Weaker and more fragmented circadian rest-activity rhythms and later peak activity time were associated with elevated dementia risk in this study.



Huang made his feelings about AI skeptics, haters, and doom-mongers clear on a recent episode of the No Priors podcast.
The boss of the world’s most valuable company said “the battle of the narratives” between those who think AI will benefit society and those who believe it will degrade or even destroy it was one of his biggest takeaways from 2025.
Huang did admit that “it’s too simplistic” to dismiss either of these views entirely, but he believes some naysayers’ views are having a detrimental effect.
This video explores aliens, mind uploading to other species, genetic engineering, and future robots.
SOURCES:
• https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eagle_eye#:~… https://www.scientificamerican.com/ar… • https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_c… ___ 💡 Future Business Tech explores the future of technology and the world. Examples of topics I cover include: • Artificial Intelligence & Robotics • Virtual and Augmented Reality • Brain-Computer Interfaces • Transhumanism • Genetic Engineering SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/3geLDGO ___ This video explores the future of ChatGPT and 10 ways it could change society. Other related terms: aliens, alien species, advanced civilization, genetic engineering, robot, mind upload, mind uploading, brain computer interface, artificial intelligence, ai, future business tech, future technology, future technologies, etc. ℹ️ Some links are affiliate links. They cost you nothing extra but help support the channel so I can create more videos like this. #alien #aliens #avatar #avatar2 #geneticengineering #braincomputerinterface.
• https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pe…
• https://www.scientificamerican.com/ar…
• https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_c…
💡 Future Business Tech explores the future of technology and the world.
Examples of topics I cover include:
• Artificial Intelligence & Robotics.
• Virtual and Augmented Reality.
• Brain-Computer Interfaces.
• Transhumanism.
• Genetic Engineering.
SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/3geLDGO
This video explores the future of ChatGPT and 10 ways it could change society. Other related terms: aliens, alien species, advanced civilization, genetic engineering, robot, mind upload, mind uploading, brain computer interface, artificial intelligence, ai, future business tech, future technology, future technologies, etc.

face_with_colon_three Year 2025
Dartmouth researchers conducted the first-ever clinical trial of a generative AI-powered therapy chatbot and found that the software resulted in significant improvements in participants’ symptoms, according to results published March 27 in NEJM AI.
People in the study also reported they could trust and communicate with the system, known as Therabot, to a degree that is comparable to working with a mental health professional.
The trial consisted of 106 people from across the United States diagnosed with major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, or an eating disorder. Participants interacted with Therabot through a smartphone app by typing out responses to prompts about how they were feeling or initiating conversations when they needed to talk.
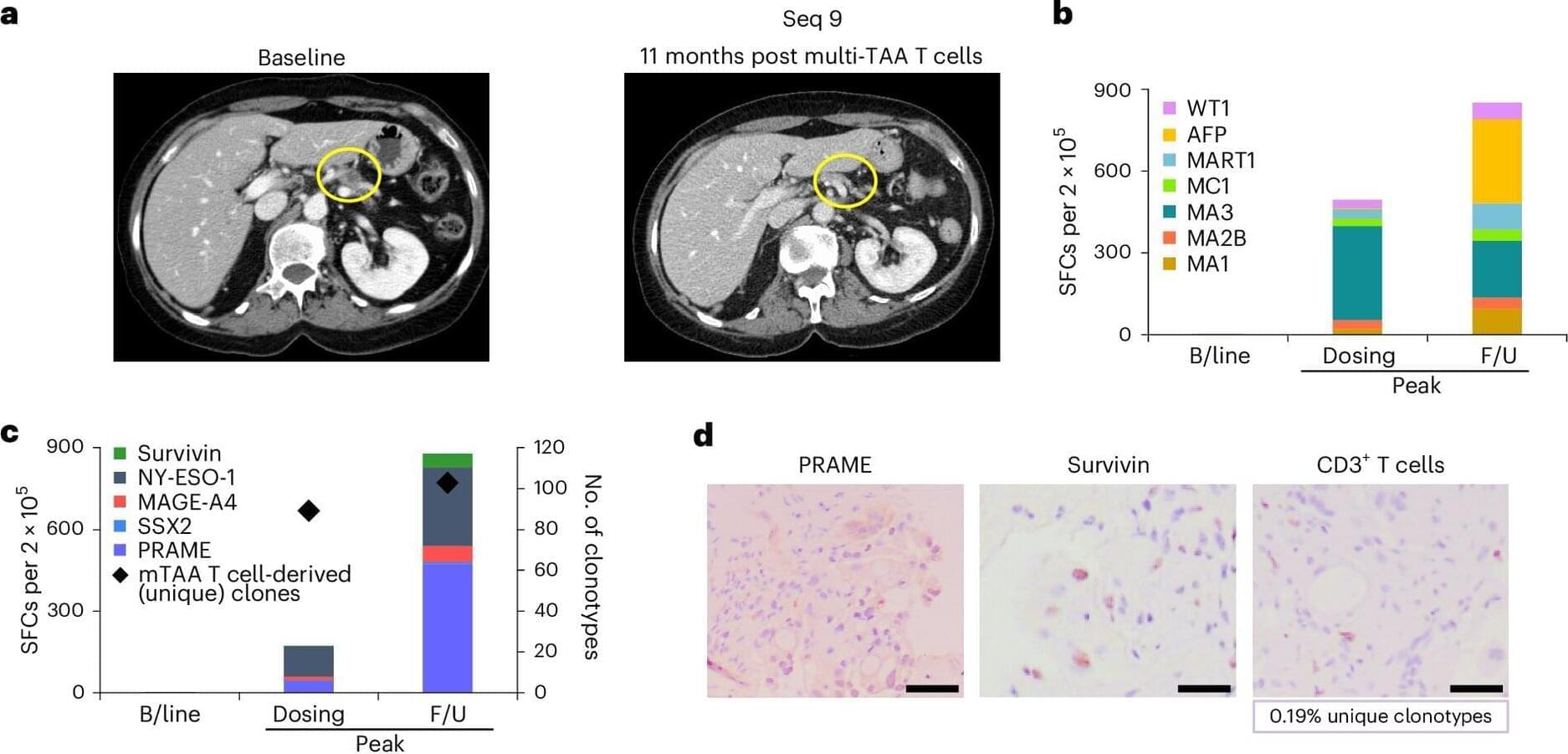
A recent publication in Nature Medicine describes a novel immunotherapy targeting pancreatic cancer that has shown promising results in a first in-human phase 1/2 trial.
The TACTOPS trial, which investigated the safety and clinical effects of autologous T cell therapy targeting multiple tumor antigens, was a collaboration among researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, the Dan L Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center, the Center for Cell and Gene Therapy, Texas Children’s Hospital and Houston Methodist Hospital.
“We wanted to develop a targeted therapeutic that would hone the immune system on tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) that were present on malignant cells. We targeted five different antigens to deal with the polyclonal nature of the disease,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Ann Leen, professor of pediatrics–hematology and oncology in the Center for Cell and Gene Therapy.

For this study, the researchers focused on a type of colorectal cancer that accounts for 80% to 85% of all colorectal cancers — microsatellite stable (MSS) with proficient mismatch repair (MMRp), meaning the tumors’ DNA is relatively stable. These cancers are largely resistant to checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapies.
Previous groundbreaking research found checkpoint inhibitors alone could successfully treat rectal cancer and several other cancers with the opposite tumor type — those with high microsatellite instability (MSI-H) and mismatch repair deficiency (MMRd). This allows doctors to spare many patients from surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
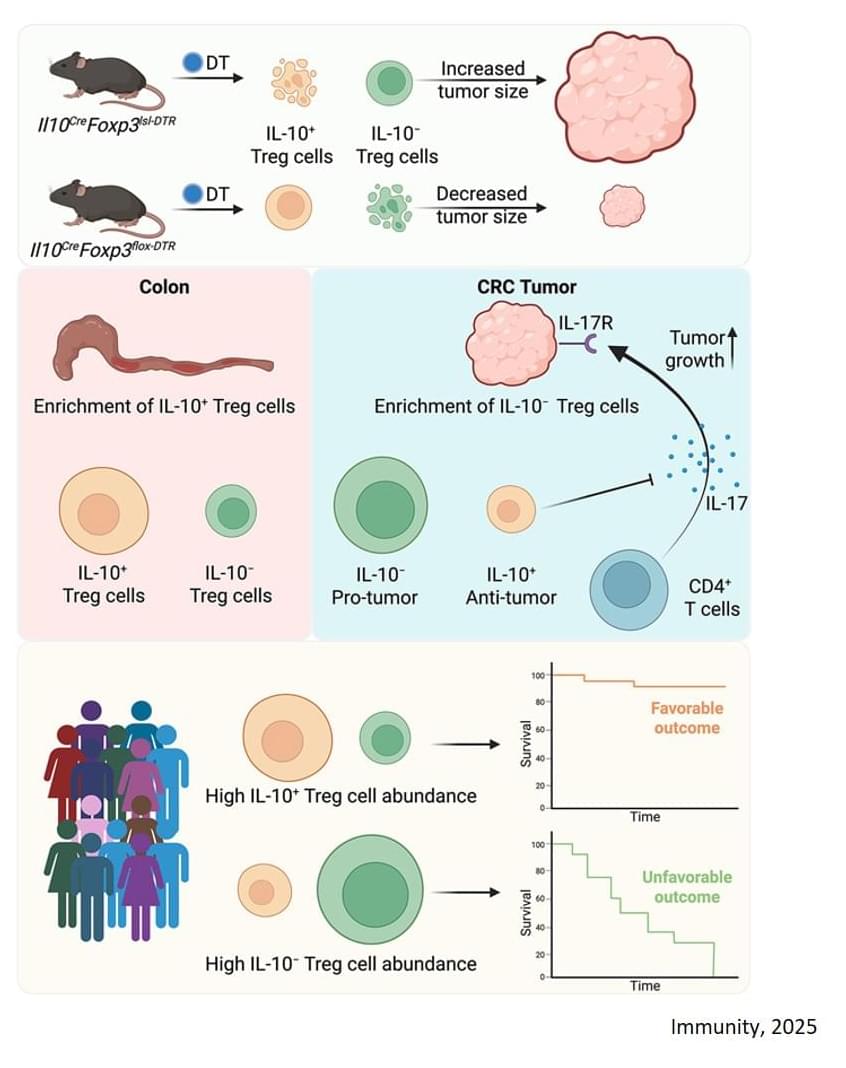
Here the team employed an mouse model that accurately recreates the common mutations, behaviors, and immune cell composition of human colorectal cancer. They found that the regulatory T cells associated with the cancer are split between two types: Cells that make a signaling molecule (cytokine) called interleukin‑10 (IL-10) and cells that don’t.
Through a series of sophisticated experiments that selectively eliminated each type of cell, the researchers discovered:
When IL-10-positive cells were removed, tumor growth accelerated.
In most solid tumors, high numbers of regulatory T (Treg) cells are associated with poorer outcomes because they dampen the immune system’s ability to fight against a tumor.

By Nina Bai
Stanford Medicine researchers recorded stem cells performing a previously unknown type of movement, dubbed cell tumbling, which may help them differentiate.
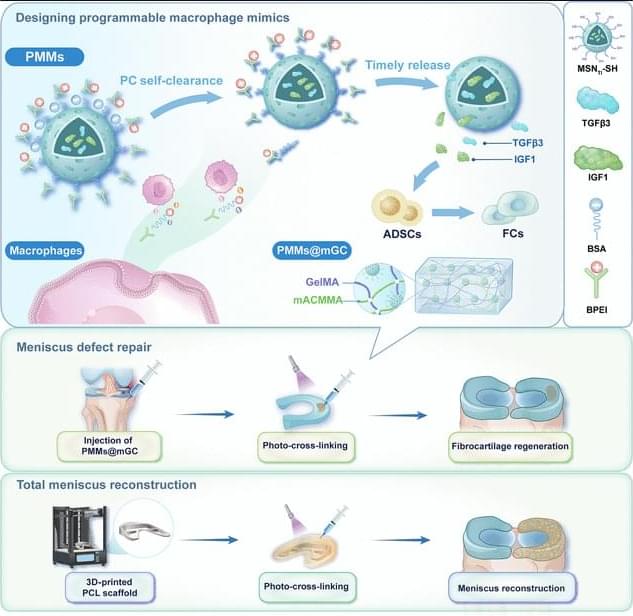
JUST PUBLISHED: programmable macrophage mimics for inflammatory meniscus regeneration via nanotherapy
Click here to read the latest free, Open Access Article from Research.
The meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous tissue and organ in the human knee joint that serves critical functions, including load transmission, shock absorption, joint stability, and lubrication. Meniscal injuries are among the most common knee injuries, typically caused by acute trauma or age-related degeneration [1– 3]. Minor meniscal injuries are usually treated with in situ arthroscopic procedures or conservative methods, whereas larger or more severe injuries often necessitate total meniscus replacement. Recent advances in materials science and manufacturing techniques have enabled transformative tissue-engineering strategies for meniscal therapy [4, 5]. Several stem cell types, including synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells, bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), have been investigated as candidate seed cells for meniscal regeneration and repair. Notably, ADSCs are clinically promising because of their ease of harvest, high inducibility, innate anti-inflammatory properties, and potential to promote fibrocartilage regeneration [6– 8]. Our group has developed a series of decellularized matrix scaffolds for auricular, nasal, tracheal, and articular cartilage repair using 3-dimensional (3D) bioprinting techniques, successfully repairing meniscus defects and restoring physiological function [9– 12]. However, current tissue-engineering strategies for meniscus defect repair commonly rely on a favorable regenerative microenvironment. Pathological conditions such as osteoarthritis (OA) [13 – 16], the most prevalent joint disorder, often create inflammatory environments that severely hinder meniscus regeneration [17 – 21]. Moreover, meniscal injury exacerbates the local inflammatory milieu, further impeding tissue healing and inevitably accelerating OA progression. Therefore, there is an urgent need to establish a cartilaginous immune microenvironment that first mitigates early-stage inflammation after meniscal injury and then sequentially promotes later-stage fibrocartilage regeneration [22 – 25].
Currently, targeted regulation using small-molecule drug injections is commonly employed to treat inflammatory conditions in sports medicine [26,27]. Most of these drugs exhibit broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory effects and inevitably cause varying degrees of side effects by activating nonspecific signaling pathways. Polyethyleneimine is a highly cationic polymer. It is widely used to modulate inflammation by adsorbing and removing negatively charged proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), via electrostatic interactions [28–31]. Notably, modifying polyethyleneimine into its branched form (branched polyethyleneimine [BPEI]) has been shown to improve cytocompatibility and enhance in vivo metabolic cycling.