I have added a link to a.cbr file (Comic Book Archive) to download and read on your electronic device if that would be easier for your enjoyment of the story. The Religious Experience of Philip K.



When an interdisciplinary conference lasts a little longer…
929 likes, — adamdthompson on July 22, 2024: ‘Mine in this week’s @newyorkermag’
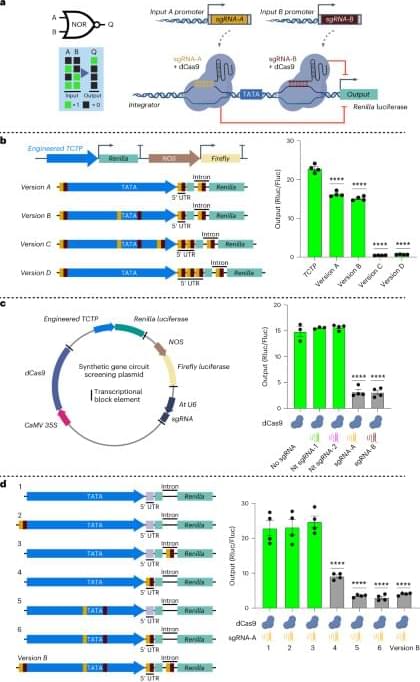


Images that NASA’s DART spacecraft captured of an asteroid moments before it intentionally collided with the object in 2022 have now allowed researchers to gain fresh insights into the celestial bodies.
The slew of studies published this week using data gathered from the asteroids Didymos and Dimorphos are an indication, researchers say, that the DART mission accomplished far more than just proving that potentially dangerous asteroids can be redirected from a trajectory toward Earth.
The findings published Tuesday across five research papers help to characterize the origin, evolution and physical characteristics of the two asteroids, located within 7 million miles of Earth. What the researchers discovered could help scientists better understand binary asteroids, such as Didymos and Dimorphos, in which the smaller body orbits the other.
Earth and Venus share some interesting similarities. Some of those similarities extend deep into the planets’ interiors.
Welcome to the visual audiobook of “Mr. Spaceship” by Philip K. Dick. This classic science fiction tale, first published in 1953, explores themes of human consciousness, artificial intelligence, and the potential of human-machine integration. Follow the story of a daring experiment where a human brain is used to pilot a spaceship, leading to unexpected and profound consequences. *Story Synopsis:* In “Mr. Spaceship,” humanity is locked in a devastating war with an alien race known as the Yucconae. Traditional automated spacecraft controlled by mechanical systems have proven ineffective against the aliens’ superior living defenses. Faced with a seemingly insurmountable challenge, scientists come up with a radical solution: replace the mechanical control systems of a spaceship with a human brain. Professor Thomas, an elderly academic on the brink of death, volunteers to have his consciousness integrated into the spaceship. As the ship, now controlled by Thomas’s mind, ventures into space, the crew soon discovers that the Professor has his own plans, leading to unexpected and profound consequences. *About Philip K. Dick:* Philip K. Dick (1928−1982) was a prolific American writer known for his groundbreaking works in the science fiction genre. His stories often delve into themes of altered states of reality, the nature of consciousness, and dystopian futures. Many of his works have been adapted into major films, including “Blade Runner,” “Total Recall,” and “Minority Report.” Dick’s profound and imaginative storytelling has left an enduring legacy, making him one of the most influential science fiction writers of the 20th century. *About the Creation Process:* The narration was produced using ElevenLabs for dialogue, ensuring a clear and engaging listening experience. The story’s visuals were crafted using OpenAi generated illustrations, inspired by vintage science fiction aesthetics. Each image was designed to capture the essence of Philip K. Dick’s imaginative worlds. The final compilation and editing were done using Logic, bringing together the audio and visual elements into a cohesive and immersive experience. *Credits:* — Story by Philip K. Dick — Visuals and production by Michael A. Terrill using ChatGPT — Narration generated using ElevenLabs — Music and sound design by Michael A. Terrill using Logic *Follow and Subscribe:* If you enjoyed this visual audiobook, please like, comment, and subscribe for more classic science fiction stories brought to life through innovative technology and creative storytelling. #MrSpaceship #PhilipKDick #ScienceFiction #Audiobook #VisualAudiobook #ClassicSciFi #ArtificialIntelligence #AI #SpaceAdventure #SciFiStory #VintageSciFi #PKD #AudiobookExperience #SciFiAudiobook #FuturisticStory #ElevenLabs #FiresOfDenmark
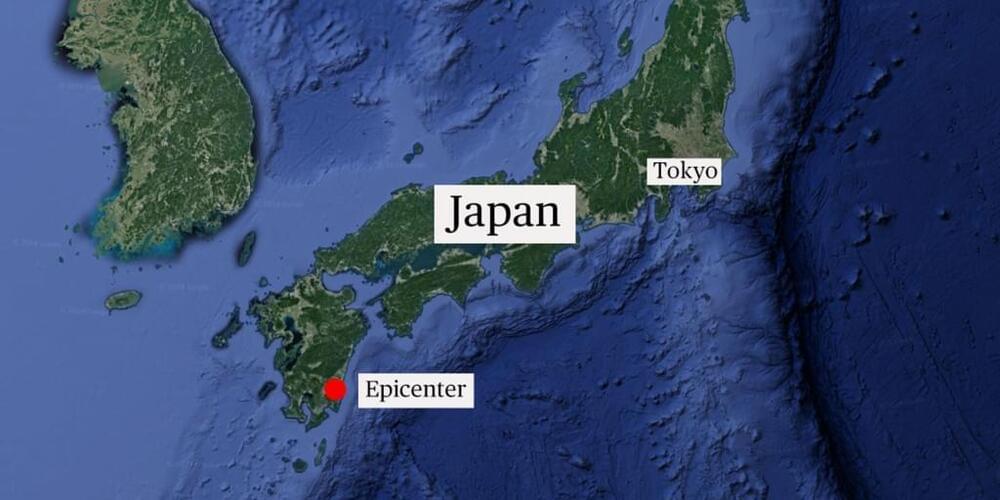
TOKYO — Japan issued its first warning Thursday about the possibility of a long-feared “megaquake” after a powerful 7.1-magnitude temblor struck off its southern coast, sparking a tsunami advisory but no immediate reports of serious damage or injuries.
The earthquake occurred off the coast of Miyazaki Prefecture on the main island of Kyushu at 4:42 p.m. local time (3:42 a.m. ET), at a depth of about 18 miles, according to the Japan Meteorological Agency.
Three people were reported injured, Japan’s Chief Cabinet Secretary Yoshimasa Hayashi said, although he added that there had been no blackouts or damage to the water or communications systems reported in the region. Police in Miyazaki Prefecture said there had been 10 reports of damage. Hayashi urged residents to stay away from the coastline.

Researchers at TMOS, the ARC Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optical Systems, and their collaborators at RMIT University have developed a new 2D quantum sensing chip using hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) that can simultaneously detect temperature anomalies and magnetic field in any direction in a new, groundbreaking thin-film format.
In a paper released in Nature Communications (“Multi-species optically addressable spin defects in a van der Waals material”), they detail a sensor that is significantly thinner than current quantum technology for magnetometry, paving the way for cheaper, more versatile quantum sensors.
Experimental set-up of hBN quantum sennsor. (Image: RMIT University)