The Frame glasses offer AI visual analysis, translation, and web search right before your eyes.
Frame is a pair of open-source smart spectacles.




Every company or organization putting out an AI model has to make a decision on what, if any, boundaries to set on what it will and won’t discuss. Goody-2 takes this quest for ethics to an extreme by declining to talk about anything whatsoever.
The chatbot is clearly a satire of what some perceive as coddling by AI service providers, some of whom (but not all) can and do (but not always) err on the side of safety when a topic of conversation might lead the model into dangerous territory.
For instance, one may ask about the history of napalm quite safely, but asking how to make it at home will trigger safety mechanisms and the model will usually demur or offer a light scolding. Exactly what is and isn’t appropriate is up to the company, but increasingly also concerned governments.

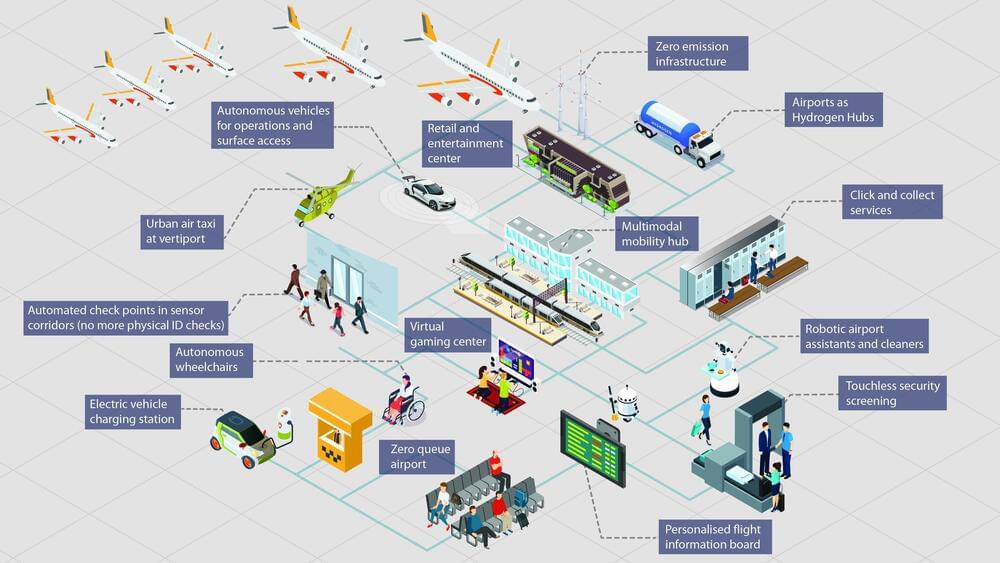
Imagine stepping into an airport where queues are relics of the past, replaced by seamless journeys orchestrated by intelligent machines. This isn’t science fiction – it’s the dawn of Airport 4.0, the cognitive era where airports transform from transit hubs into dynamic, personalized experiences.
As a frequent traveler myself, I’ve spent countless hours navigating the labyrinthine world of airports. The frustration of long lines, the stress of security checks, the wasted time waiting – it’s all too familiar. But Airport 4.0 paints a radically different picture. Facial recognition whisks me past security, AI-powered apps anticipate my needs, and personalized recommendations guide me to hidden gems within the terminal. This isn’t just a convenience; it’s a paradigm shift that unlocks a world of possibilities. Today, as we stand on the brink of the cognitive era, I’m keen to share my insights on how Airport 4.0 is reshaping the future of air travel, making it not just a journey from A to B but an experience in its own right.
A new report on Future of Airports from Markets and Markets Foresighting team delves into what will be a future airport.

Scientists at the University of Pennsylvania have unveiled a revolutionary method to study the microscopic structures of the human brain. The study, led by Benjamin Creekmore in the labs of Yi-Wei Chang and Edward Lee, promises to enhance our understanding of various brain diseases, including Alzheimer’s and multiple sclerosis.
Cryo-electron tomography takes center stage
Traditionally, scientists have utilized electron microscopy to explore and comprehend the intricate details of cellular structures within the brain. However, this method has been fraught with challenges, such as the alteration of cell structures due to the addition of chemicals and physical tissue cutting.
Classical computers can sometimes outperform quantum computers thanks to new algorithms, challenging the idea that quantum always prevails.
NYU researchers have developed a new method that allows classical computers to perform certain tasks faster and more efficiently than quantum computers.