Exercise for a long period of time forces the human body to resort to its energy reserves. When running a marathon, for example, the body mainly consumes carbohydrates, such as glycogen, as a source of energy, but it resorts to fats when the glycogen in the muscles is used up. Myelin, which surrounds neurons in the brain and acts as an electrical insulator, mainly comprises lipids, and previous research in rodents suggests that these lipids can act as an energy reserve in extreme metabolic conditions.
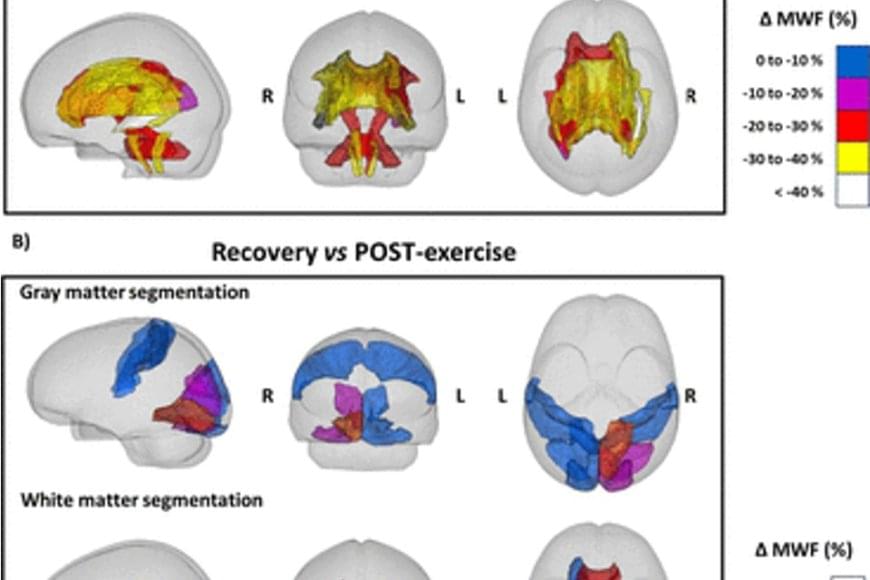
A study conducted by researchers shows that people who run a marathon experience a decrease in the amount of myelin in certain regions of the brain. According to the study published by Nature Metabolism, this effect is completely reversed two months after the marathon.
The researchers used magnetic resonance imaging to obtain images of the brains of ten marathon runners (eight men and two women) before and 48 hours after the 42-kilometre race. Likewise, the researchers took images of the brains of two of the runners two weeks after the race, and of six runners two months after the race as a follow-up.