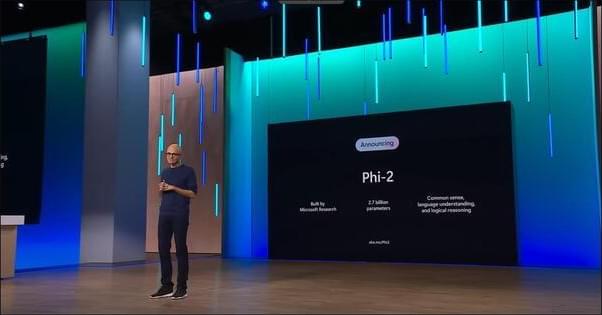
Microsoft research releases Phi-2 and promptbase.
Phi-2 outperforms other existing small language models, yet it’s small enough to run on a laptop or mobile device.
Over the past few months, our Machine Learning Foundations team at Microsoft Research has released a suite of small language models (SLMs) called “Phi” that achieve remarkable performance on a variety of benchmarks. Our first model, the 1.3 billion parameter Phi-1 (opens in new tab), achieved state-of-the-art performance on Python coding among existing SLMs (specifically on the HumanEval and MBPP benchmarks). We then extended our focus to common sense reasoning and language understanding and created a new 1.3 billion parameter model named Phi-1.5 (opens in new tab), with performance comparable to models 5x larger.
We are now releasing Phi-2 (opens in new tab), a 2.7 billion-parameter language model that demonstrates outstanding reasoning and language understanding capabilities, showcasing state-of-the-art performance among base language models with less than 13 billion parameters. On complex benchmarks Phi-2 matches or outperforms models up to 25x larger, thanks to new innovations in model scaling and training data curation.
With its compact size, Phi-2 is an ideal playground for researchers, including for exploration around mechanistic interpretability, safety improvements, or fine-tuning experimentation on a variety of tasks. We have made Phi-2 (opens in new tab) available in the Azure AI Studio model catalog to foster research and development on language models.