Acute or short-lived pain, despite its bad reputation, is usually a lifesaver. It acts as a transient negative sensory experience that helps us avoid danger. Touch a hot stove, stub a toe, or bonk your head on a low branch, and the nervous system cues up an “Ow!” Over time, the sting fades, the wound heals, but the lesson sticks.
Chronic pain is different; the alarm keeps blaring long after the fire is out, and then the pain itself becomes the problem. Nearly 50 million people in the United States live with chronic pain, an invisible and often untreatable condition that can linger for decades. “It’s not just an injury that won’t heal,” says neuroscientist at the University of Pennsylvania J. Nicholas Betley, “it’s a brain input that’s become sensitized and hyperactive, and determining how to quiet that input could lead to better treatments.”
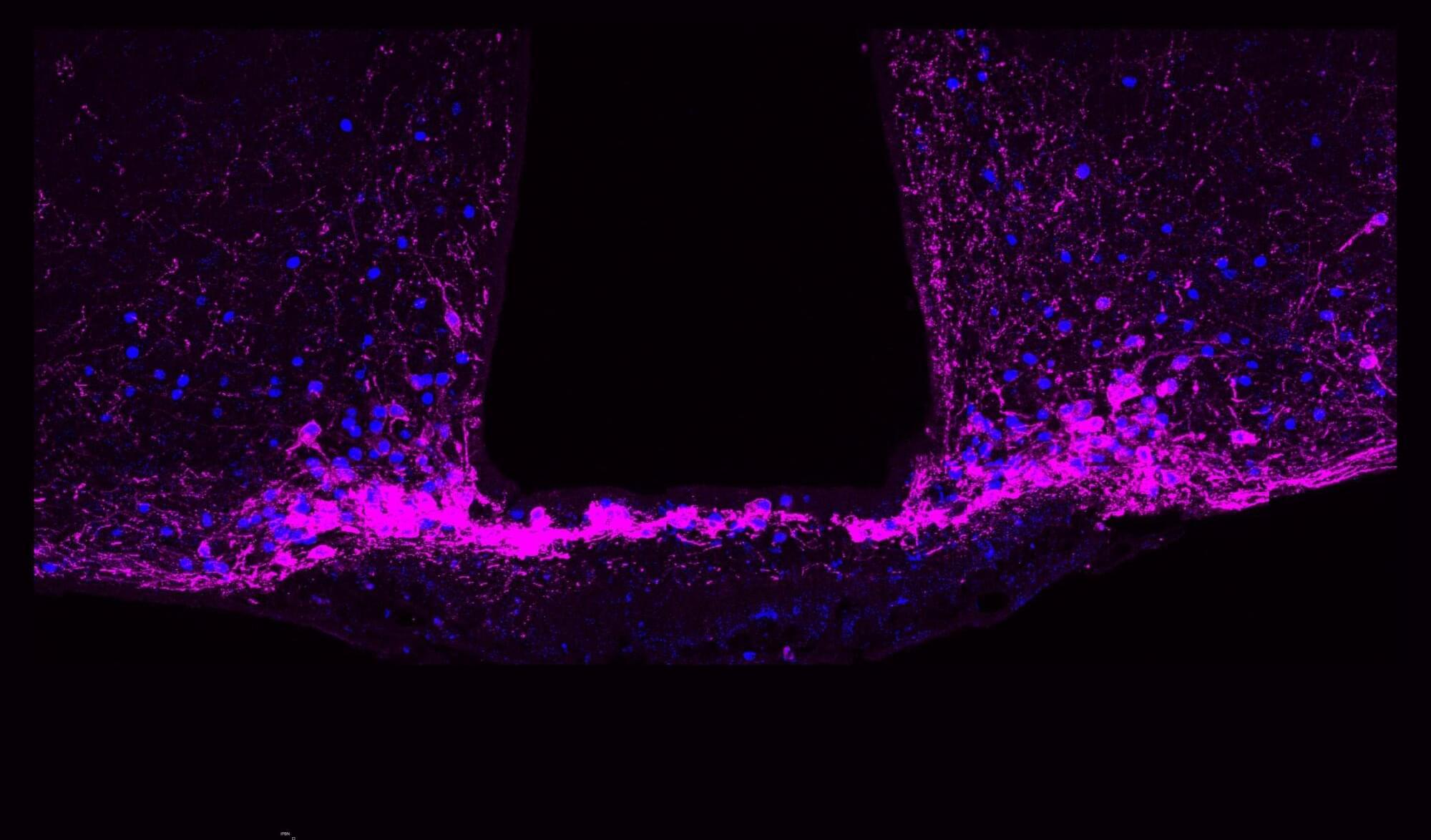
Now, research led by Betley and collaborators at the University of Pittsburgh and Scripps Research Institute has identified a key to regulating long-term pain states: a group of cells called Y1 receptor (Y1R)-expressing neurons in the brainstem’s lateral parabrachial nucleus (lPBN). These neurons are activated during enduring pain states, but they also integrate information about hunger, fear and thirst, allowing for pain signals to be modulated by other brain circuits signaling more urgent needs.