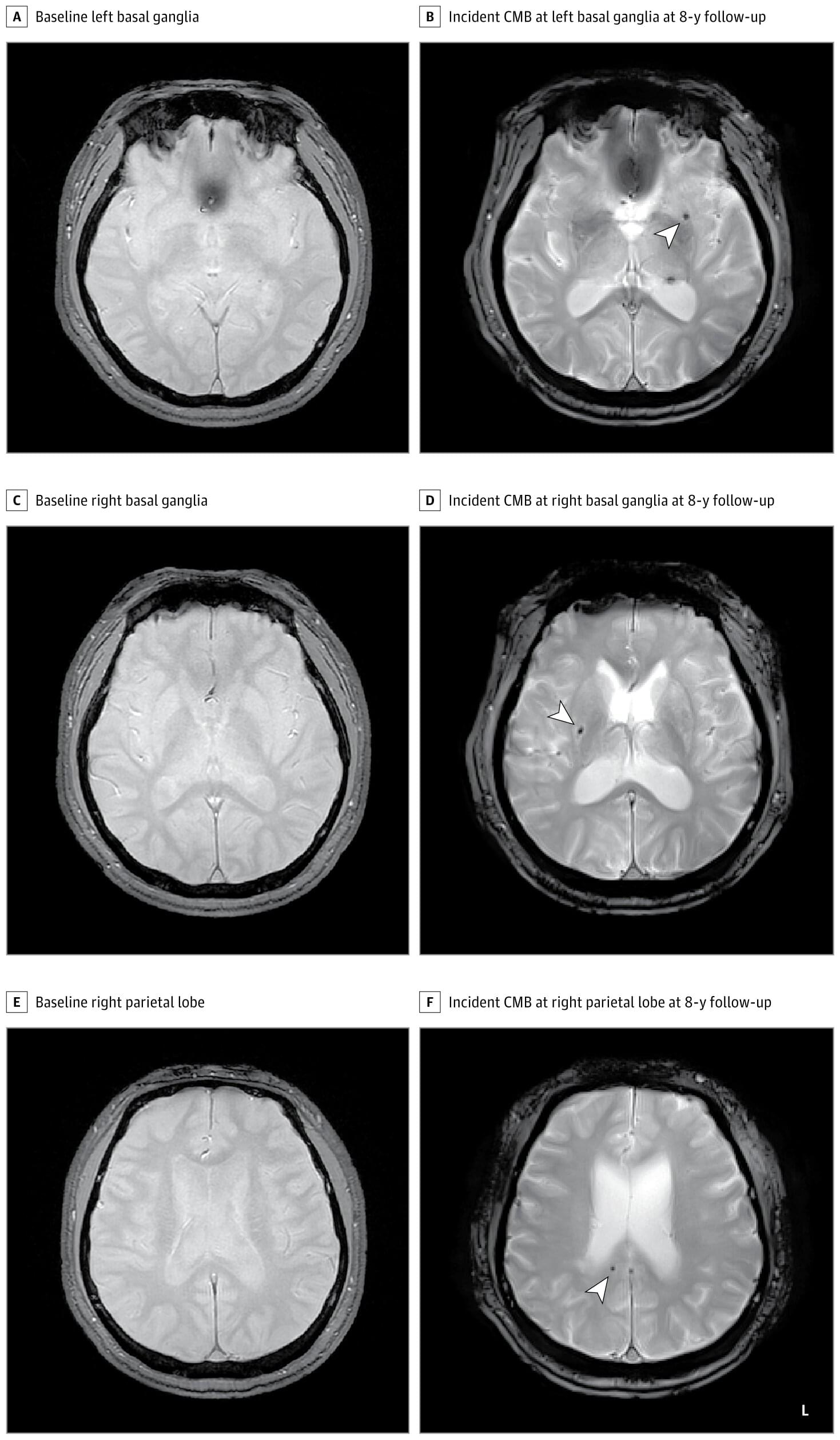
Research led by Korea University Ansan Hospital reports finding an association between moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of cerebral microbleeds.
Cerebral microbleeds appear as small lesions on MRI scans and are regarded as early markers of brain damage. Links with symptomatic stroke and dementia have been well documented, with prevalence ranging from 3% in middle age to 23% in older adults.
Known modifiable factors include smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and cardiocerebrovascular disease. Previous studies probing sleep apnea and microbleeds have yielded mixed results, suggesting the need for more comprehensive study.