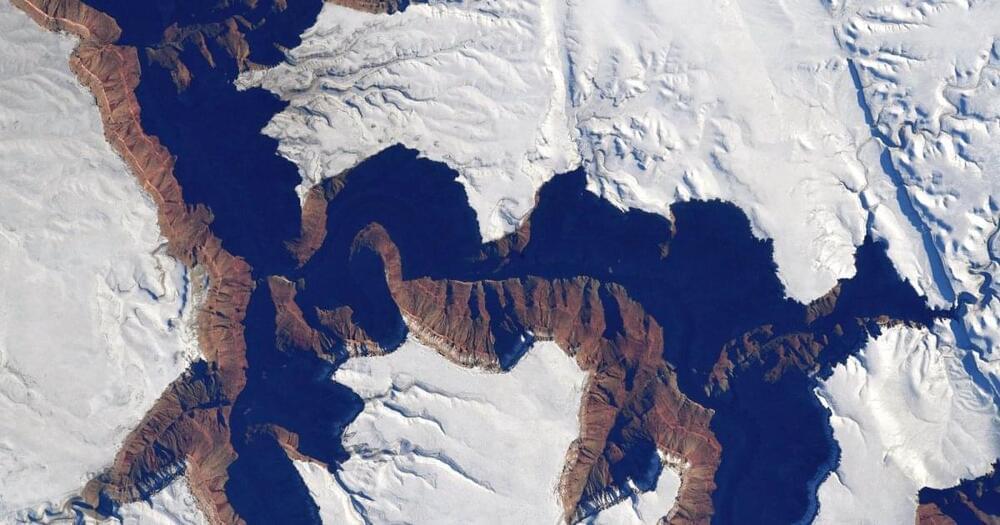

Astronaut captures stunning images of a snowy Grand Canyon
In the final days of his six-month stint aboard the International Space Station (ISS), Danish astronaut Andreas Mogensen took some time out of his science work to snap some striking photos of a snow-covered Grand Canyon.
The images were captured from the station in recent days as it orbited Earth at an altitude of around 250 miles.

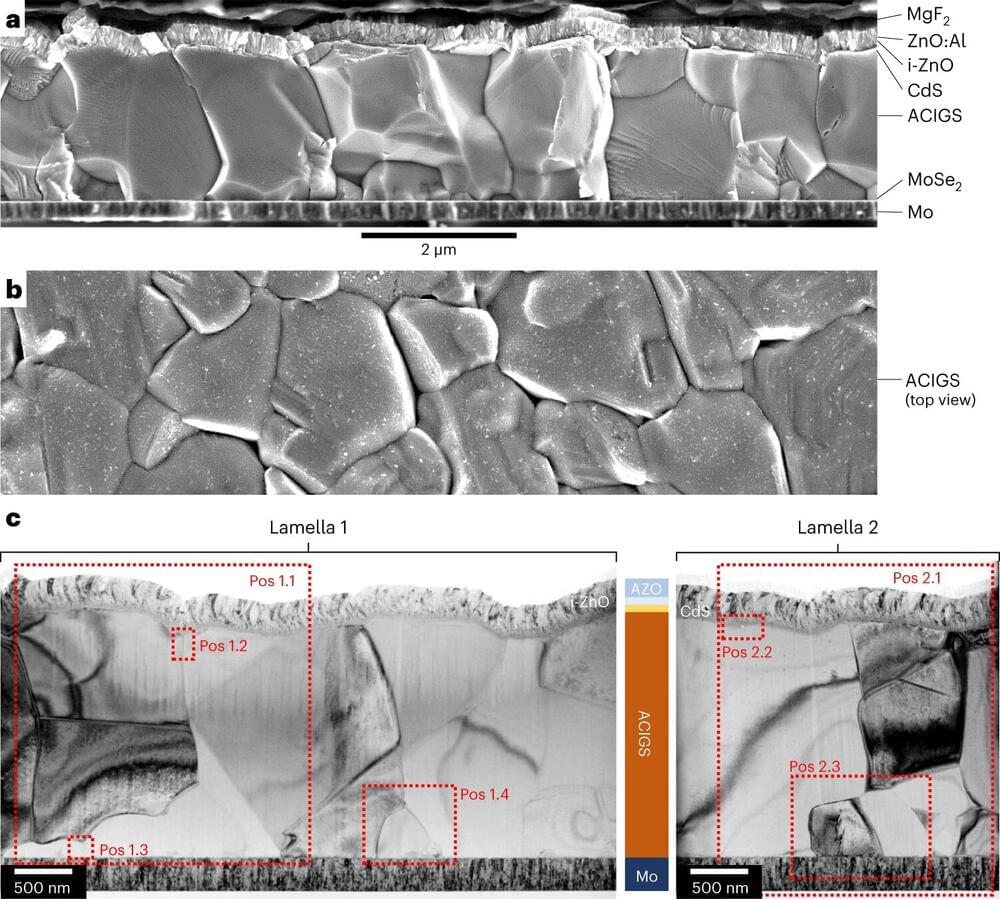
Researchers set new world record for CIGS solar cells
Uppsala University is the new world record holder for electrical energy generation from copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cells. The new world record is 23.64% efficiency. The measurement was made by an independent institute, and the results are published in Nature Energy.
The record results from a collaboration between the company First Solar European Technology Center (formerly known as Evolar) and solar cell researchers at Uppsala University.
“The measurements that we have made ourselves for this solar cell and other solar cells produced recently are within the margin of error for the independent measurement. That measurement will also be used for an internal calibration of our own measurement methods,” says Marika Edoff, Professor of Solar Cell Technology at Uppsala University, who is responsible for the study.

