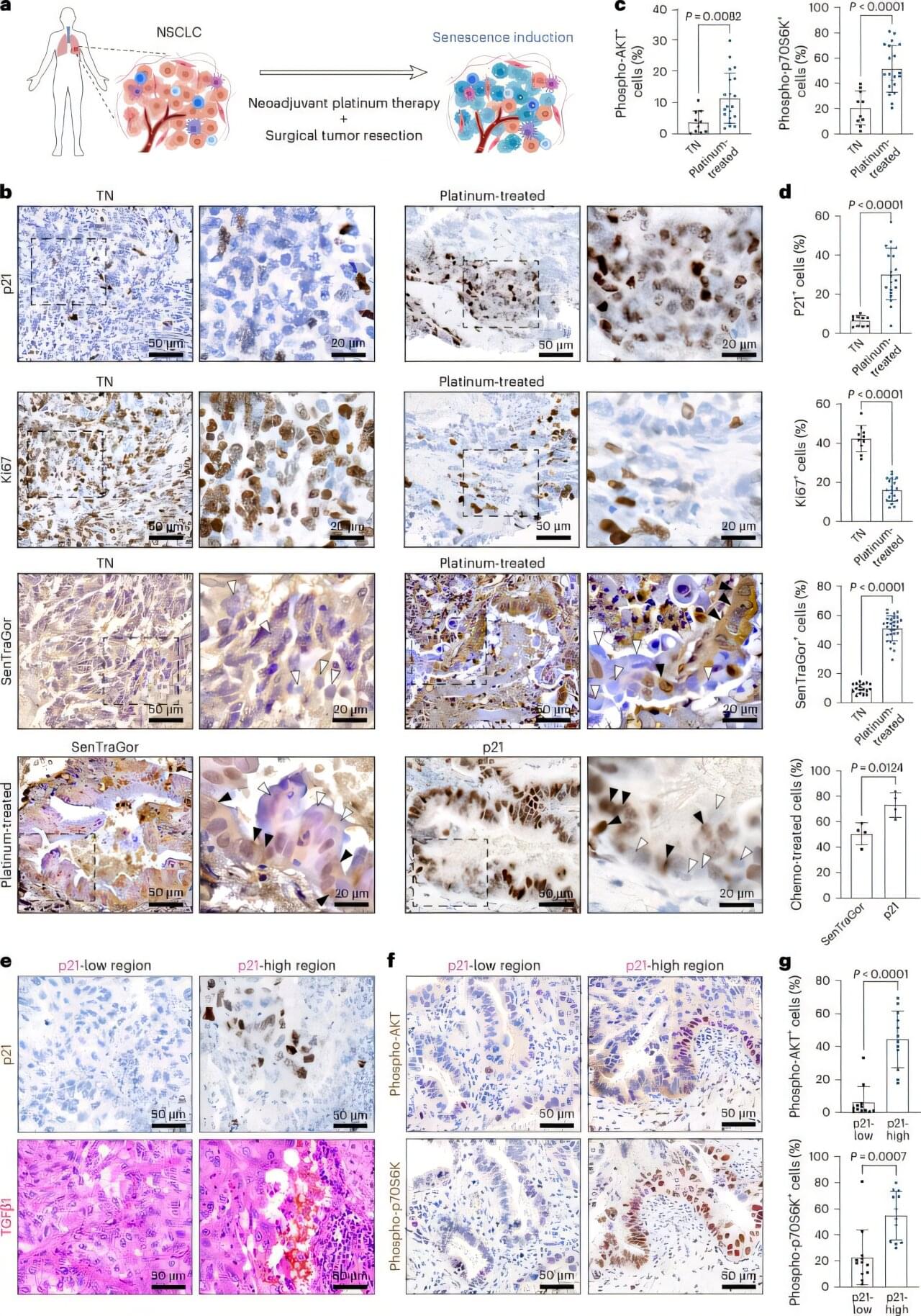
In a study published today, Friday, February 13, 2026, in the journal Nature Aging, researchers show that blood-based biomarkers can support accurate dementia diagnosis across diverse populations when integrated with cognitive and neuroimaging measures. Blood-based biomarkers are emerging as one of the most promising advances for the global diagnosis of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. These tests offer a more accessible, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional diagnostic tools such as brain imaging or cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
However, most blood-based biomarkers have been developed and validated primarily in relatively homogeneous populations. Genetic background, overall physical health, and environmental and social exposures can substantially influence biomarker levels, raising concerns about how well these tests perform across diverse populations worldwide.