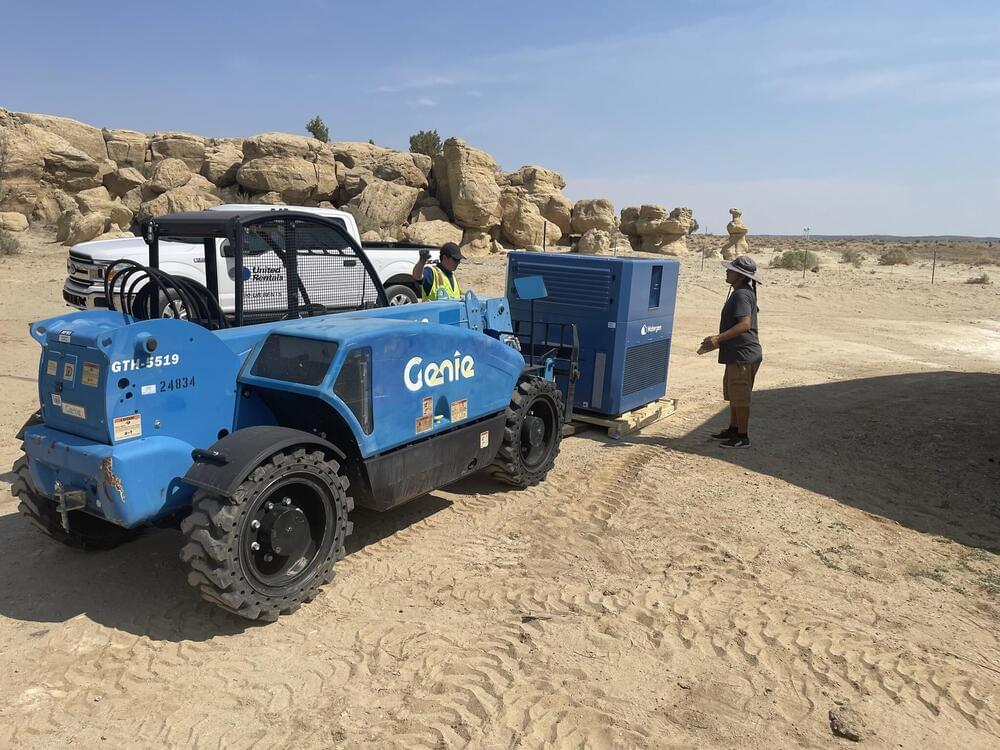
Israeli startup Watergen, which has developed a technology to produce water from air, has installed a generator for a Navajo Nation Native American community in Arizona to help them deal with a crippling water shortage.
The first generator was set up at the Rocky Ridge Gas & Market in northeast Arizona and aims to address the lack of access to clean drinking water within the Hard Rock community there, according to a joint press statement issued Thursday.
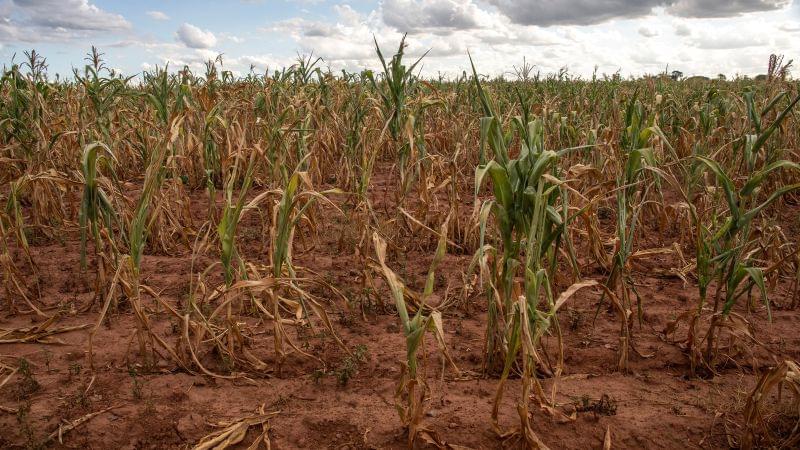
Nearly 10,000 families across Navajo Nation lack access to running water, per recent estimates. Local groundwaters have been contaminated over the years by mining and the situation has been exacerbated by the devastating drought affecting the Western United States.