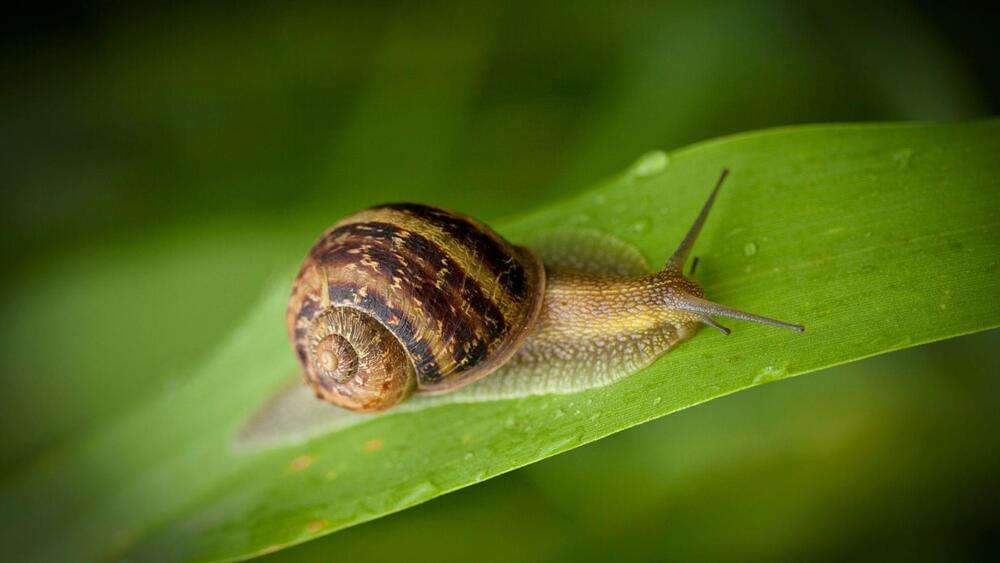
Researchers emulate snail-like movement in robots, a significant leap in bio-inspired engineering that could shape the future of robotics.



The Wave House took a mere 140 hours to be printed.
Researchers unveil live reinforcement learning-based whole-body humanoid teleoperation system, promising significant advancements.
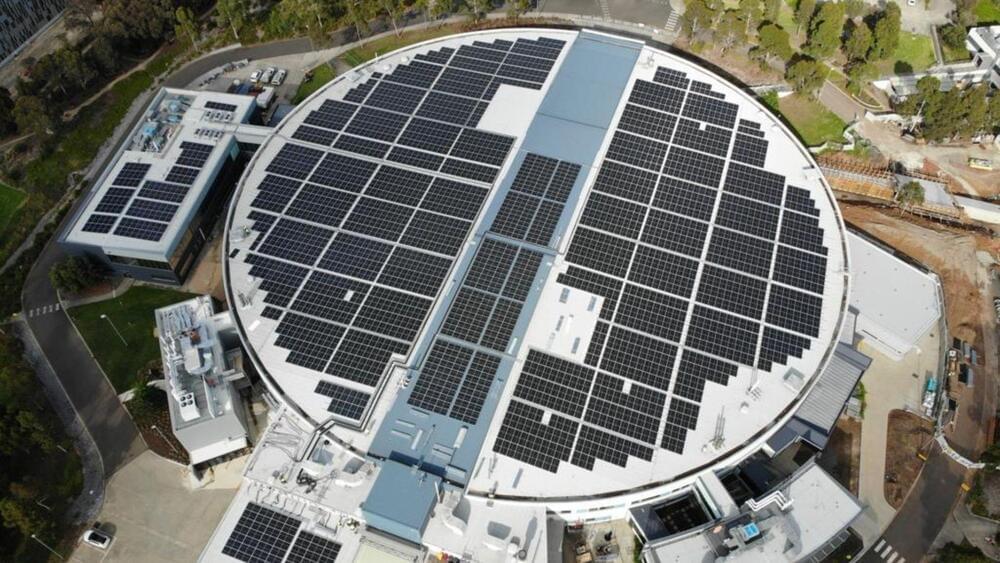

The Australian Synchrotron, a crown jewel of Australian scientific infrastructure, is making major strides towards sustainable energy independence. The nuclear research facility recently completed the installation of 3,200 solar panels which now blankets the facility’s rooftops. This move is expected to generate substantial savings and support Synchrotron’s world-class research.
The state-of-the-art particle accelerator has now gone green with a 1.59 MW/ 1,668 kWh rooftop solar system. The facility will save about $2 million in energy costs over the next five years.
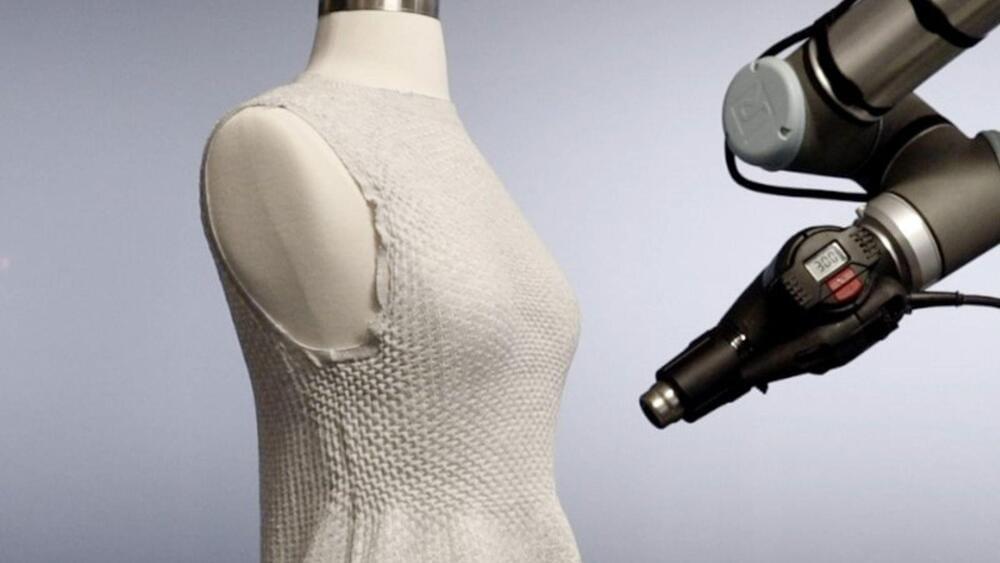

Imagine a dress that doesn’t just fit you perfectly – it morphs along with your style, body, and the shifting trends of the season. It sounds futuristic, but this ‘smart’ garment exists thanks to a collaboration between textile innovators at MIT and a forward-thinking fashion house. It makes sustainable fashion more innovative.
Traditionally, bespoke tailoring—making clothes to a customer’s measurements—was the only way to ensure a perfect fit for one’s body. However, this option was too expensive for most people. A new invention of active fibers and innovative knitting processes is making custom clothing more accessible and eco-friendly.
This is a sci-fi documentary, looking at what it takes to build an underground city on Mars. The choice to go underground is for protection, from the growing storm radiation that rains down on the surface every day. And to further advance the Mars colonization efforts.
Where will the materials to build the city come from? How will the crater be covered to protect the inhabitants? And what will it feel like to live in this city, that is in a hole in the ground?
It is a dream of building an advanced Mars colony, and showing the science and future space technology needed to make it happen.
Personal inspiration in creating this video comes from: The Expanse TV show and books, and The Martian.
Other topics in the video include: the plan and different phases of construction, the robots building the city, structures that are on the surface versus below the surface, pressurizing a habitat on Mars, the soil and how to turn it in Martian concrete, the art of terraforming, and the different materials that can be extracted from the planet. And the future plans of the Mars colony, from building upwards to venturing to the asteroid belt and Jupiter’s 95 moons.
PATREON