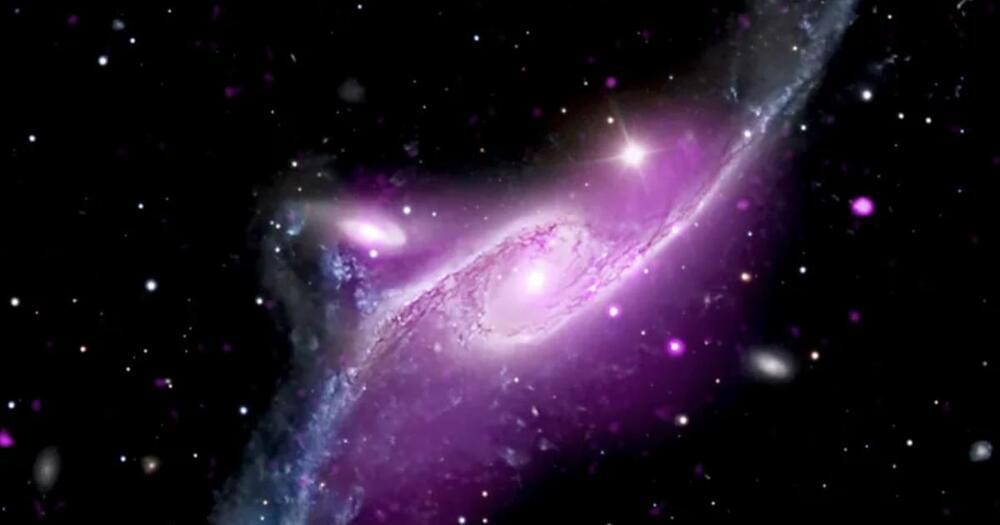
NASA is celebrating the 25th anniversary of its Chandra X-ray Observatory launch by sharing never-before-seen photos of the largest known spiral galaxy in the universe.
The Chandra X-ray observatory was launched on July 23, 1999. Since then, it has scoured the universe to look for X-ray emissions from exploded stars, clusters of galaxies and more, according to NASA. The observatory returns data to the Chandra X-ray Center at Harvard University’s Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.