Compared to the Meta Quest 3, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg argues the Apple Vision Pro is packed with ‘trade-offs.’


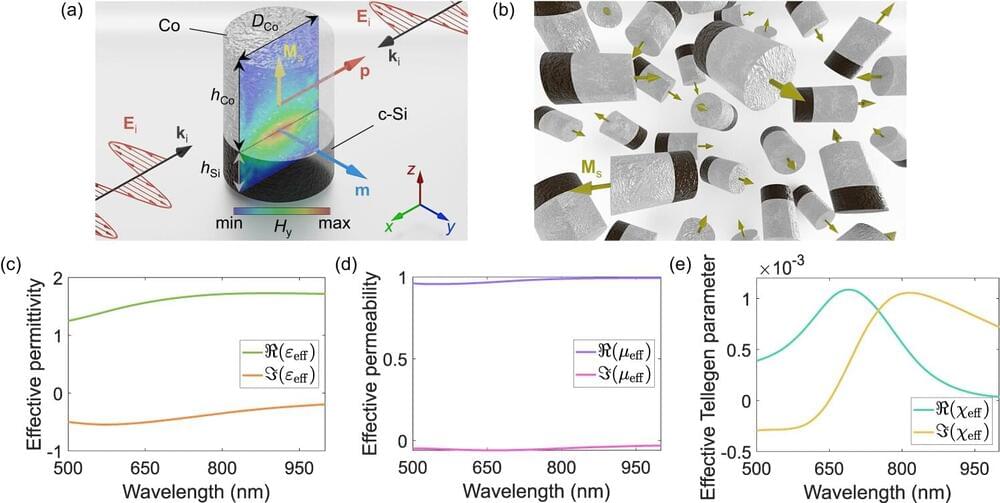
A new approach has allowed researchers at Aalto University to create a kind of metamaterial that has so far been beyond the reach of existing technologies. Unlike natural materials, metamaterials and metasurfaces can be tailored to have specific electromagnetic properties, which means scientists can create materials with features desirable for industrial applications.
The new metamaterial takes advantage of the nonreciprocal magnetoelectric (NME) effect. The NME effect implies a link between specific properties of the material (its magnetization and polarization) and the different field components of light or other electromagnetic waves. The NME effect is negligible in natural materials, but scientists have been trying to enhance it using metamaterials and metasurfaces because of the technological potential this would unlock.
The work is published in the journal Nature Communications.
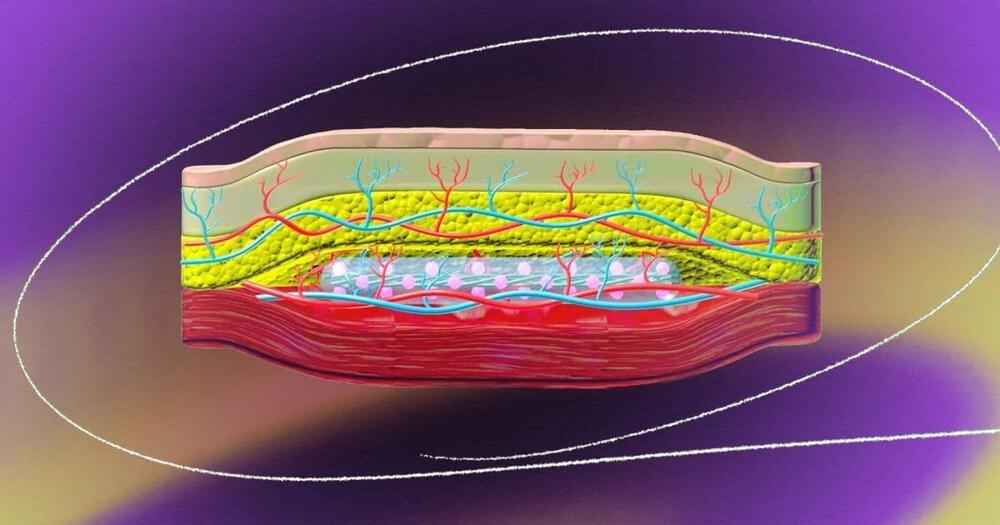
A new kind of implant could one day make it far easier for people with type 1 diabetes to manage their disease. The insulin-making implant is a mixture of transplanted islets cells and medical technology, inserted just below the skin in a person’s arm, and if it perform well in clinical trials, it could potentially last for years.
The challenge: Insulin is a hormone that our bodies use to convert sugar in our blood into energy. People with type 1 diabetes don’t produce enough (or any) insulin — if left untreated, this causes dangerously high blood sugar levels, leading to serious health issues or even death.
Regularly checking blood sugar levels and injecting synthetic insulin when they’re high is the most common way to treat type 1 diabetes, but it isn’t the only way.
Speaker: Dr. Zhongrui WangAbstract: The rapid development in the field of artificial intelligence has relied principally on the advances in computing hardwar…
Jesse Watters discusses the very vague alleged threat to Americans that lawmakers are keeping under wraps on ‘Jesse Watters Primetime.’
Watch more Fox News Video: http://video.foxnews.com.
Watch Fox News Channel Live: http://www.foxnewsgo.com/
FOX News Channel (FNC) is a 24-hour all-encompassing news service delivering breaking news as well as political and business news. The number one network in cable, FNC has been the most-watched television news channel for 18 consecutive years. According to a 2020 Brand Keys Consumer Loyalty Engagement Index report, FOX News is the top brand in the country for morning and evening news coverage. A 2019 Suffolk University poll named FOX News as the most trusted source for television news or commentary, while a 2019 Brand Keys Emotion Engagement Analysis survey found that FOX News was the most trusted cable news brand. A 2017 Gallup/Knight Foundation survey also found that among Americans who could name an objective news source, FOX News was the top-cited outlet. Owned by FOX Corporation, FNC is available in nearly 90 million homes and dominates the cable news landscape, routinely notching the top ten programs in the genre.
Watch full episodes of your favorite shows.
The Five: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/t…
Special Report with Bret Baier: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/s…
Jesse Watters Primetime: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/j…
Hannity: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/h…
The Ingraham Angle: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/i…
Gutfeld!: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/g…
Fox News @ Night: https://www.foxnews.com/video/shows/f…
Follow Fox News on Facebook: / foxnews.
Follow Fox News on Twitter: / foxnews.
Follow Fox News on Instagram: / foxnews.
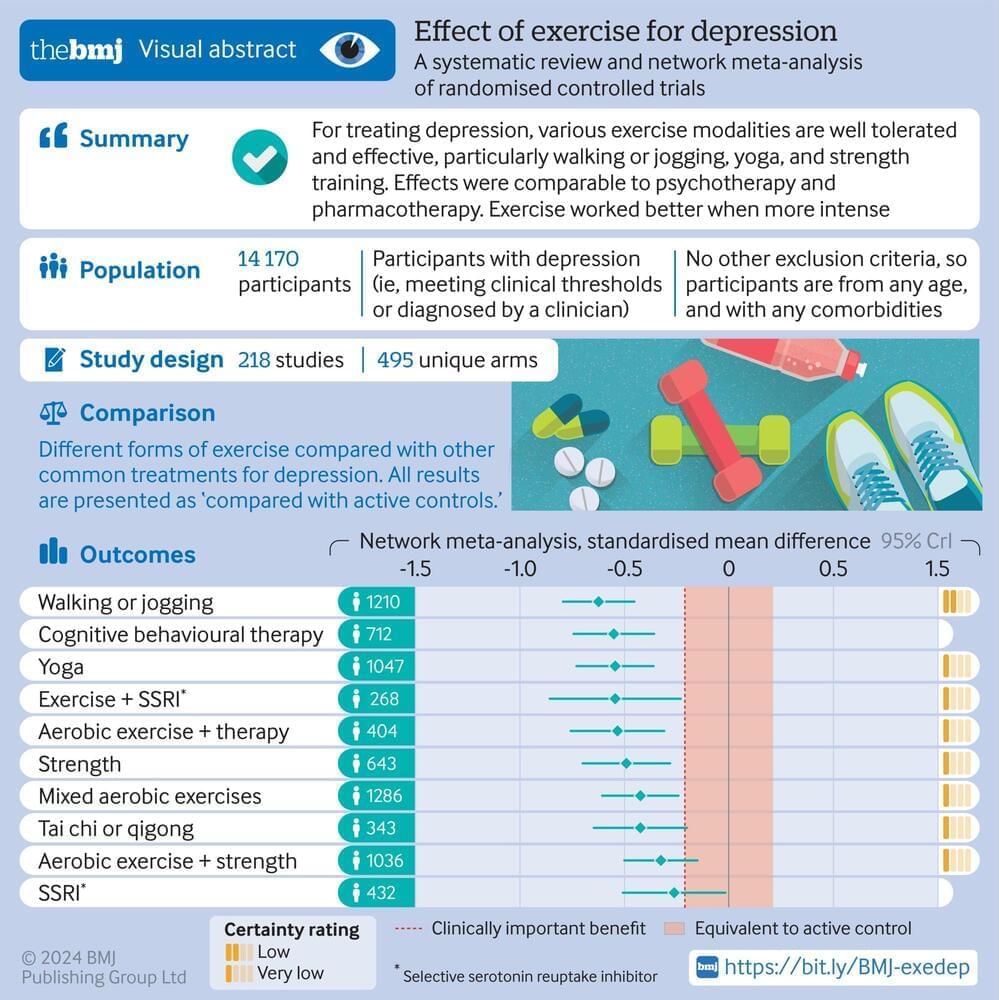
Cecile G. Tamura Lifeboat Foundation An effective treatment for depression from a systematic review of 200 unique RCTs:
Exercise.
Objective To identify the optimal dose and modality of exercise for treating major depressive disorder, compared with psychotherapy, antidepressants, and control conditions.
Design Systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Methods Screening, data extraction, coding, and risk of bias assessment were performed independently and in duplicate. Bayesian arm based, multilevel network meta-analyses were performed for the primary analyses. Quality of the evidence for each arm was graded using the confidence in network meta-analysis (CINeMA) online tool.
Data sources Cochrane Library, Medline, Embase, SPORTDiscus, and PsycINFO databases.

“Focus has been on how cells become mechanosensitive, how cell adhesion became mechanosensitive through the recruitment of mechanosensitive proteins like talin, vinculin, and also other proteins,” said Sangyoon Han, a mechanobiologist at Michigan Technological University who was not involved in the study. “But not many studies were around to tell if there is any kind of premechanosensitive processes that act as a seed for the original binding of this mechanosensitive binding.”
Cooper’s team imaged adhesion formation at the cell surface interface using total internal reflection (TIRF) microscopy and observed that activated Cas clustered at this site almost a full minute before mechanosensing proteins arrived or β1 integrin was activated. They depleted Cas with siRNA and inactivated it to determine this protein’s role in the developing adhesion site. “When we remove Cas from cells, or inhibit its phosphorylation, or inhibit stuff downstream of Cas, the integrin clustering doesn’t really happen,” Cooper said. The Cas-depleted cells attached poorly to surfaces and were immobile.
Finally, the group identified a positive feedback loop between Cas and Rac1, which drives actin polymerization and is important in forming focal complexes that promoted cell adhesion formation.5,6 Cas phosphorylation activated Rac1, which in turn generated reactive oxygen species, which promoted additional Cas activation. Cas degradation regulated this loop.
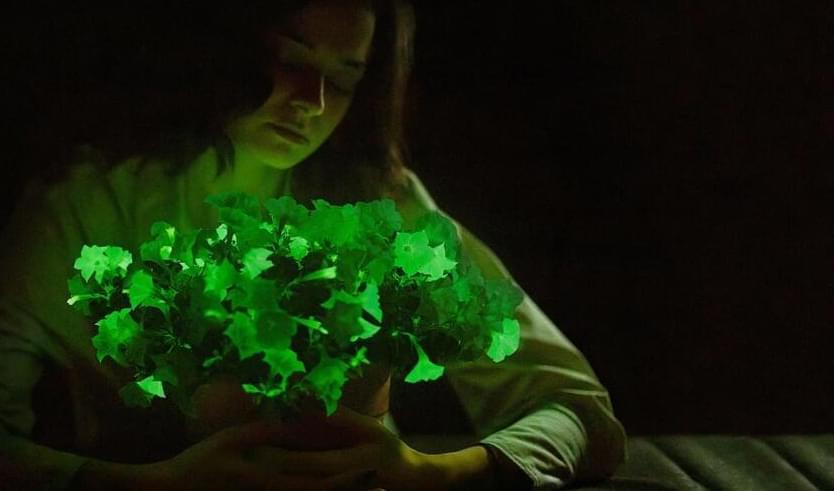

The sci-fi dream that gardens and parks would one day glow like Pandora, the alien moon in Avatar, is decades old. Early attempts to splice genes into plants to make them glow date back to the 1980s, but experiments emitted little light and required special food.
Then in 2020, scientists made a breakthrough. Adding genes from luminous mushrooms yielded brightly glowing specimens that needed no special care. The team has refined the approach—writing last month they’ve increased their plants’ luminescence as much as 100-fold—and spun out a startup called Light Bio to sell them.
Light Bio received USDA approval in September and this month announced the first continuously glowing plant, named the firefly petunia, is officially available for purchase in the US. The petunias look and grow like their ordinary cousins—green leaves, white flowers—but after sunset, they glow a gentle green. The company is selling the plants for $29 on its website and says a crop of 50,000 will ship in April.

Summary: Researchers developed an innovative AI tool, DeepGO-SE, that excels in predicting the functions of unknown proteins, marking a significant advance in bioinformatics. Leveraging large language models and logical entailment, this tool can deduce molecular functions even for proteins without existing database matches, offering a groundbreaking approach to understanding cellular mechanisms.
Its precision has placed DeepGO-SE among the top algorithms in an international function prediction competition, demonstrating its potential in drug discovery, metabolic pathway analysis, and beyond. The team aims to apply this tool to explore proteins in extreme environments, opening new doors for biotechnological advancements.
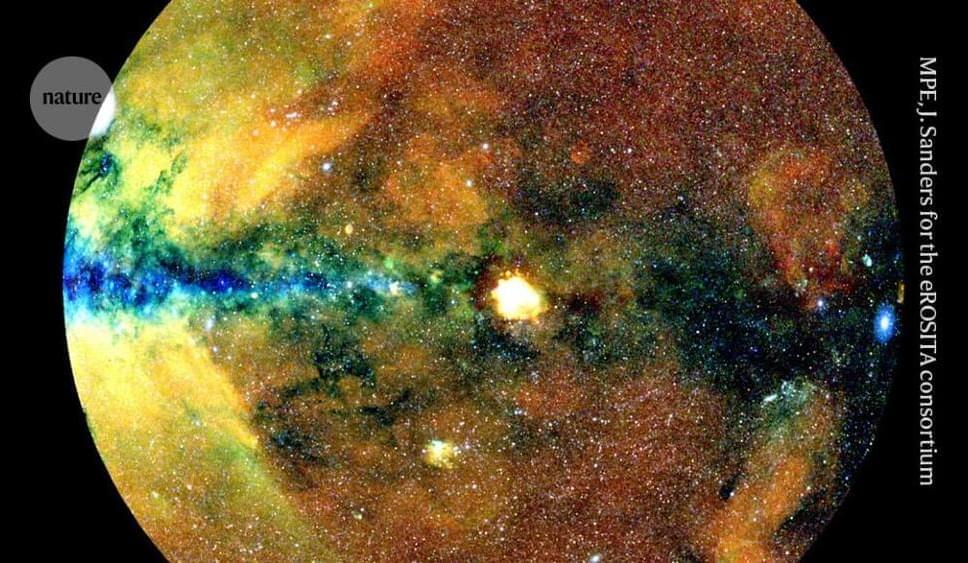

The picture was the result of the first six months of operation of eROSITA (Extended Roentgen Survey with an Imaging Telescope Array), one of two X-ray telescopes that were launched into space in July 2019 aboard the Russian spacecraft SRG (Spectrum-Roentgen-Gamma). eROSITA scans the sky as the spacecraft spins, and collects data over wider angles than are possible for most other X-ray observatories. This enables it to slowly sweep the entire sky every six months.
By an unusual arrangement, the eROSITA team is split into two — with a group based in Germany and one based in Russia — and each has exclusive access to eROSITA data from only half of the sky. The mission was originally intended to cover the sky eight times. But Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022 led the German government to freeze its collaborations, and eROSITA was put on stand-by. By then, it had completed four full sky scans.
The data that Bulbul and her collaborators have used so far were from their half of the sky, collected during the first scan. Even so, the results are already among the most precise cosmological measurements ever made. It is unclear when the Russia-based group will publish its data and analysis.