New vaccine platforms are being developed that could transform access and ease of use for future pandemics, as well as for fighting existing diseases.
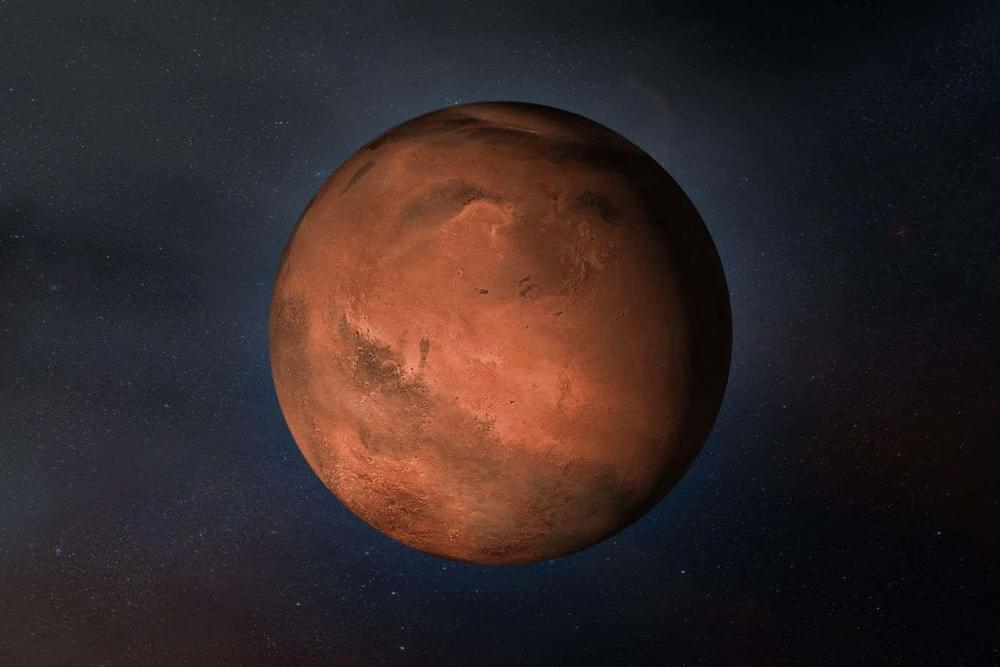



Seems like there was water on Mars, for those that subscribe or want to, you can read the whole article.
A large formation near the equator of Mars is now thought to be made of water ice, which could indicate that the Martian climate went through huge temperature swings in the past.
By Leah Crane

“Measles is extremely contagious and there has been an increase in measles cases around the world (with a million more measles cases reported in 2022 than 2021 by the WHO) due to setbacks in measles vaccination rates during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Dr. Monica Gandhi, MPH, a professor of medicine at the University of California San Francisco’s Division of HIV, Infectious Diseases, and Global Medicine, told Healthline. “Members of the public are at risk if they have not been vaccinated (which usually happens in childhood) so the larger population need not be concerned if vaccinations are kept up to date.”
In the last half of 2023, there were more than 20,000 cases of measles in Yemen, the country with the leading outbreak. This is an indicator that without widespread immunity or vaccination, the virus can spread widely, Dr. Tina Tan, an attending physician at Division of Infectious Diseases at the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, told Healthline.
“There are multiple countries around the world where measles is endemic and circulates widely in the community,” Tan said. “With international travel on the increase, unimmunized individuals are getting exposed to measles in the foreign countries that they are visiting, they are getting sick and exposing unimmunized, under immunized and persons that are too young to be immunized or who are unable to be immunized for medical reasons to measles. This has been reported on a number of occasions where exposure is occurring on airplanes, in airports or in the unimmunized person’s community.”
My people.
The Picts, a people who inhabited Scotland during the Middle Ages, have always had a sense of mystery to them. A new study using DNA has revealed new details about their origins.
Historical sources first mention the Picts in the late 3rd century AD. They resisted the Romans and ruled over a large territory in northern Britain. However, around the 9th and 10th centuries the Pictish culture would decline and those lands would form into what would be the medieval kingdom of Scotland. There are different theories to the origins – were the Picts native to Britain or did they migrate from other parts of Europe?

Of all the organisms that photosynthesize, land plants have the most complex bodies. How did this morphology emerge? A team of scientists led by the University of Göttingen has taken a deep dive into the evolutionary history of morphological complexity in streptophytes, which include land plants and many green algae.
The team’s research allowed them to go back in time to investigate lineages that emerged long before land plants existed. Their results revise the understanding of the relationships of a group of filamentous algal land colonizers much older than land plants. Using modern gene sequencing data, researchers pinpoint the emergence of multicellularity to almost a billion years ago. The results were published in the journal Current Biology.
The study focused on Klebsormidiophyceae, a class of green algae known for its ability to colonize diverse habitats worldwide. The team of researchers conducted extensive sampling, investigating habitats ranging from streams, rivers, and lake shores to bogs, soil, natural rocks, tree bark, acidic post-mining sites, sand dunes, urban walls, and building façades.
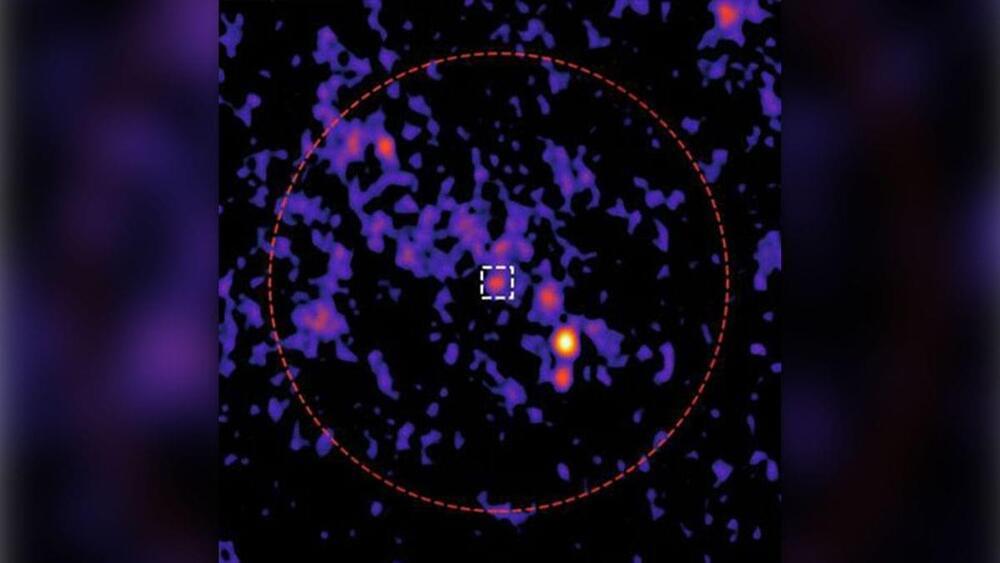

Astronomers have discovered a mysterious radio signal at the heart of an ancient, tightly packed ball of stars, and it may be coming from a long-hidden black hole.
The radio signal was picked up by the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) radio telescope as it created the most sensitive image of a globular cluster — a clump of ancient stars like these — ever taken. The ball of stars in question, named 47 Tucanae, is the second-brightest globular cluster in the sky over Earth and is located around 13,000 light-years from our planet.
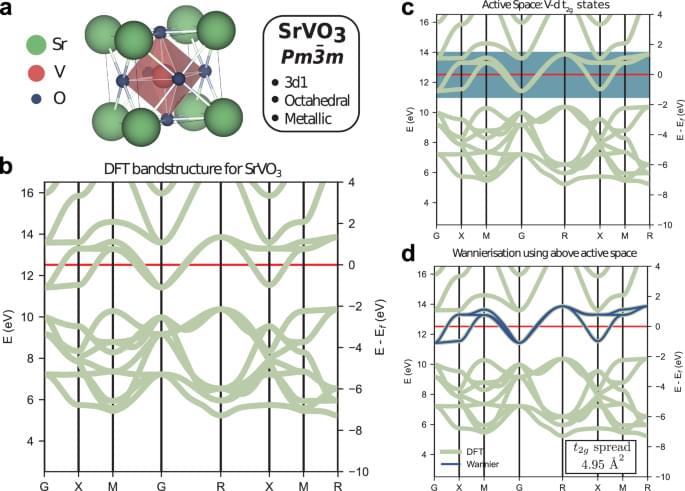
The use of NISQ devices for useful quantum simulations of materials and chemistry is still mainly limited by the necessary circuit depth. Here, the authors propose to combine classically-generated effective Hamiltonians, hybrid fermion-to-qubit mapping and circuit optimisations to bring this requirement closer to experimental feasibility.