Although a significant number of neuromorphic devices applied to RC have been reported in recent years, the majority of these efforts have focused on shallow-RC with monotonic reservoir state spaces19. This can be attributed to the heavy reliance on monotonic carrier dynamics when using reported neuromorphic devices as reservoirs to map sequence signals, which gives rise to several noteworthy issues for RC when performing different spatiotemporal tasks. One major issue is that the narrow range ratio of spatial characteristics makes it difficult to extract the diversity spatial feature of sequence signal, which greatly limits the richness of the reservoir space state. As a result, during the process of mapping complex sequence signals, the reservoir state tends to overlap, making it difficult to effectively separate the spatial characteristics within complex information and subsequently reducing recognition accuracy. Another issue is the limited rang ratio of temporal characteristic, which hinders efficient extraction of temporal feature from sequential signals with diverse time-scales. For example, when performing dynamic trajectory prediction with abundant time-scales, the limited range ratio of temporal characteristic is difficult to adapt to the signal with different temporal feature, which severely limit the correlation of prediction. Despite researchers have achieved multi-scale temporal characteristics by increasing the number of signal modes in the input layer based on shallow-RC networks20, as shown in the Supplement Information Fig. S1, the limitation of shallow-RC on spatial characteristics remain unresolved. Furthermore, increasing the input layer also means the requirement of more encoding design for sequence signals and the utilization of more physical devices to receive different modes of physical signals. This significantly increases the signal error rate and pre-processing cost of the input signals, which is detrimental to the robustness of RC. Therefore, developing new neuromorphic reservoir devices along with new RC networks to simultaneously meet large-scale spatial and temporal characteristics are highly required, which is crucial for achieving high-performance recognition and prediction in complex spatiotemporal tasks for RC networks.
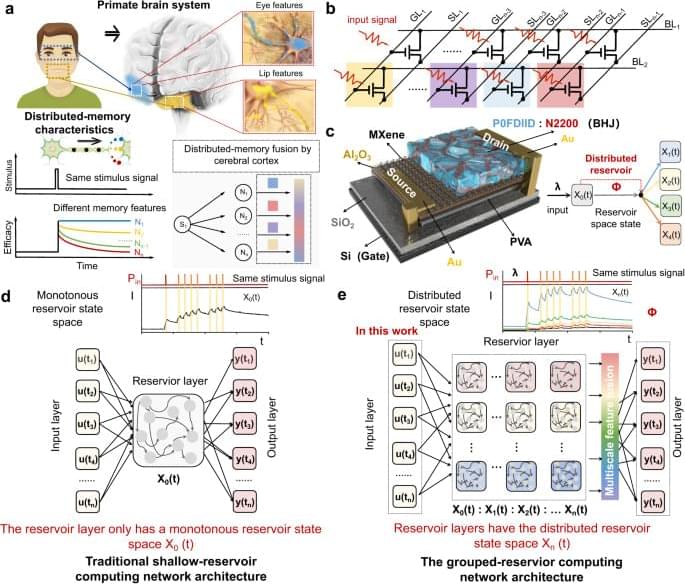
Interestingly, primates in nature are able to quickly and accurately recognize complex object information, such as facial recognition, with the help of advanced synaptic dynamics mechanisms. Brain science research on primates has confirmed20,21,22 that primates use a distributed memory characteristic for processing complex information. When the nervous system processes a task, each neuron and neural circuit processes only a part of the information and generates a part of the output. For example, as shown in Fig. 1a, when a primate observes an unfamiliar face, neurons in the temporal polar (TP) region (blue) respond to familiar eye features, forming TP feature memory. Neuron cells in the anterior-medial (AM) region respond to unfamiliar lip features, forming AM feature memory23. In this way, all outputs are integrated by the cerebral cortex to form the final output result, significantly improving the computational efficiency and accuracy for complex information processing. The physiological significance of distributed memory characteristics in primates serves as inspiration for the design of physical node devices with distributed reservoir states in the reservoir layer of the RC system. These devices are intended to facilitate the distributed mapping of spatiotemporal signals. However, to date, no such devices have been demonstrated.
In this work, inspired by the distributed memory characteristic of primates, an ultra-short channel organic neuromorphic vertical field effect transistor with distributed reservoir states is proposed and used to implement grouped-RC networks. By coupling multivariate physical mechanisms into a single device, the dynamic states of carriers are greatly enriched. As reservoir nodes, sequential signals can be mapped to a distributed reservoir state space by various carrier dynamics, rather than by monotonic carrier dynamics. Additionally, a vertical architecture with ultra-short nanometers transport distance is adopted to eliminate the driving force of the dissociation exciton, thereby improving the feedback strength of the device and the reducing the overlap between different reservoir state space, which only cause negligible additional power. Consequently, the device serves as a reservoir capable of mapping sequential signals into distributed reservoir state space with 1,152 reservoir states, and the range ratio of temporal (key parameters for prediction) and spatial characteristics (key parameters for recognition) can simultaneously reach 2,640 and 650, respectively, which are superior to the reported neuromorphic devices. Therefore, the grouped-RC network implemented based on the device can simultaneously meet the requirements of two different spatiotemporal types task (broad-spectrum image recognition and dynamic trajectory prediction) and exhibits over 94% recognition accuracy and over 95% prediction correlation, respectively. This work proposes a strategy for developing neural hardware for complex reservoir computing networks and has great potential in the development of a new generation of artificial neuromorphic hardware and brain-like computing.