Researchers found that adolescents treated with the antibiotic doxycycline were ~30% less likely to develop schizophrenia as adults. The findings suggest that targeting brain inflammation could help reduce the future risk of severe mental illness.


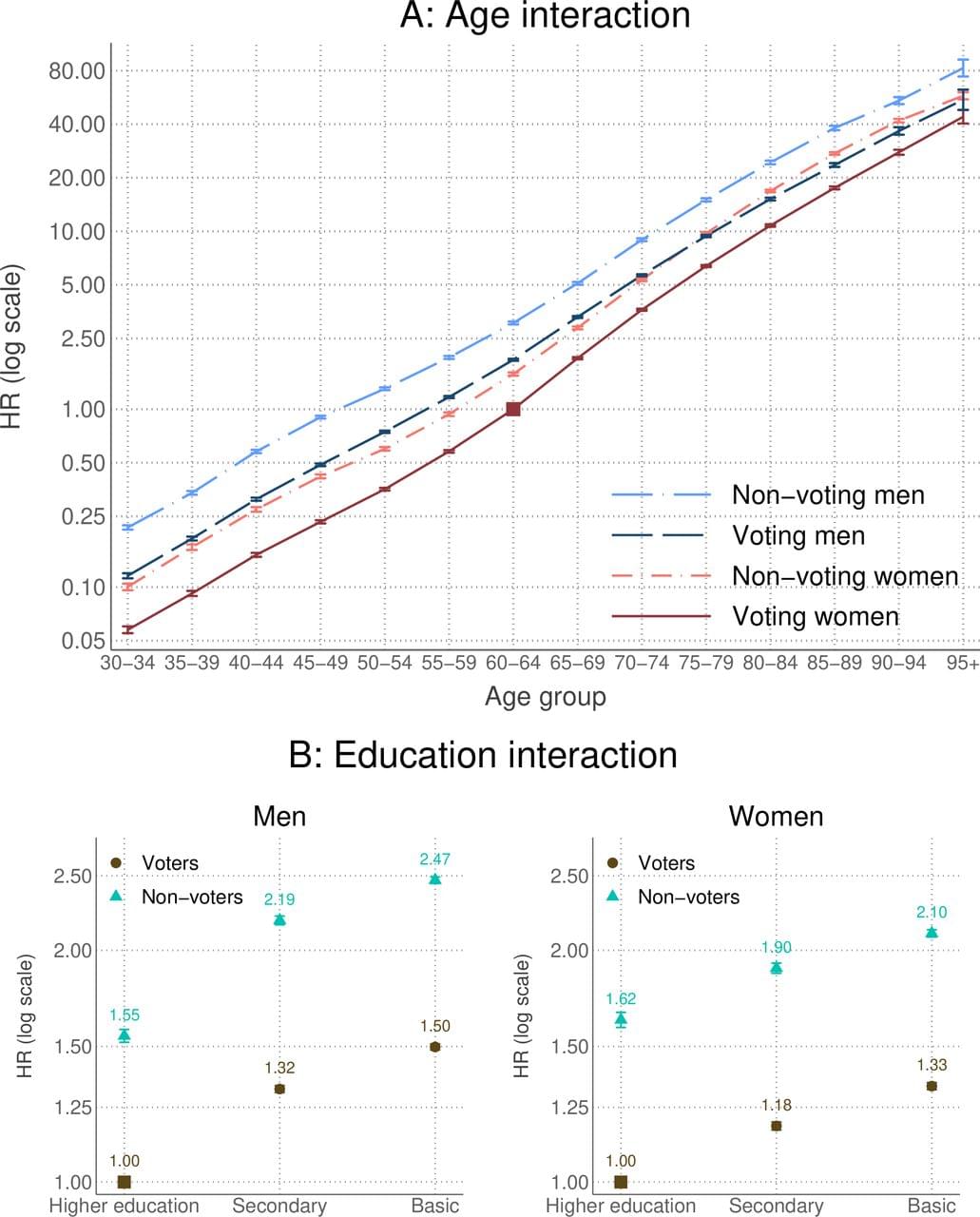
Background Although voting is recognised as a social determinant of health, the association between electoral participation and subsequent mortality at an individual level has not been established.
Objective To assess whether voters and non-voters differ in mortality risk.
Methods We used register-based information on electoral participation in the 1999 parliamentary elections from the full electorate of at least 30-year-old Finnish citizens living in mainland Finland linked to registers containing sociodemographic and mortality information by Statistics Finland. Mortality was assessed with Cox proportional hazards regression models, with follow-up until the end of 2020 (n=3 185 572 individuals; 58 133 493 person-years; 1 053 483 deaths).
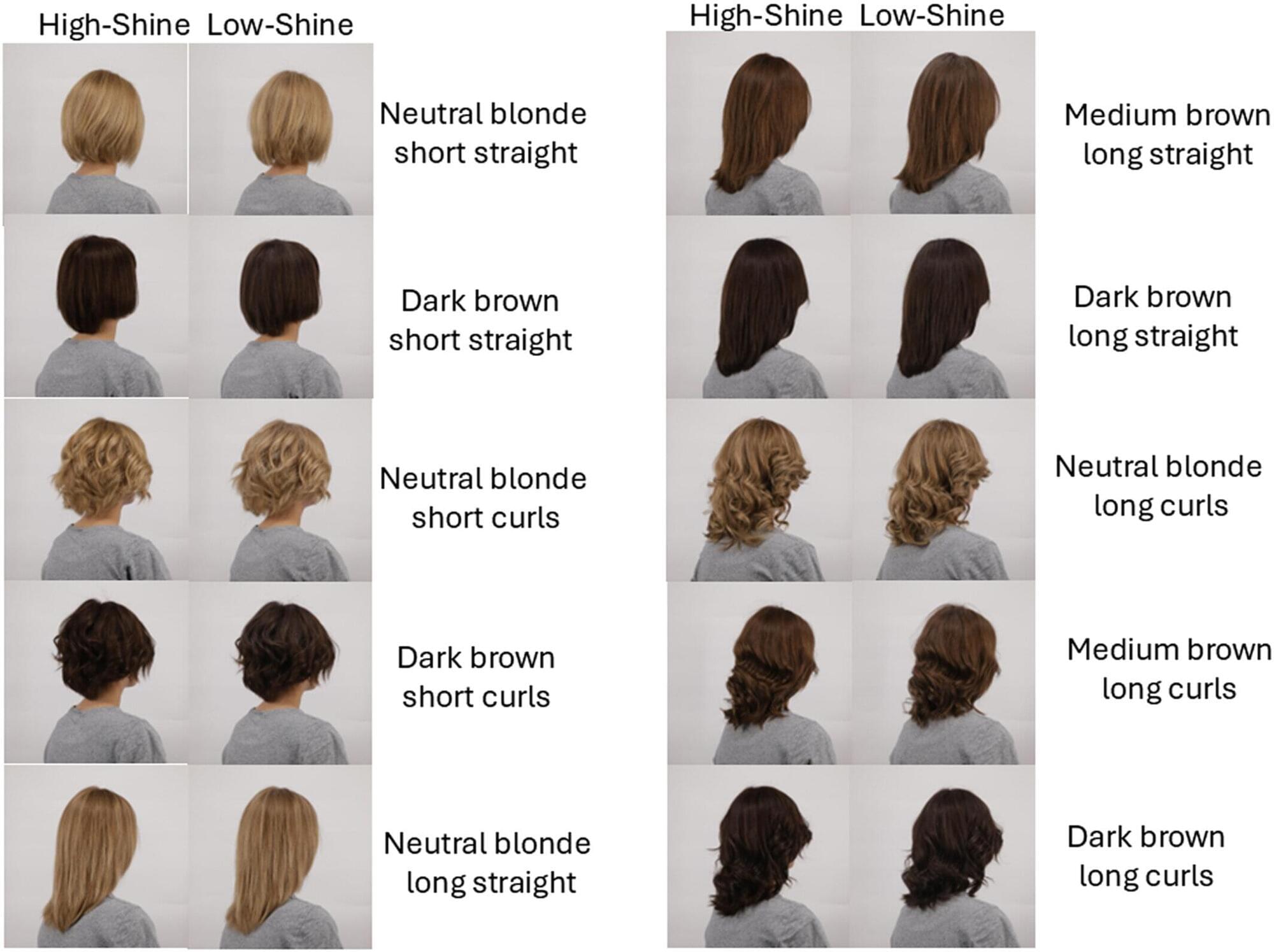

Straight-aligned hair paired with higher shine evokes the appearance of greater youth, health, and attractiveness, according to researchers at The Procter & Gamble Company, which owns several brands of hair care products, including ones designed to make hair shinier.
Studies on appearance often center on facial shape and skin condition. Previous studies also note that skin topography and coloration can influence judgments of age, health, and attractiveness across populations. Facial studies often remove hair cues to avoid biasing feature focused framing of perception.
Hair holds social cues that observers can read quickly. Work with computer-rendered hair has tied diameter, density, style, and color to shifts in perceived age, health, and attractiveness, and some studies previously associated healthier-looking hair with the appearance of better reproductive health.
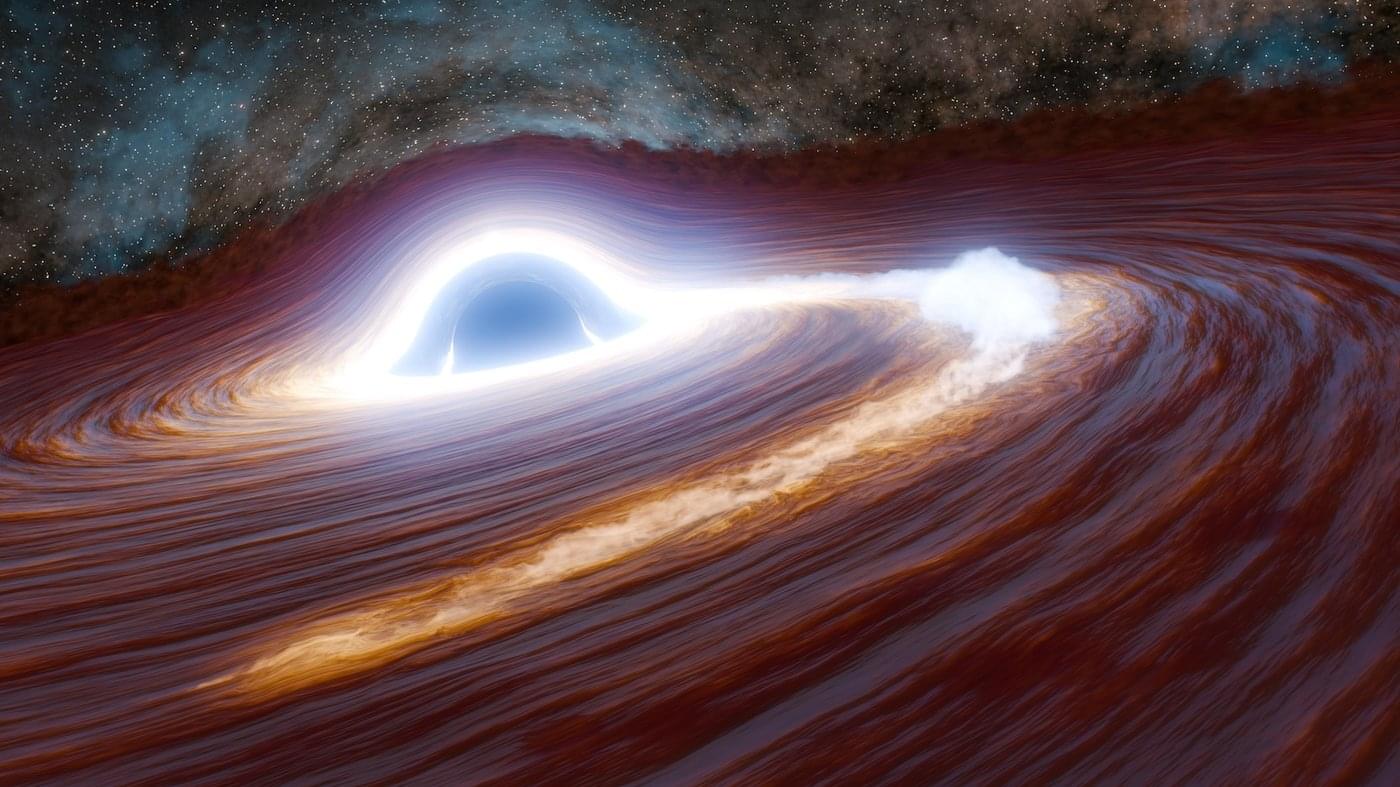

The most massive stars in the universe are destined to explode as brilliant supernova before collapsing into black holes. Yet one huge star appears to have never fulfilled its destiny; in a twist of irony, the star wandered too close to a gargantuan black hole, which gobbled it up, shredding the star to bits and pieces.
That is the most likely explanation to come from authors of a new study published in Nature Astronomy describing the most powerful and most distant flare of energy ever recorded from a supermassive black hole.
The cosmic object was first observed in 2018 by the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF), based at Caltech’s Palomar Observatory, and the Caltech-led Catalina Real-Time Transient Survey. The flare rapidly brightened by a factor of 40 over a period of months, and, at its peak, was 30 times more luminous than any previous black hole flare seen to date. At its brightest, the flare shined with the light of 10 trillion suns.
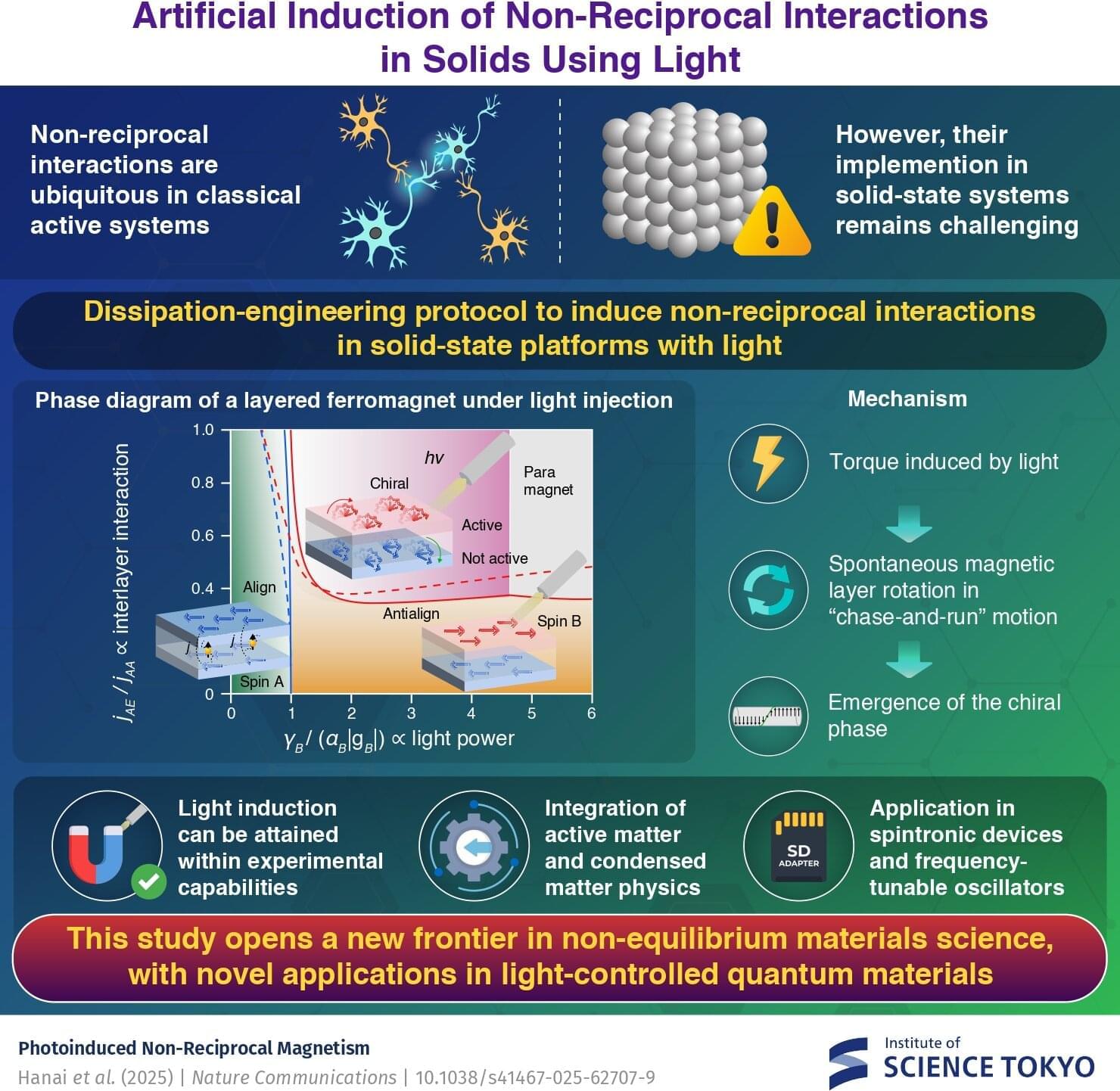
A theoretical framework predicts the emergence of non-reciprocal interactions that effectively violate Newton’s third law in solids using light, report researchers from Japan. They demonstrate that by irradiating light of a carefully tuned frequency onto a magnetic metal, one can induce a torque that drives two magnetic layers into a spontaneous, persistent “chase-and-run” rotation. This work opens a new frontier in non-equilibrium materials science and suggests novel applications in light-controlled quantum materials.
In equilibrium, physical systems obey the law of action and reaction as per the free energy minimization principle. However, in non-equilibrium systems such as biological or active matter—interactions that effectively violate this law—the so-called non-reciprocal interactions are common.
For instance, the brain comprises inhibitory and excitatory neurons that interact non-reciprocally; the interaction between predator and prey is asymmetric, and colloids immersed in an optically active media demonstrate non-reciprocal interactions as well. A natural question arises: Can one implement such non-reciprocal interaction in solid-state electronic systems?
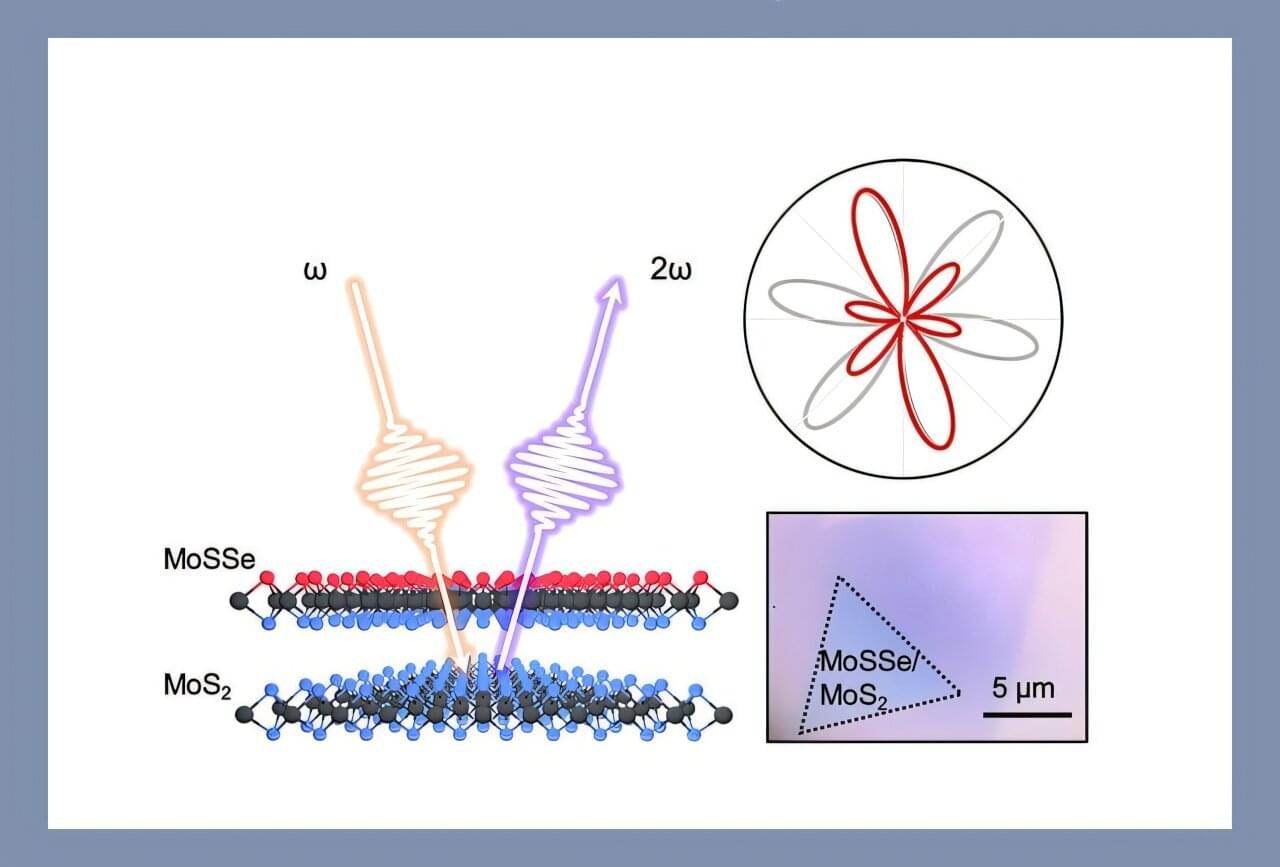
Rice University researchers studying a class of atom-thin semiconductors known as transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have discovered that light can trigger a physical shift in their atomic lattice, creating a tunable way to adjust the materials’ behavior and properties.
The effect, observed in a TMD subtype named after the two-faced Roman god of transitions, Janus, could advance technologies that use light instead of electricity, from faster and cooler computer chips to ultrasensitive sensors and flexible optoelectronic devices.
“In nonlinear optics, light can be reshaped to create new colors, faster pulses or optical switches that turn signals on and off,” said Kunyan Zhang, a Rice doctoral alumna who is a first author on a study documenting the effect. “Two-dimensional materials, which are only a few atoms thick, make it possible to build these optical tools on a very small scale.”
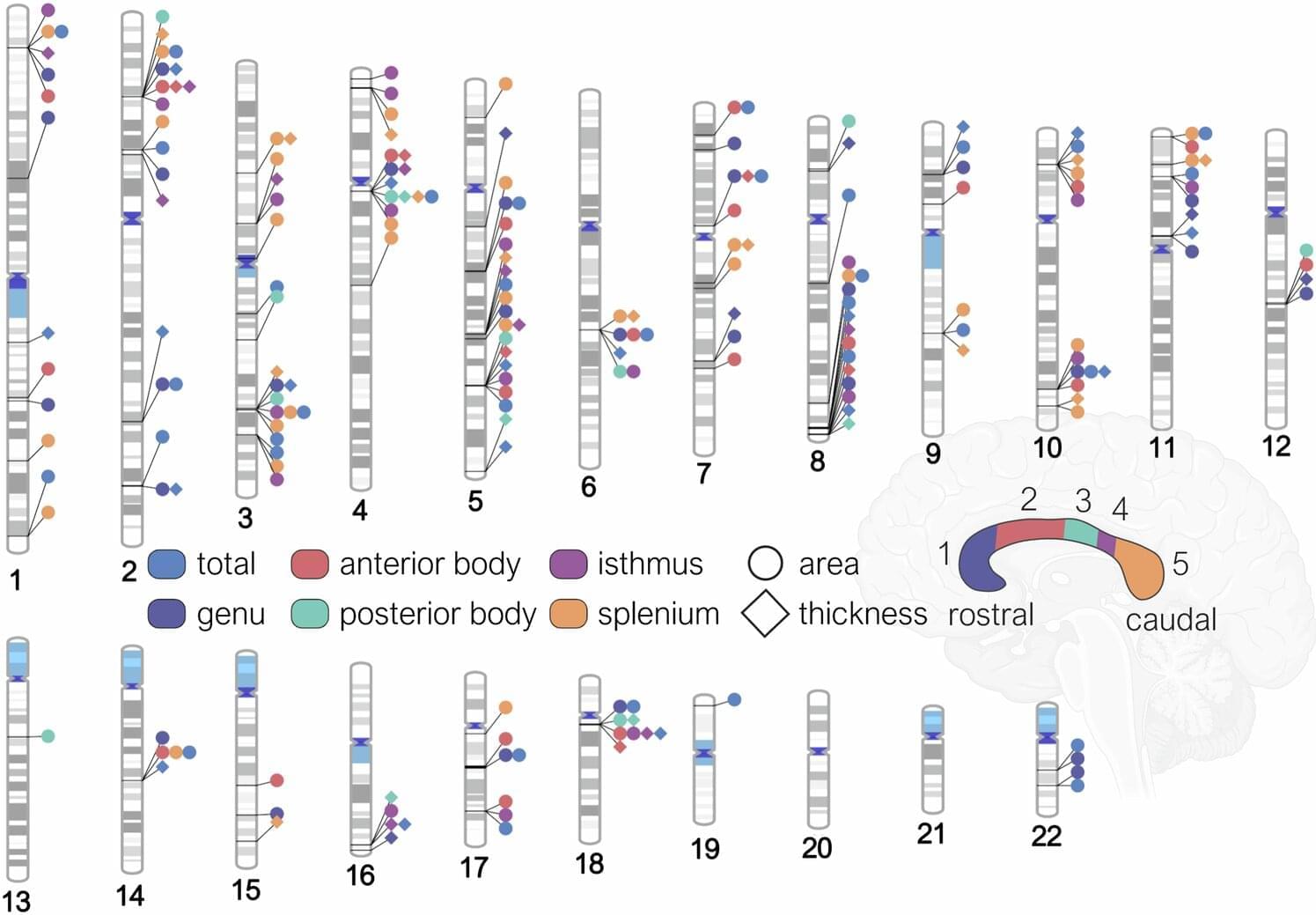
For the first time, a research team led by the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute (Stevens INI) at the Keck School of Medicine of USC has mapped the genetic architecture of a crucial part of the human brain known as the corpus callosum—the thick band of nerve fibers that connects the brain’s left and right hemispheres. The findings open new pathways for discoveries about mental illness, neurological disorders and other diseases related to defects in this part of the brain.
The corpus callosum is critical for nearly everything the brain does, from coordinating the movement of our limbs in sync to integrating sights and sounds, to higher-order thinking and decision-making. Abnormalities in its shape and size have long been linked to disorders such as ADHD, bipolar disorder, and Parkinson’s disease. Until now, the genetic underpinnings of this vital structure had remained largely unknown.
In the new study, published in Nature Communications, the team analyzed brain scans and genetic data from over 50,000 people, ranging from childhood to late adulthood, with the help of a new tool the team created that leverages artificial intelligence.
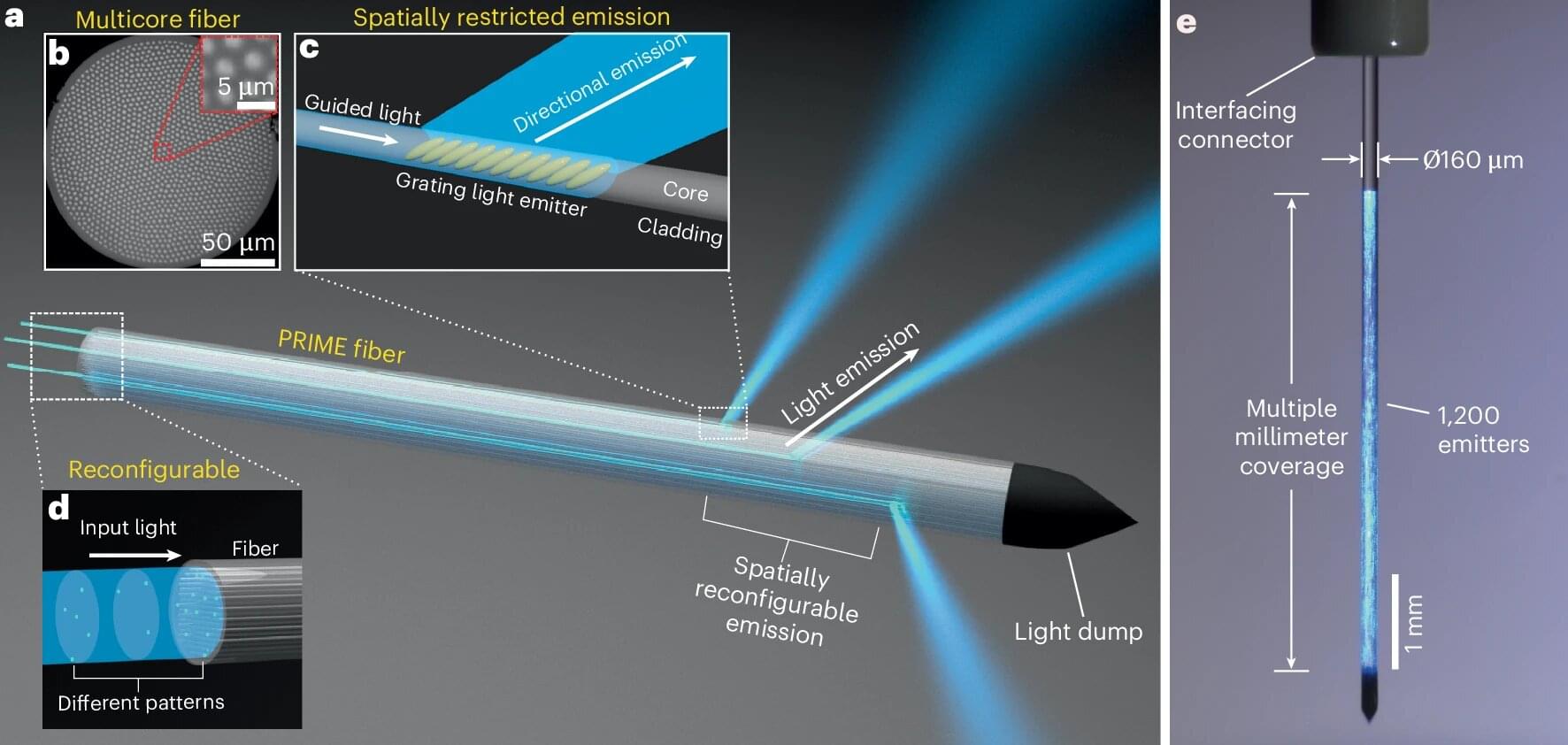
Fiber-optic technology revolutionized the telecommunications industry and may soon do the same for brain research.
A group of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis in both the McKelvey School of Engineering and WashU Medicine have created a new kind of fiber-optic device to manipulate neural activity deep in the brain. The device, called PRIME (Panoramically Reconfigurable IlluMinativE) fiber, delivers multi-site, reconfigurable optical stimulation through a single, hair-thin implant.
“By combining fiber-based techniques with optogenetics, we can achieve deep-brain stimulation at unprecedented scale,” said Song Hu, a professor of biomedical engineering at McKelvey Engineering, who collaborated with the laboratory of Adam Kepecs, a professor of neuroscience and of psychiatry at WashU Medicine.
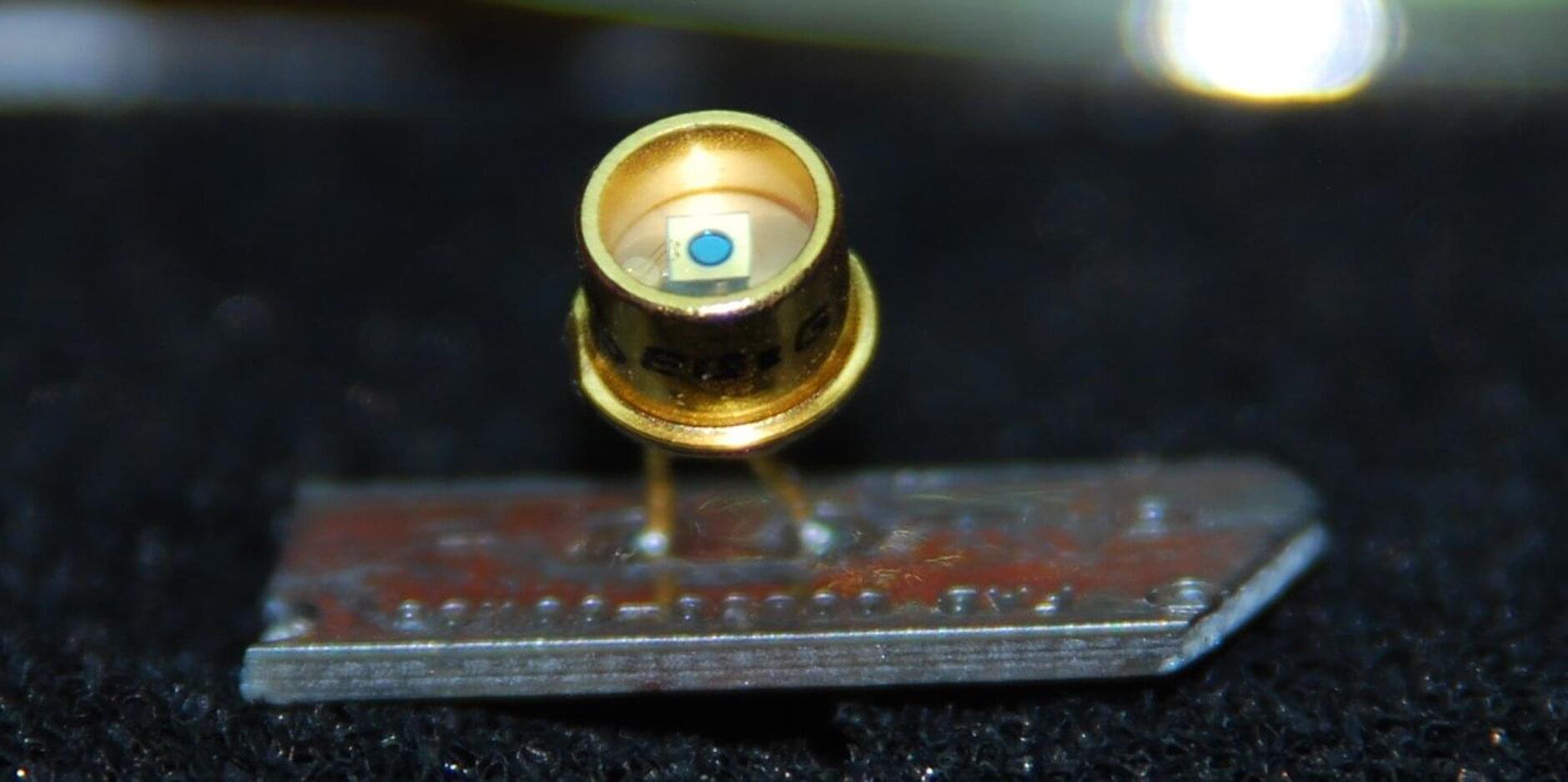
Geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes (GM-APDs) are highly sensitive light detectors, capable of detecting single photons. Photons of certain wavelengths, when absorbed by photodiodes, generate electron-hole pairs in a process called impact ionization which can result in a multiplication of charges when occurring in an electric field.
An avalanche photodiode is biased above its “breakdown voltage,” at which point impact ionizations reach a self-sustaining rate, resulting in a distinct electrical pulse that is readily detectable. To detect single photons in the presence of other mechanisms that generate impact ionization, the avalanche diode must simultaneously have a high probability to absorb incident photons of the desired wavelength, known as the unity-gain quantum efficiency (QE). Both being able to support high fields and having good QE at the desired wavelength are critical factors in determining the device’s sensitivity.
Certain GM-APDs based on 4H-silicon carbide (4H-SiC) have high single-photon detection efficiency in the deep-ultraviolet (DUV) wavelengths around 280 nanometers. To reliably detect photons at higher wavelengths where absorption is weaker, SiC GM-APDs need to improve their baseline photon capture efficiency, as indicated by its unity-gain QE. To accomplish this, researchers often employ APDs with much thicker absorber layers. However, this can often lead to design challenges.
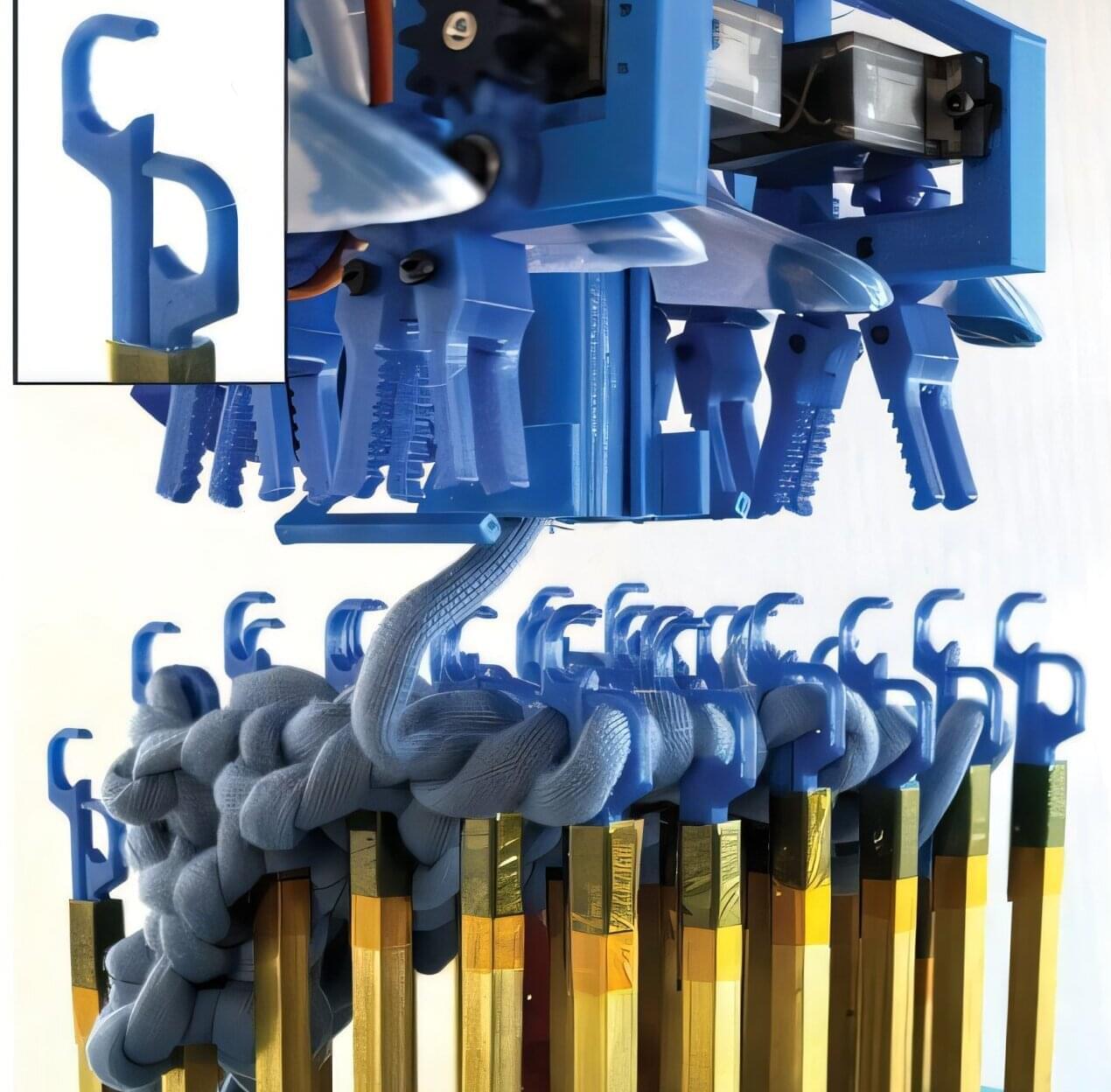
A new prototype of a knitting machine creates solid, knitted shapes, adding stitches in any direction—forward, backward and diagonal—so users can construct a wide variety of shapes and add stiffness to different parts of the object.
Unlike traditional knitting, which yields a 2D sheet of stitches, this proof-of-concept machine—developed by researchers at Cornell University and Carnegie Mellon University—functions more like a 3D printer, building up solid shapes with horizontal layers of stitches.
“We establish that not only can it be done, but because of the way we attach the stitch, it will give us access to a lot of flexibility about how we control the material,” said François Guimbretière, professor of information science at Cornell. “The expressiveness is very similar to a 3D printer.”